Delving into the Realm of Map Radius Drawing: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Delving into the Realm of Map Radius Drawing: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Delving into the Realm of Map Radius Drawing: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Delving into the Realm of Map Radius Drawing: A Comprehensive Guide

Map radius drawing, a fundamental tool in spatial analysis and visualization, allows users to define and represent circular areas of interest on maps. This technique, often employed in geographic information systems (GIS) and mapping software, is crucial for numerous applications, ranging from urban planning and resource management to emergency response and market analysis. This article provides a comprehensive exploration of map radius drawing, elucidating its underlying principles, highlighting its diverse applications, and offering insights into its practical implementation.
Understanding the Fundamentals of Map Radius Drawing
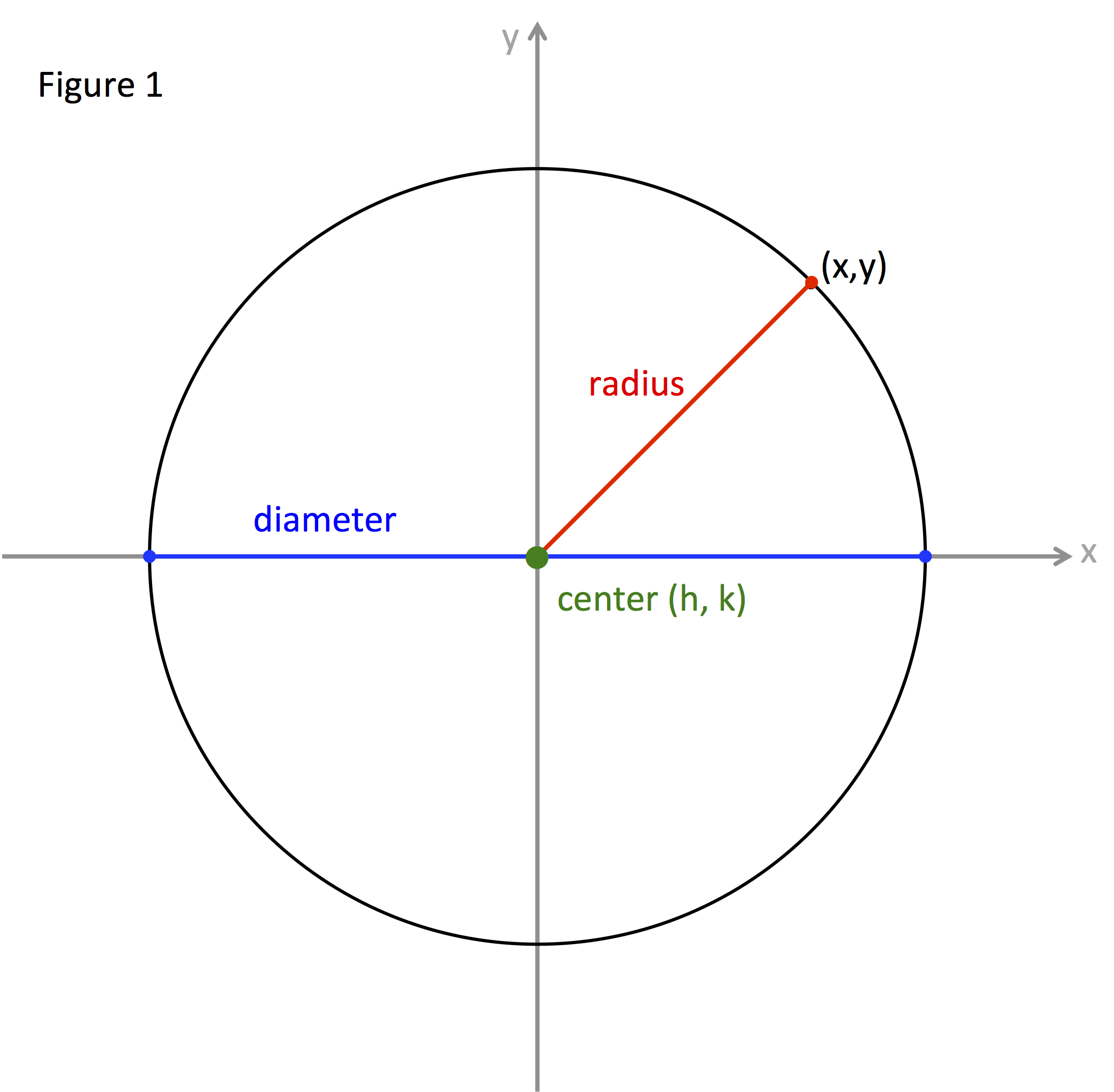
At its core, map radius drawing involves defining a central point on a map and then drawing a circle with a specified radius around that point. This radius can be expressed in various units, including kilometers, miles, meters, or any other relevant measurement. The resulting circle represents a defined area of influence or a region encompassing all points within a certain distance from the central location.
