Exploring the Power of map in Python 3: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Exploring the Power of map in Python 3: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Exploring the Power of map in Python 3: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Exploring the Power of map in Python 3: A Comprehensive Guide
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Exploring the Power of map in Python 3: A Comprehensive Guide
- 3.1 Understanding the Essence of map
- 3.2 Beyond Basic Usage: Exploring map’s Capabilities
- 3.3 The Benefits of Using map
- 3.4 FAQs About map in Python 3
- 3.5 Tips for Effective map Usage
- 3.6 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Exploring the Power of map in Python 3: A Comprehensive Guide

Python’s map function is a powerful tool for applying a function to every element of an iterable, streamlining code and enhancing efficiency. This guide delves into the intricacies of map in Python 3, showcasing its versatility and highlighting its significant advantages in various programming scenarios.
Understanding the Essence of map
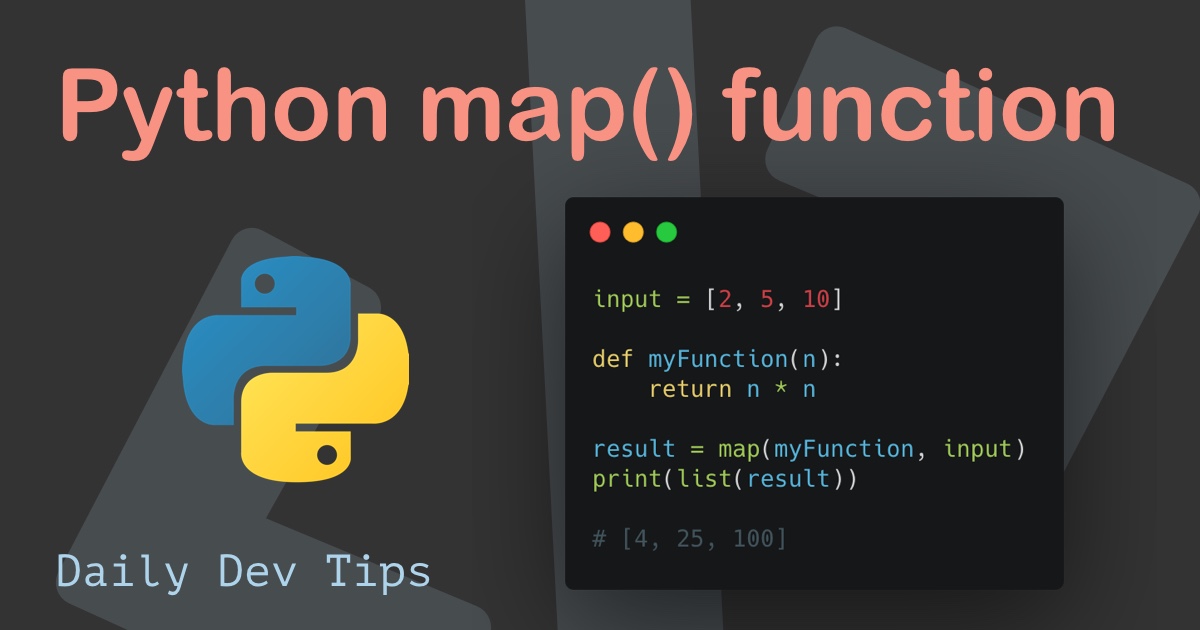
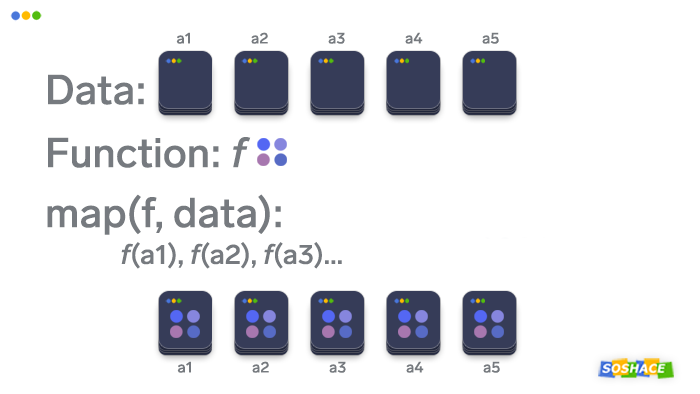
At its core, map takes two arguments: a function and an iterable (e.g., list, tuple, string). It applies the provided function to each element of the iterable, generating a new iterable containing the results. This elegant approach allows for concise and efficient manipulation of data, especially when dealing with sequences.
