Demystifying the Power of Map Radius Drawing Tools: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Demystifying the Power of Map Radius Drawing Tools: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Demystifying the Power of Map Radius Drawing Tools: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Demystifying the Power of Map Radius Drawing Tools: A Comprehensive Guide
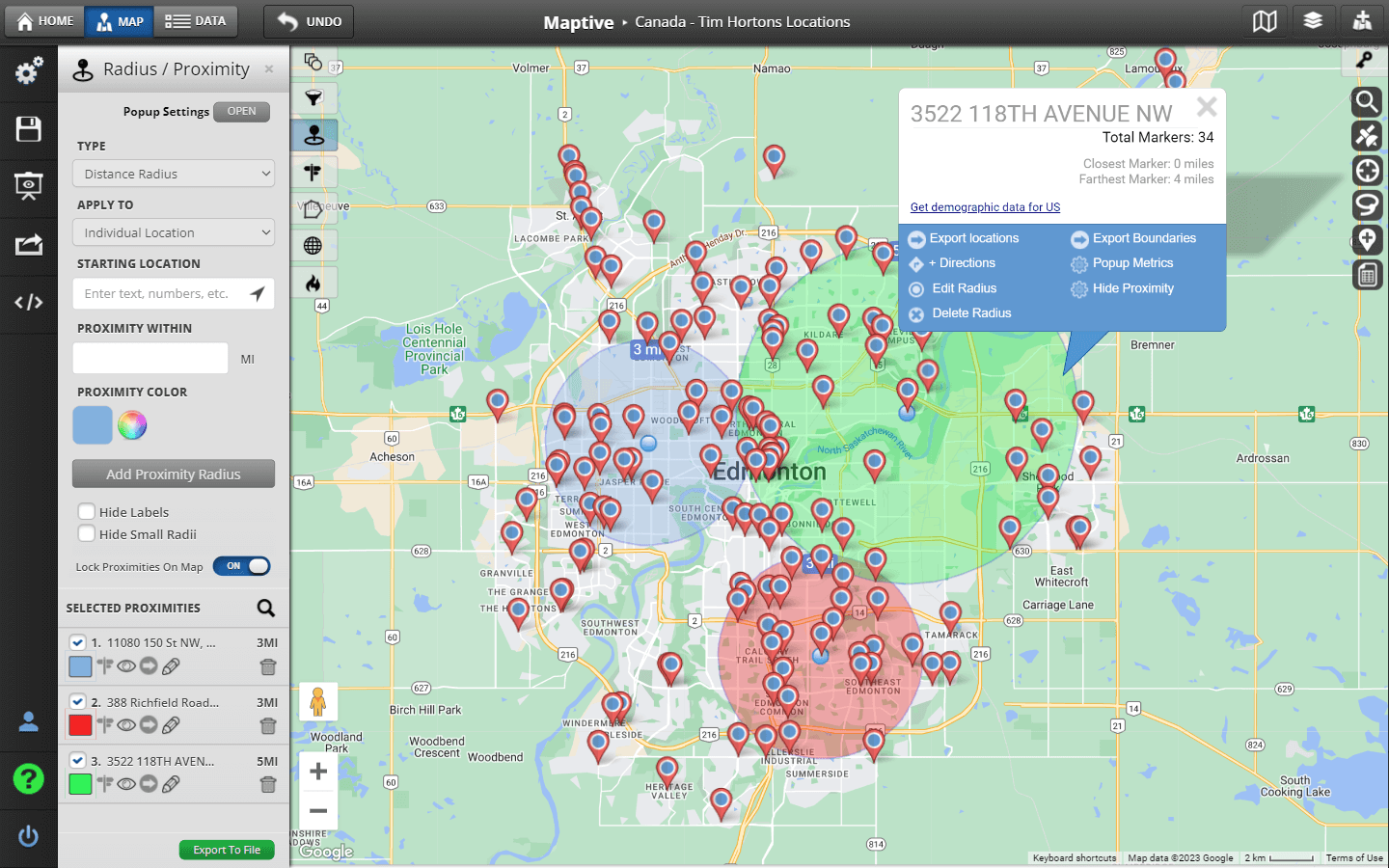
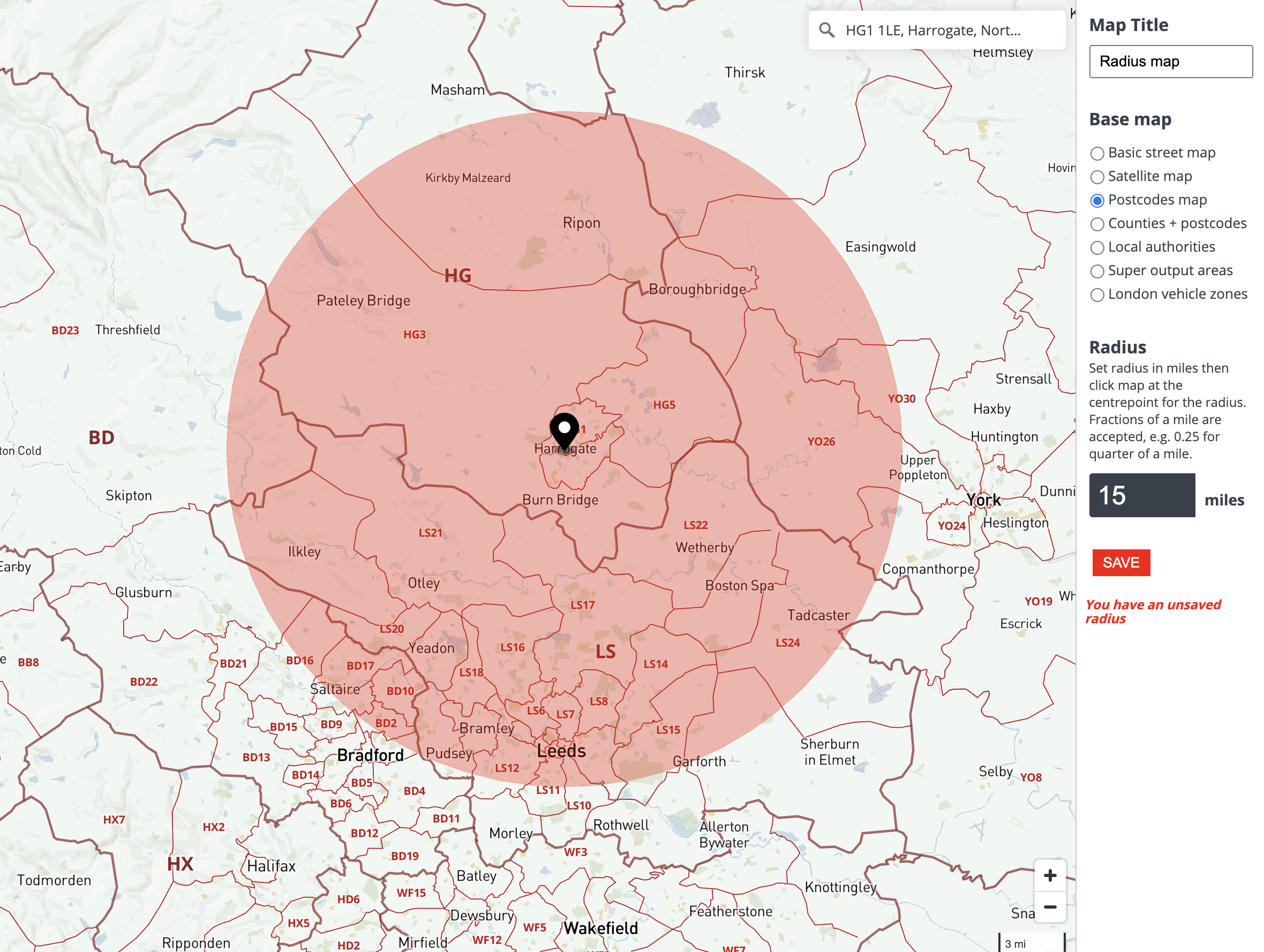
In the realm of geographic information systems (GIS) and spatial analysis, the ability to visualize and analyze areas of interest based on distance is crucial. This is where map radius drawing tools, often referred to as circle drawing tools, come into play. These tools empower users to define and explore geographic regions based on a specific distance from a central point, offering invaluable insights for diverse applications ranging from urban planning to disaster response.
Understanding the Fundamentals: How Map Radius Drawing Tools Work
At their core, map radius drawing tools function by utilizing a simple yet powerful concept: the calculation of distance from a central point. Users specify a starting location (the center) and a desired radius (the distance from the center). The tool then generates a circle or a buffer zone encompassing all points within that specified distance. This visual representation facilitates the understanding of spatial relationships and allows users to analyze geographic data within a defined area.
Beyond Simple Circles: Exploring the Capabilities of Advanced Tools
While basic radius drawing tools offer a fundamental functionality, advanced tools often come equipped with additional features that enhance their versatility and analytical power. These features may include:
- Variable Radii: Some tools allow users to define multiple radii from a single center, creating concentric circles or buffers with varying distances. This enables the analysis of areas with different levels of influence or impact.