Key Components of Map Radius Drawing
-
Central Point: This serves as the origin of the circular area. It can be a specific location, such as a business address, a natural landmark, or a point of interest.
-
Radius: The distance from the central point to the edge of the circle. The radius determines the size of the circular area and can be adjusted based on the specific application.
-
Map Projection: The underlying map projection used to display the data significantly impacts the accuracy of radius drawing. Different projections distort distances and shapes differently, influencing the representation of the circular area.
Applications of Map Radius Drawing: Unlocking Spatial Insights
The versatility of map radius drawing makes it a valuable tool across diverse disciplines and industries:
1. Urban Planning and Development:
- Service Area Analysis: Determining the optimal locations for new businesses, schools, or healthcare facilities by identifying areas with sufficient population density within a defined radius.
- Neighborhood Planning: Analyzing the accessibility of amenities, public transportation, and green spaces within specific neighborhoods.
- Traffic Management: Identifying areas with high traffic congestion within a certain radius of major intersections or roadways.
2. Resource Management and Environmental Planning:
- Protected Area Management: Defining buffer zones around protected areas to mitigate potential threats from human activities.
- Wildlife Conservation: Identifying critical habitat areas for endangered species based on their movement patterns and home ranges.
- Pollution Monitoring: Assessing the potential impact of pollution sources by defining areas affected by air or water contamination.
3. Emergency Response and Disaster Management:
- Emergency Evacuation Planning: Defining evacuation zones around potential hazards like wildfire outbreaks, floods, or chemical spills.
- Resource Allocation: Identifying areas requiring immediate assistance based on the proximity to the disaster zone.
- Search and Rescue Operations: Defining search areas based on the last known location of missing persons or objects.
4. Market Analysis and Business Strategy:
- Customer Segmentation: Identifying potential customer bases based on their proximity to retail outlets or service providers.
- Competitive Analysis: Mapping the locations of competitors and analyzing their market reach within specific geographic areas.
- Site Selection: Identifying optimal locations for new businesses or franchises based on customer demographics, competition, and accessibility.
5. Public Health and Disease Surveillance:
- Epidemiological Studies: Mapping the spread of infectious diseases by identifying cases within a certain radius of known outbreaks.
- Vaccination Campaigns: Defining target areas for vaccination efforts based on population density and disease prevalence.
- Health Facility Planning: Assessing the accessibility of healthcare services within specific communities.
Implementation of Map Radius Drawing: Tools and Techniques
Various tools and techniques can be employed for map radius drawing, each offering distinct advantages and limitations:
1. Geographic Information Systems (GIS) Software:
- ArcGIS: A comprehensive GIS platform providing advanced tools for map radius drawing, including the ability to create buffer zones, calculate distances, and perform spatial analysis.
- QGIS: An open-source GIS software offering a user-friendly interface and a wide range of functionalities for map radius drawing and spatial analysis.
2. Online Mapping Platforms:
- Google Maps: Offers basic map radius drawing functionality, allowing users to define circles around specific locations.
- Mapbox: A cloud-based platform for creating and customizing maps, providing advanced tools for map radius drawing and spatial analysis.
3. Spreadsheet Software:
- Microsoft Excel: Can be used to calculate distances and create radius-based areas using formulas and geographic coordinates.
4. Manual Drawing Methods:
- Compass and Ruler: Traditional tools for drawing circles on paper maps, offering a simple and readily available approach.
Challenges and Considerations in Map Radius Drawing
While map radius drawing offers valuable insights, it is crucial to acknowledge potential challenges and considerations:
- Map Projection Distortion: Different map projections can distort distances and shapes, affecting the accuracy of radius drawing.
- Data Accuracy: The accuracy of the map radius drawing depends on the precision of the underlying data, including geographic coordinates and measurement units.
- Real-World Complexity: Map radius drawing often simplifies complex real-world scenarios, neglecting factors like obstacles, terrain variations, and transportation networks.
FAQs about Map Radius Drawing
1. What are the different units used for defining the radius?
The radius can be expressed in various units, including kilometers, miles, meters, feet, or any other relevant measurement, depending on the scale and specific application.
2. How does map projection affect the accuracy of radius drawing?
Different map projections distort distances and shapes differently. For example, a cylindrical projection may accurately represent distances along the equator but distort them towards the poles. Choosing an appropriate projection is crucial for accurate radius drawing.
3. Can I draw irregular or non-circular areas using map radius drawing techniques?
While map radius drawing primarily focuses on circular areas, some software tools allow for drawing more complex shapes, such as polygons or buffer zones with irregular boundaries.
4. What are some common applications of map radius drawing in business?
Map radius drawing is widely used in business for market analysis, site selection, customer segmentation, and competitive analysis. It helps businesses understand their target market, identify potential customers, and make informed decisions about location, pricing, and marketing strategies.
Tips for Effective Map Radius Drawing
- Choose the Appropriate Map Projection: Select a projection that minimizes distortion in the area of interest.
- Use Accurate Data: Ensure that the underlying data, including geographic coordinates and measurement units, is accurate and up-to-date.