Syntax:
map(function, iterable)Example:
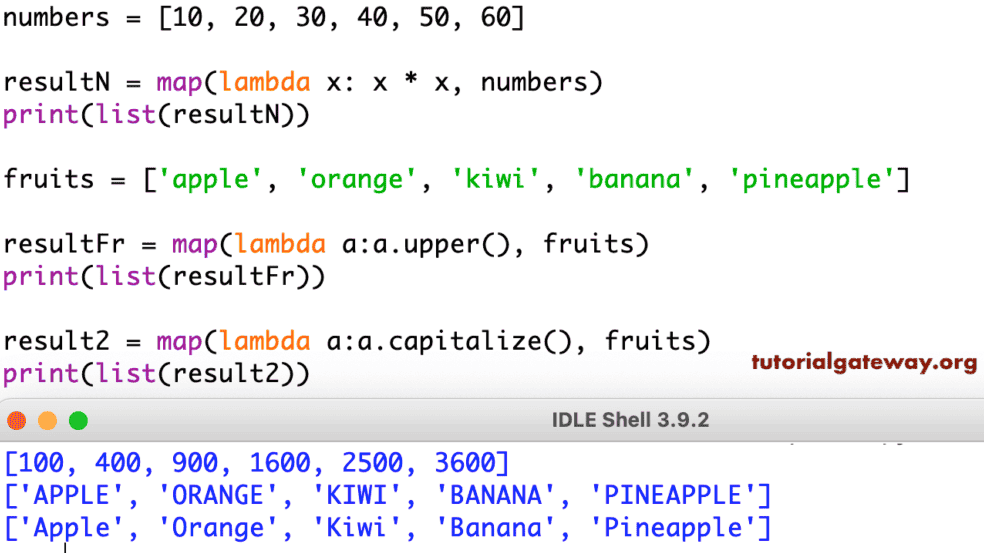
numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
# Square each number using map
squared_numbers = map(lambda x: x**2, numbers)
# Convert the map object to a list for display
print(list(squared_numbers)) # Output: [1, 4, 9, 16, 25]In this example, map applies the anonymous function lambda x: x**2 to each element in the numbers list. The resulting map object, when converted to a list, yields the squares of the original numbers.
Beyond Basic Usage: Exploring map’s Capabilities
The true power of map lies in its ability to handle complex operations with ease. Let’s explore some key scenarios where map shines:
1. Transforming Data:
map excels at transforming data within iterables. For instance, you can use it to convert a list of strings to uppercase:
names = ["john", "jane", "peter"]
uppercase_names = map(str.upper, names)
print(list(uppercase_names)) # Output: ['JOHN', 'JANE', 'PETER']2. Applying Multiple Functions:
map can apply multiple functions to an iterable by chaining them together. Imagine you need to convert a list of Celsius temperatures to Fahrenheit:
celsius_temps = [25, 30, 35]
# Define functions for conversion and rounding
def celsius_to_fahrenheit(c):
return (c * 9/5) + 32
def round_to_nearest_integer(temp):
return round(temp)
fahrenheit_temps = map(round_to_nearest_integer, map(celsius_to_fahrenheit, celsius_temps))
print(list(fahrenheit_temps)) # Output: [77, 86, 95]Here, map first applies celsius_to_fahrenheit to convert Celsius to Fahrenheit, then round_to_nearest_integer to round the results.
3. Working with Multiple Iterables:
map can also handle multiple iterables simultaneously. For example, you can combine two lists element-wise using a custom function:
numbers1 = [1, 2, 3]
numbers2 = [4, 5, 6]
def add_elements(x, y):
return x + y
combined_numbers = map(add_elements, numbers1, numbers2)
print(list(combined_numbers)) # Output: [5, 7, 9]4. Handling Functions with Multiple Arguments:
map can accommodate functions with multiple arguments by providing multiple iterables. For example, you can calculate the product of corresponding elements from two lists:
numbers1 = [1, 2, 3]
numbers2 = [4, 5, 6]
def multiply_elements(x, y):
return x * y
products = map(multiply_elements, numbers1, numbers2)
print(list(products)) # Output: [4, 10, 18]The Benefits of Using map
Beyond its versatility, map offers several advantages that make it a valuable tool in Python programming:
-
Conciseness:
mapprovides a concise and elegant way to apply operations to iterables, reducing code clutter. -
Readability: The declarative nature of
mapmakes code more readable, enhancing understanding and maintainability. -
Efficiency:
mapoften leads to more efficient code, especially for large datasets, as it leverages Python’s internal optimizations. -
Functional Programming:
mapaligns with functional programming principles, promoting code reuse and modularity.
FAQs About map in Python 3
1. Can map handle nested iterables?
Yes, map can handle nested iterables. You can use nested map calls or custom functions to process data within nested structures.
2. How does map handle different iterable lengths?
map stops iterating when the shortest iterable is exhausted. This behavior ensures consistent results even when iterables have different lengths.
3. Is map always the best choice for data transformation?
While map is powerful, it may not always be the optimal solution. For complex transformations, list comprehensions or generator expressions might provide better clarity and control.
4. Can map be used with custom classes?
Yes, map can be used with custom classes as long as they implement the __iter__ method to enable iteration.
5. Can I modify the original iterable using map?
map itself does not modify the original iterable. It generates a new iterable containing the transformed elements.
Tips for Effective map Usage
-
Choose the Right Tool: Consider using
mapwhen applying a function to each element of an iterable, especially for simple transformations. -
Use Anonymous Functions:
lambdafunctions are often convenient for concisely defining functions withinmap. - Handle Iterables Carefully: Be mindful of iterable lengths and potential differences in sizes when using multiple iterables.
-
Test Thoroughly: Test your code with various input data to ensure
mapfunctions as expected.
Conclusion
map is a powerful and versatile function in Python 3, offering a concise and efficient way to apply functions to iterables. Its ability to handle complex transformations, enhance code readability, and promote functional programming principles makes it an indispensable tool for Python developers. By understanding the nuances of map and leveraging its capabilities effectively, programmers can write cleaner, more efficient, and maintainable code, ultimately leading to more robust and scalable applications.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Exploring the Power of map in Python 3: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!