Delving into the Realm of Map Radius Calculations: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Delving into the Realm of Map Radius Calculations: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Delving into the Realm of Map Radius Calculations: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Delving into the Realm of Map Radius Calculations: A Comprehensive Guide
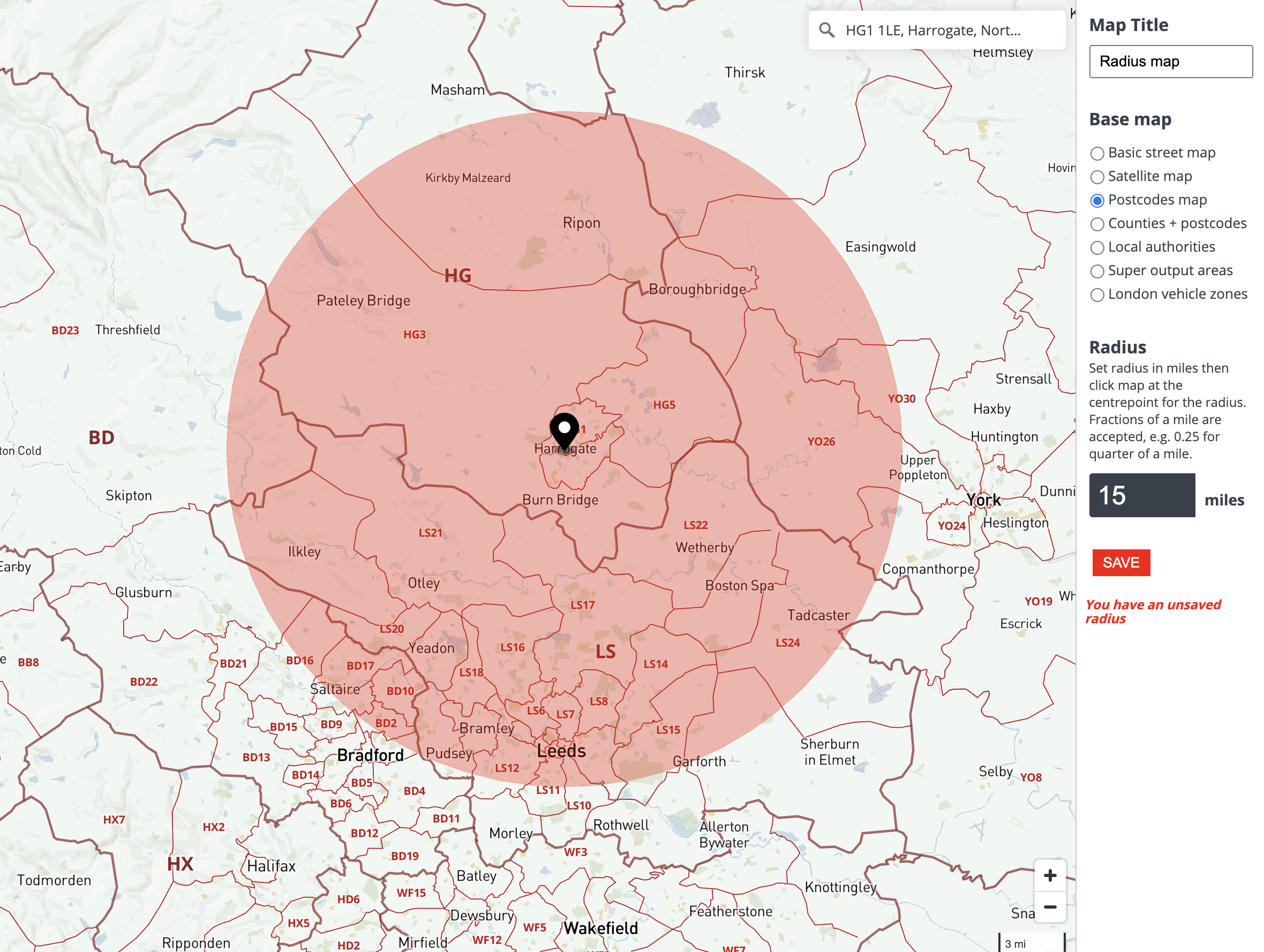
In the digital age, where information is readily available at our fingertips, the ability to understand and utilize spatial data has become increasingly crucial. One fundamental aspect of spatial analysis is the calculation of map radius, a process that plays a vital role in various applications, from optimizing delivery routes to understanding disease spread. This article aims to provide a comprehensive exploration of map radius calculation, outlining its methodology, applications, and significance in the modern world.