- Consider Real-World Constraints: Account for factors like obstacles, terrain variations, and transportation networks when interpreting the results of map radius drawing.
- Experiment with Different Radii: Explore various radius values to understand the impact on the area of influence and identify optimal settings for specific applications.
- Visualize the Results: Utilize different map layers and symbols to effectively communicate the results of map radius drawing.
Conclusion: Empowering Spatial Understanding
Map radius drawing serves as a powerful tool for visualizing and analyzing spatial data, providing valuable insights across diverse disciplines. By defining circular areas of interest, users can gain a deeper understanding of proximity, influence, and accessibility, enabling informed decision-making in urban planning, resource management, emergency response, business strategy, and public health. As technology advances and data availability increases, map radius drawing will continue to play a crucial role in unlocking the potential of spatial information for a wide range of applications.





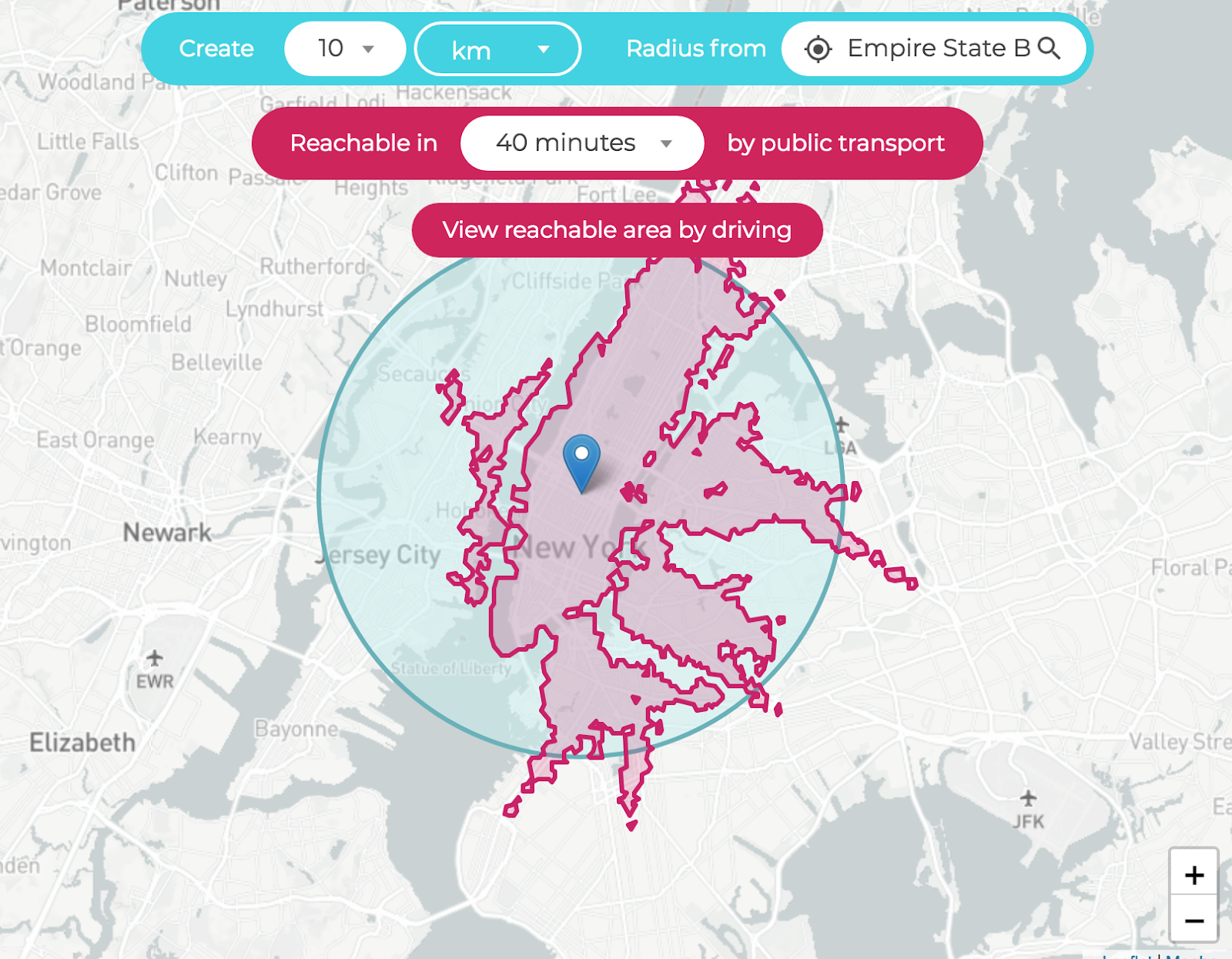
![Radius Map [Tool For Drawing & Creation] Distance & Driving Tim - Smappen](https://www.smappen.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/radius-map-1024x635.jpg)
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Delving into the Realm of Map Radius Drawing: A Comprehensive Guide. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!