Exploring the Power of map in Python: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Exploring the Power of map in Python: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Exploring the Power of map in Python: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Exploring the Power of map in Python: A Comprehensive Guide
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Exploring the Power of map in Python: A Comprehensive Guide
- 3.1 Understanding the Essence of map
- 3.2 Advantages of Using map
- 3.3 Exploring map in Action: Real-World Examples
- 3.4 Beyond the Basics: Advanced map Techniques
- 3.5 Addressing Common Questions
- 3.6 Tips for Effective map Usage
- 3.7 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Exploring the Power of map in Python: A Comprehensive Guide

The map function in Python is a powerful tool that enables efficient application of functions to iterable objects. It provides a concise and elegant way to perform operations on collections of data, enhancing code readability and efficiency. This article delves into the intricacies of map, exploring its functionalities, applications, and advantages, while providing practical examples to illustrate its usage.
Understanding the Essence of map
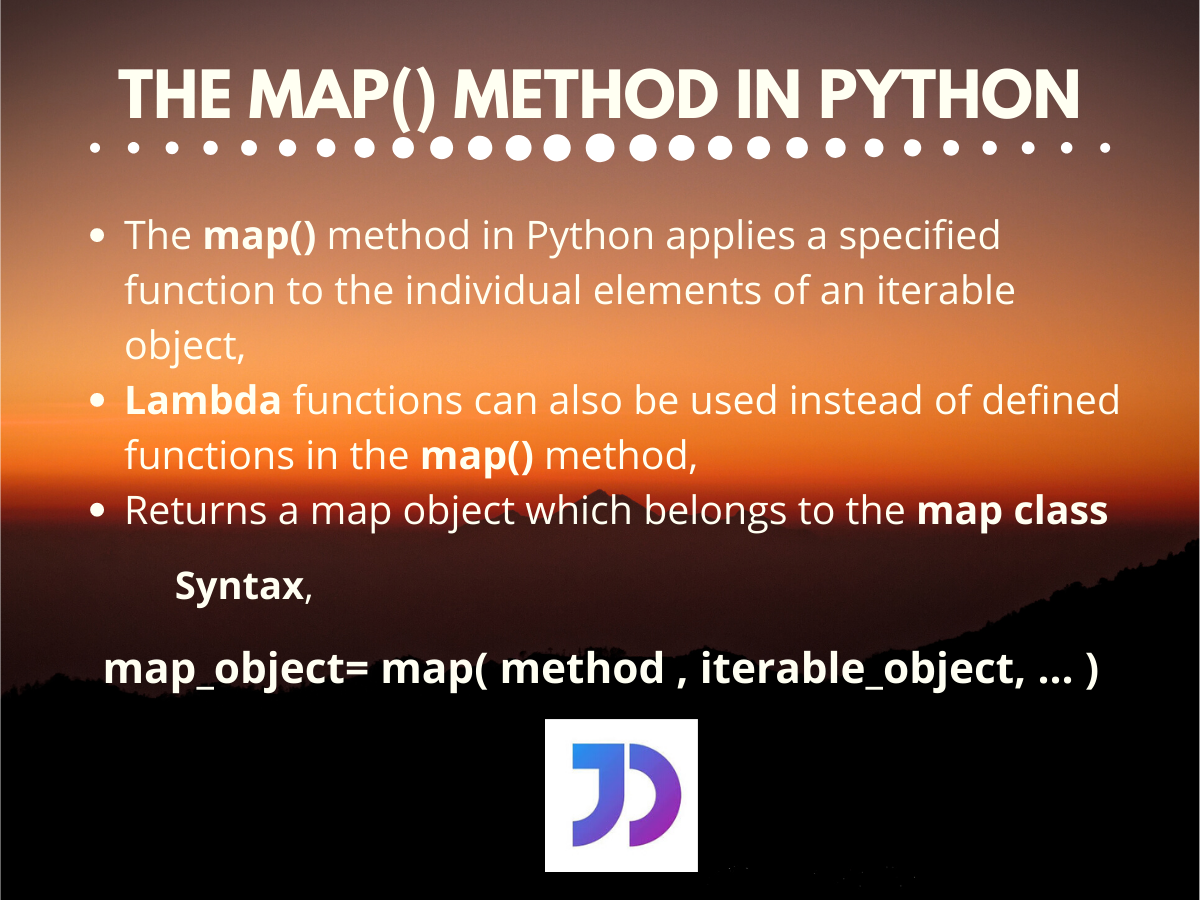
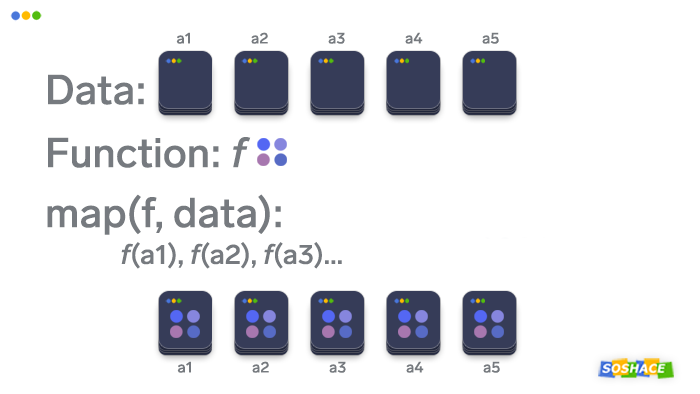
At its core, the map function takes two arguments: a function and an iterable. It iterates through each element in the iterable, applies the provided function to each element, and returns an iterator containing the results. This process of applying a function to every element of an iterable is known as "mapping".