Understanding the Concept of Map Radius
At its core, map radius calculation involves determining the area encompassed within a specific distance from a central point. This distance, known as the radius, can be measured in various units, including kilometers, miles, or even meters, depending on the scale and purpose of the analysis. The resulting area, often depicted as a circle on a map, represents the geographical extent of influence or reach from the central point.
The Importance of Map Radius Calculations
The significance of map radius calculations extends far beyond mere geographical visualization. Its applications span a wide range of fields, including:
- Logistics and Transportation: Determining the optimal radius for delivery services, identifying service areas, and optimizing route planning.
- Retail and Marketing: Analyzing customer demographics within a specific radius, targeting marketing campaigns to relevant audiences, and selecting optimal store locations.
- Public Health and Epidemiology: Assessing the potential spread of diseases, identifying high-risk areas, and planning public health interventions.
- Environmental Science and Conservation: Determining the impact of environmental hazards, mapping protected areas, and analyzing the distribution of natural resources.
- Real Estate and Urban Planning: Evaluating property values based on proximity to amenities, identifying potential development areas, and understanding urban growth patterns.
Methods for Calculating Map Radius
The calculation of map radius can be achieved using various methods, each with its own strengths and limitations. The most common approaches include:
1. Using Geographic Coordinate Systems (GCS)
- Haversine Formula: This formula, derived from spherical trigonometry, calculates the great-circle distance between two points on a sphere. It is widely used in applications involving long distances, where the Earth’s curvature becomes significant.
- Vincenty’s Formula: This formula provides a more accurate calculation of the distance between two points on an ellipsoid, taking into account the Earth’s oblate shape. It is particularly useful for high-precision applications.
2. Using Projected Coordinate Systems (PCS)
- Euclidean Distance: In projected coordinate systems, where distances are represented in a planar format, the Euclidean distance formula can be used to calculate the radius. This method is simpler than the formulas used in GCS but is less accurate for larger distances.
3. Using Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
- Buffer Tools: GIS software provides dedicated tools for creating buffer zones, which represent areas within a specific distance from a point, line, or polygon. These tools automatically account for the Earth’s curvature and ensure accurate representation of the radius.
Factors Influencing Map Radius Calculations
Several factors can influence the accuracy and validity of map radius calculations:
- Earth’s Curvature: For long distances, the Earth’s curvature becomes a significant factor, requiring the use of formulas that account for this curvature.
- Coordinate System: The choice of coordinate system (GCS or PCS) can affect the accuracy of the calculations, particularly for larger distances.
- Data Resolution: The resolution of the underlying data used for the calculations can impact the accuracy of the radius.
- Terrain and Obstacles: The presence of terrain features or obstacles can affect the actual distance within the radius, especially in urban areas.
Choosing the Right Method
The selection of the appropriate method for map radius calculation depends on several factors, including:
- Distance: For short distances, the Euclidean distance formula may suffice, while for longer distances, the Haversine or Vincenty’s formula is recommended.
- Accuracy: For applications requiring high accuracy, Vincenty’s formula or GIS buffer tools are preferable.
- Software Availability: The availability of GIS software or programming libraries supporting specific formulas can influence the chosen method.
- Data Format: The format of the input data (coordinates, shapefiles, etc.) can determine the applicable methods.
Illustrative Applications of Map Radius Calculations
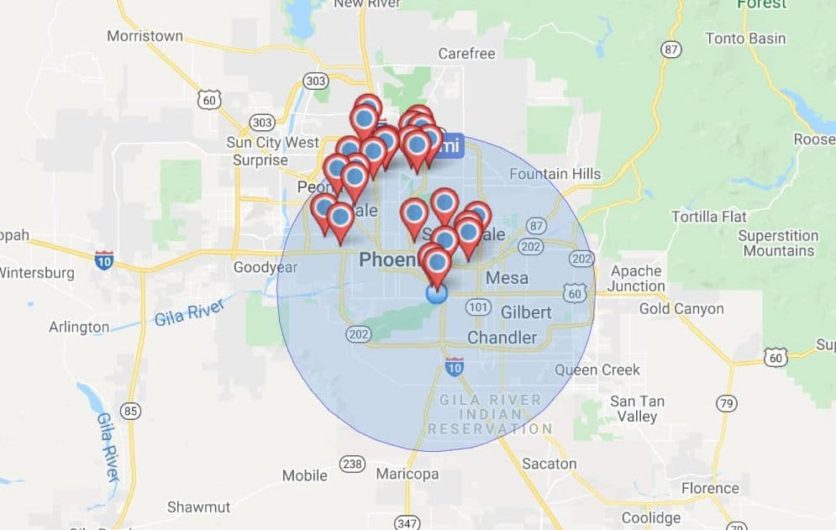
- Delivery Route Optimization: Companies like Amazon and Uber use map radius calculations to optimize delivery routes, ensuring efficient service coverage within designated areas.