- Custom Shapes: Beyond circular buffers, advanced tools may support the creation of custom shapes like ellipses, polygons, or even irregular shapes defined by user-drawn points. This expands the tool’s applicability to scenarios where a circular shape might not accurately represent the area of interest.
- Integration with GIS Data: Many map radius drawing tools integrate seamlessly with GIS software and databases, allowing users to overlay and analyze the generated circles or buffers with various spatial data layers. This enables the extraction of valuable information like population density, land use, or infrastructure within the defined area.
- Interactive Functionality: Some tools provide interactive features that allow users to adjust the radius, shape, or center point in real-time. This dynamic interaction allows for rapid exploration and analysis, facilitating the identification of optimal locations or areas of interest.
Applications Spanning Industries and Disciplines
The versatility of map radius drawing tools makes them indispensable across a wide range of disciplines and industries:
- Urban Planning: Determining service areas for schools, hospitals, or public transportation; identifying areas within walking distance of amenities; analyzing potential impact zones for infrastructure projects.
- Emergency Response: Defining evacuation zones during natural disasters; identifying areas affected by pollution or disease outbreaks; mapping the proximity of emergency resources to affected populations.
- Marketing and Business: Targeting potential customers within a specific radius of a store or service location; analyzing market competition within a defined geographic area; identifying areas with high customer density.
- Environmental Management: Mapping wildlife habitats or protected areas; analyzing the impact of deforestation or pollution on surrounding ecosystems; identifying areas suitable for renewable energy projects.
- Law Enforcement: Defining crime hot spots; mapping witness locations; analyzing the potential impact of crime on surrounding areas.
Unveiling the Benefits: Why Map Radius Drawing Tools Matter
The significance of map radius drawing tools lies in their ability to simplify complex spatial relationships and provide actionable insights. They offer several key benefits:
- Visual Clarity: They transform abstract data into easily digestible visual representations, making it easier to understand spatial relationships and trends.
- Targeted Analysis: They enable focused analysis of geographic areas based on distance, allowing for the identification of specific patterns or trends within defined regions.
- Improved Decision-Making: The insights gained through these tools can inform more informed and strategic decision-making, leading to better planning, resource allocation, and overall outcomes.
- Enhanced Collaboration: Visualizing geographic data using these tools facilitates communication and collaboration among stakeholders, fostering a shared understanding of spatial relationships.
Navigating the Landscape: Choosing the Right Tool
The choice of map radius drawing tool depends on specific requirements and the intended application. Key factors to consider include:
- Functionality: The specific features and capabilities offered by the tool, such as variable radii, custom shapes, and GIS integration.
- User Interface: The ease of use and intuitiveness of the interface, particularly for users with varying levels of technical expertise.
- Data Compatibility: The ability to import and export data in various formats, ensuring compatibility with existing workflows.
- Cost and Licensing: The pricing model and licensing terms of the tool, considering budget constraints and the scale of use.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What are the different types of map radius drawing tools available?
A: Map radius drawing tools come in various forms, ranging from standalone software applications to online tools integrated within GIS platforms. Some popular options include:
- Standalone Software: ArcGIS Pro, QGIS, MapInfo Pro.
- Online Tools: Google Maps, Mapbox, Leaflet.
- GIS Platform Integrations: ArcGIS Online, GeoServer.
Q: What is the difference between a circle and a buffer in map radius drawing?
A: A circle represents a perfect circular area around a central point, while a buffer is a polygon that encompasses all points within a specified distance from a line or polygon feature. Buffers are often used to create areas of influence or impact around linear features like roads or rivers.
Q: How can I use map radius drawing tools for marketing purposes?
A: Map radius drawing tools can help businesses target potential customers within specific geographic areas. By defining radii around store locations, businesses can identify areas with high customer density and focus their marketing efforts accordingly.
Q: Can I use map radius drawing tools to analyze environmental data?
A: Absolutely. These tools can be used to visualize and analyze environmental data such as air pollution levels, water quality, or wildlife habitat distribution. By overlaying radius drawings with environmental data layers, users can identify areas of concern and prioritize mitigation efforts.
Tips for Effective Use of Map Radius Drawing Tools
- Define Clear Objectives: Clearly articulate the specific goals and questions you aim to address using the tool.
- Choose Appropriate Radii: Select radii that are relevant to the scale of your analysis and the intended application.
- Consider Data Accuracy: Be aware of the accuracy and resolution of your data sources, as this will influence the precision of your radius drawings.
- Explore Visualization Options: Experiment with different visualization techniques to enhance the clarity and impact of your results.