Syntax:
map(function, iterable)Example:
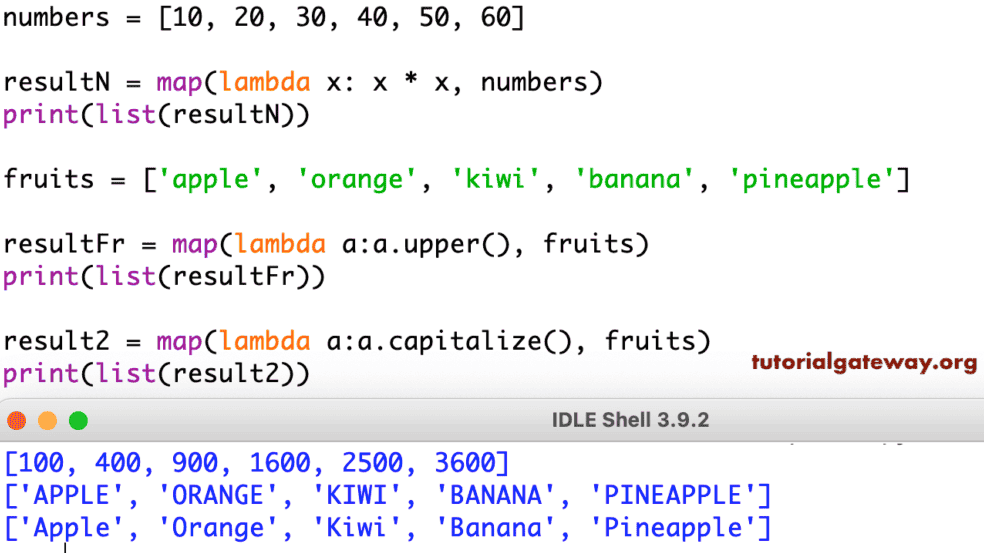
numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
squared_numbers = map(lambda x: x**2, numbers)
print(list(squared_numbers)) # Output: [1, 4, 9, 16, 25]In this example, map applies the lambda function lambda x: x**2 to each element of the numbers list, resulting in an iterator containing the squares of the original numbers.
Advantages of Using map
Employing map offers several advantages in Python programming:
-
Conciseness:
mapprovides a compact and readable way to perform operations on iterables, reducing code complexity and improving maintainability. -
Efficiency:
mapleverages the power of functional programming, often resulting in more efficient code compared to traditional loop-based approaches. -
Flexibility:
mapis highly flexible, accommodating various function types, including built-in functions, user-defined functions, and lambda functions. -
Readability: The explicit nature of
mapenhances code readability, making it easier to understand the intended operation on the iterable.
Exploring map in Action: Real-World Examples
The versatility of map allows it to be applied across diverse programming scenarios. Here are some illustrative examples:
1. Transforming Data:
names = ["Alice", "Bob", "Charlie"]
uppercase_names = map(str.upper, names)
print(list(uppercase_names)) # Output: ['ALICE', 'BOB', 'CHARLIE']This example showcases map transforming a list of names into uppercase strings using the built-in str.upper function.