- Disease Surveillance: Public health agencies utilize map radius calculations to identify areas with high disease incidence, enabling targeted interventions and resource allocation.
- Marketing Campaigns: Businesses use map radius calculations to target marketing campaigns to specific geographic areas, maximizing their reach and impact.
- Environmental Impact Assessment: Environmental agencies use map radius calculations to assess the potential impact of industrial activities on surrounding areas, ensuring environmental protection.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Map Radius Calculations
Q1: What are the limitations of map radius calculations?
A: While powerful, map radius calculations have limitations:
- Real-World Complexity: They often simplify real-world situations by assuming a uniform distance from the central point, neglecting factors like terrain, obstacles, or varying travel speeds.
- Data Accuracy: The accuracy of the calculations depends on the quality and resolution of the underlying data.
- Contextual Factors: The results can be influenced by factors not explicitly considered in the calculations, such as traffic congestion, road closures, or access restrictions.
Q2: How can I improve the accuracy of map radius calculations?
A: Several strategies can enhance accuracy:
- Use High-Resolution Data: Employing high-resolution maps and data sets with detailed terrain information can improve the accuracy of the calculations.
- Consider Terrain and Obstacles: Incorporating terrain data and obstacle information into the calculations can provide a more realistic representation of the actual distance.
- Utilize Advanced Algorithms: Implementing more sophisticated algorithms that account for complex factors like traffic patterns and road network variations can enhance accuracy.
Q3: What are some tools for performing map radius calculations?
A: Numerous tools are available:
- GIS Software: ArcGIS, QGIS, and other GIS software offer robust tools for creating buffer zones and calculating distances.
- Programming Libraries: Libraries like GeoPandas (Python) and Leaflet (JavaScript) provide functions for performing map radius calculations.
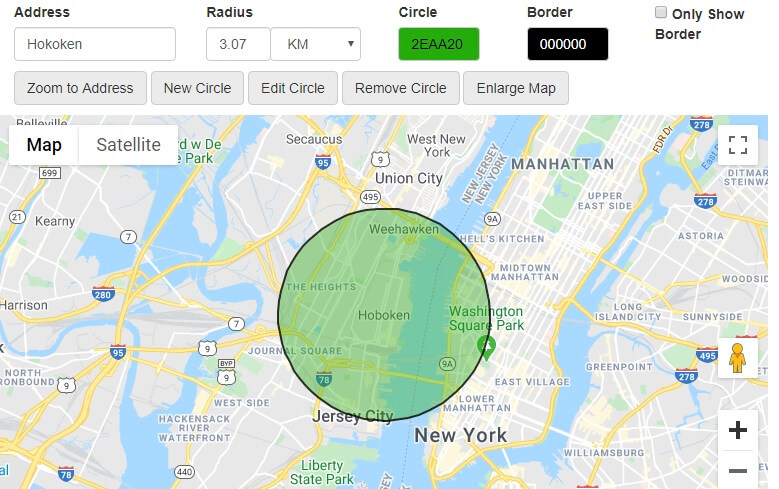
- Online Tools: Websites like MapRadius.com and GeoTools.io offer online tools for calculating map radius and creating buffer zones.
Tips for Effective Map Radius Calculations
- Define the Purpose: Clearly define the objective of the calculation to select the appropriate method and data.
- Choose the Right Coordinate System: Select a coordinate system that aligns with the scale and accuracy requirements of the analysis.
- Validate the Results: Verify the calculated radius against real-world data and adjust the method or data as necessary.
- Consider Context: Take into account factors beyond distance, such as terrain, accessibility, and relevant regulations, to ensure realistic results.
Conclusion
Map radius calculations are a fundamental tool for spatial analysis, enabling us to understand and quantify the geographical extent of influence, reach, and impact. By leveraging various methods and tools, we can effectively calculate and visualize map radius, providing valuable insights across diverse fields. As technology advances and data availability increases, map radius calculations will continue to play a vital role in navigating and understanding the complex spatial relationships that shape our world.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Delving into the Realm of Map Radius Calculations: A Comprehensive Guide. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!