- Document Your Work: Keep detailed records of your methodology, parameters, and findings for future reference and reproducibility.
Conclusion: Embracing the Power of Spatial Analysis
Map radius drawing tools serve as powerful instruments for spatial analysis, enabling users to visualize and understand geographic relationships based on distance. Their versatility and accessibility make them valuable assets across a wide range of disciplines and industries, empowering informed decision-making and facilitating the exploration of complex spatial data. By embracing these tools and harnessing their capabilities, individuals and organizations can gain deeper insights into the world around them, leading to more effective planning, problem-solving, and ultimately, a better understanding of our shared planet.

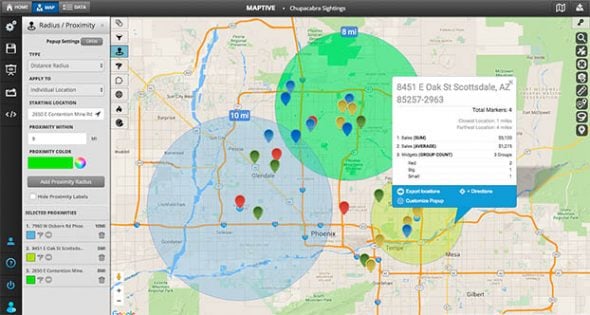
![Radius Map [Tool For Drawing & Creation] Distance & Driving Tim - Smappen](https://www.smappen.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/radius-map-1024x635.jpg)
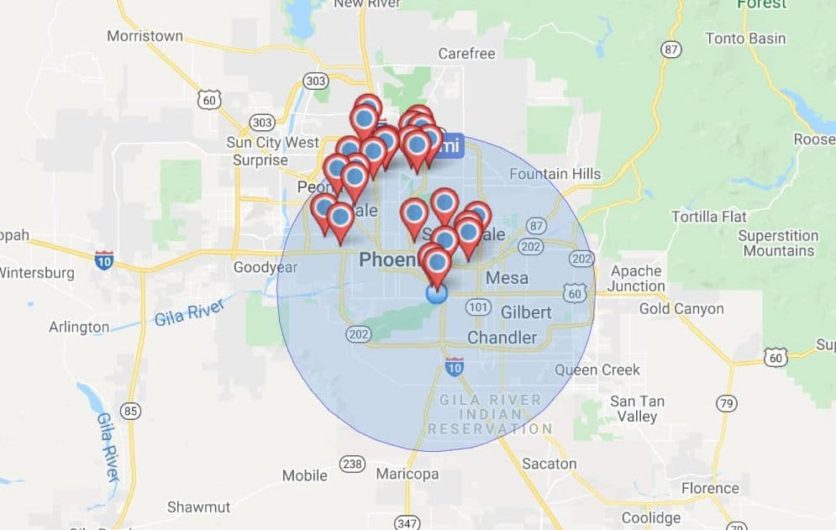

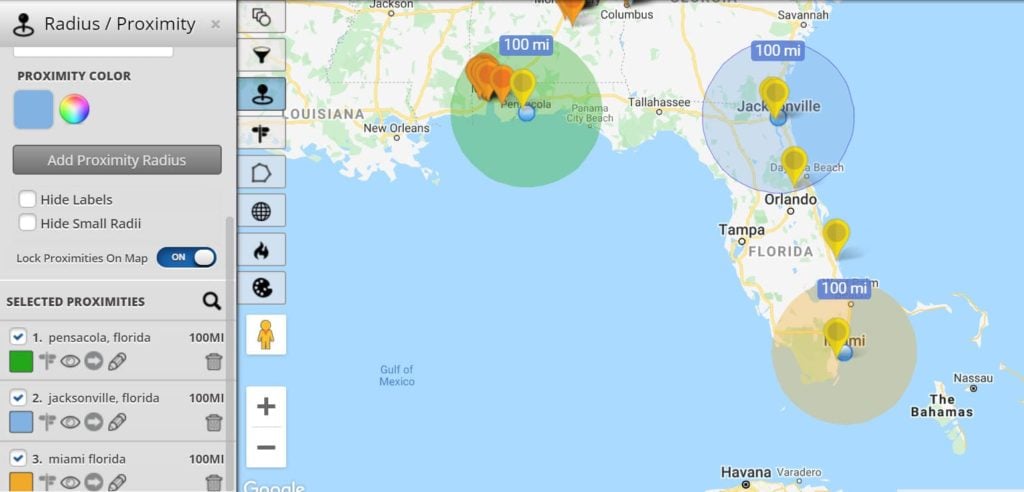

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Demystifying the Power of Map Radius Drawing Tools: A Comprehensive Guide. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!