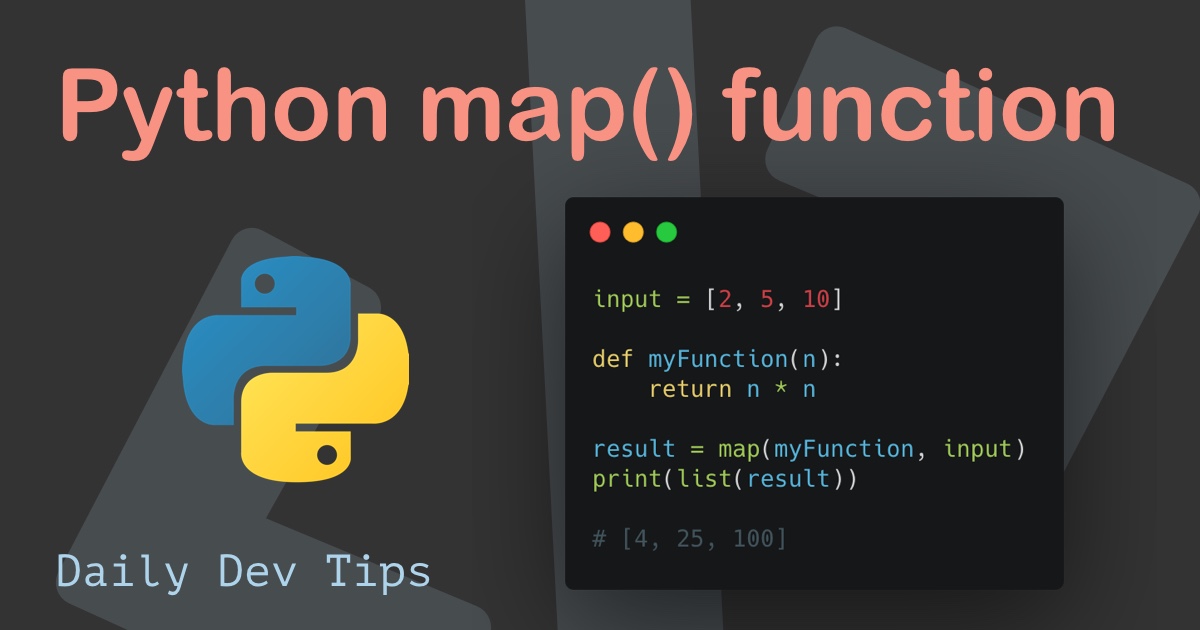
2. Applying Custom Functions:
def multiply_by_two(x):
return x * 2
numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
doubled_numbers = map(multiply_by_two, numbers)
print(list(doubled_numbers)) # Output: [2, 4, 6, 8, 10]Here, map applies a custom function multiply_by_two to each element in the numbers list, doubling each value.
3. Combining Multiple Iterables:
names = ["Alice", "Bob", "Charlie"]
ages = [25, 30, 28]
combined_data = map(lambda name, age: (name, age), names, ages)
print(list(combined_data)) # Output: [('Alice', 25), ('Bob', 30), ('Charlie', 28)]This example demonstrates map‘s ability to work with multiple iterables simultaneously. It combines elements from names and ages lists into tuples using a lambda function.
Beyond the Basics: Advanced map Techniques
The map function offers further possibilities when combined with other Python features:
-
Using
mapwithfilter:filterallows selecting elements from an iterable based on a condition. Combiningmapandfilterenables sequential transformation and filtering of data.
numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
even_squares = map(lambda x: x**2, filter(lambda x: x % 2 == 0, numbers))
print(list(even_squares)) # Output: [4, 16]-
Using
mapwithzip:zipcreates an iterator of tuples, pairing elements from multiple iterables. Combiningmapandzipallows applying a function to corresponding elements from multiple iterables.
numbers1 = [1, 2, 3]
numbers2 = [4, 5, 6]
summed_numbers = map(lambda x, y: x + y, numbers1, numbers2)
print(list(summed_numbers)) # Output: [5, 7, 9]Addressing Common Questions
Q: What are the differences between map and list comprehensions?
A: Both map and list comprehensions provide concise ways to apply functions to iterables. However, there are some key distinctions:
- Syntax: List comprehensions are more expressive and flexible, allowing for complex logic within the comprehension.
- Readability: List comprehensions often offer better readability for simple transformations.
-
Efficiency:
mapcan sometimes be more efficient, especially for large datasets.
Q: When should I use map over other techniques?
A: map is particularly beneficial when:
- You need to apply a function to every element of an iterable.
- You prefer a functional programming approach.
- You require a concise and efficient way to transform data.
Q: Can map be used with generators?
A: Yes, map can be used with generators. The resulting object will be a generator, allowing you to iterate over the transformed elements on demand.
Tips for Effective map Usage
- Choose the right function: Select the appropriate function for the desired transformation, whether it’s a built-in function, a custom function, or a lambda function.
-
Consider readability: While
mapcan be concise, prioritize readability by using clear function names and comments when necessary. -
Optimize for efficiency: For large datasets, consider whether
mapis the most efficient approach compared to other techniques like list comprehensions.
Conclusion
The map function in Python serves as a powerful tool for data transformation and manipulation. Its ability to apply functions to iterables efficiently, combined with its flexibility and readability, makes it a valuable asset for Python programmers. Understanding map‘s capabilities and its advantages over other techniques allows developers to write concise, efficient, and maintainable code. By mastering the nuances of map, programmers can unlock its potential for enhancing their Python projects.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Exploring the Power of map in Python: A Comprehensive Guide. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!