Delving into the Realm of Geographic Proximity: Understanding Map Radius and Its Applications
Related Articles: Delving into the Realm of Geographic Proximity: Understanding Map Radius and Its Applications
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Delving into the Realm of Geographic Proximity: Understanding Map Radius and Its Applications. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Delving into the Realm of Geographic Proximity: Understanding Map Radius and Its Applications
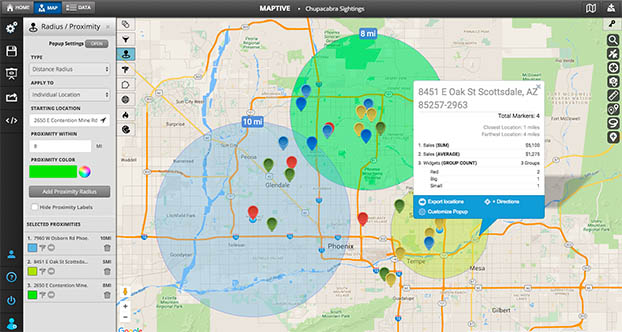
In the age of digital connectivity and globalized interactions, the concept of distance has taken on new dimensions. While traditional measures like kilometers or miles remain relevant, the need to understand proximity in a more nuanced way has led to the emergence of map radius. This concept, often employed in mapping and location-based services, provides a powerful tool for analyzing and visualizing geographic relationships.
Defining Map Radius: A Circle of Relevance
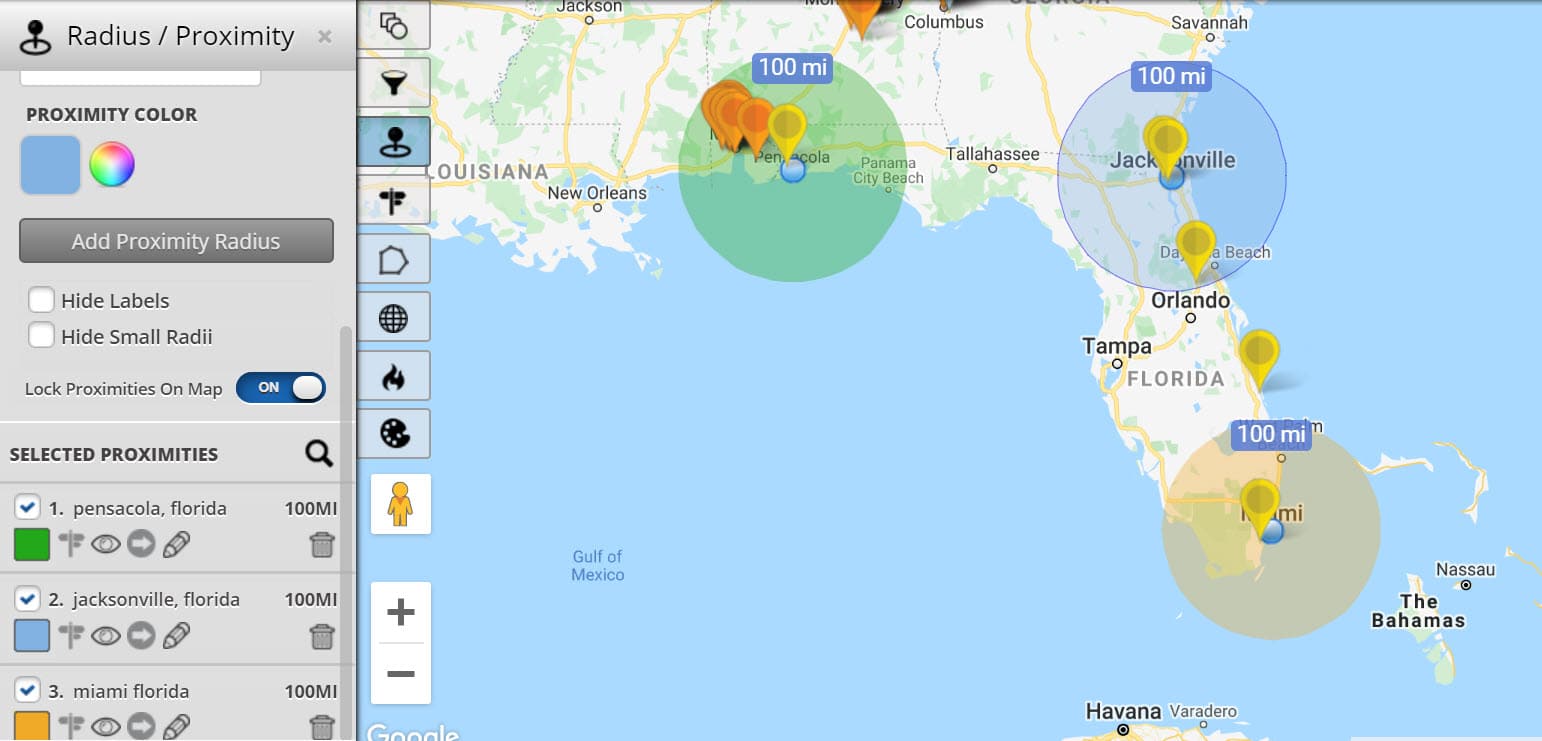
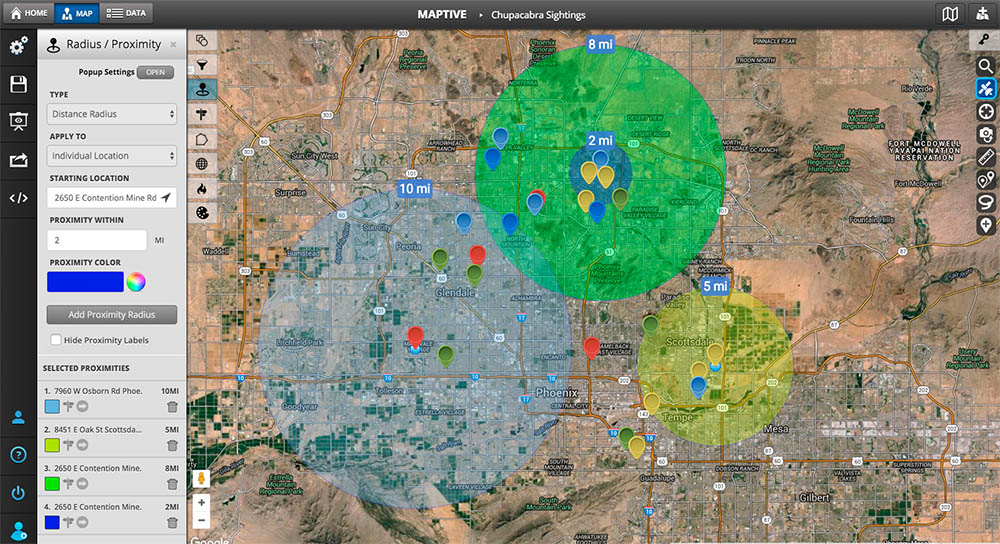
Map radius, essentially, refers to a circular area defined around a specific point on a map. This circle represents a specific distance from the central point, encompassing all locations within that radius. The radius itself can be measured in various units, including kilometers, miles, or even minutes of travel time, depending on the application.
Visualizing Geographic Proximity: The Power of Map Radius
The concept of map radius finds its strength in its ability to translate abstract distances into tangible visual representations. This allows users to:
- Identify locations within a specific range: Whether it’s finding restaurants within a 5-kilometer radius of your current location or pinpointing potential customers within a 20-mile radius of a business, map radius provides a simple and effective way to filter and visualize data based on proximity.
- Analyze spatial relationships: By drawing circles around different points of interest, users can understand how different locations relate to each other. This is particularly useful for analyzing market reach, identifying potential service areas, or understanding the distribution of resources across a region.
- Visualize data clusters and patterns: By plotting data points on a map and applying a map radius, users can identify clusters of activity and understand spatial patterns that might not be apparent through simple numerical analysis.
Applications of Map Radius: A Multifaceted Tool
The versatility of map radius extends across various domains, making it a valuable tool for professionals and individuals alike:
- Business and Marketing: Businesses utilize map radius to define service areas, target potential customers, and analyze market competition. Marketing campaigns can be tailored to specific geographic zones, ensuring targeted reach and increased effectiveness.
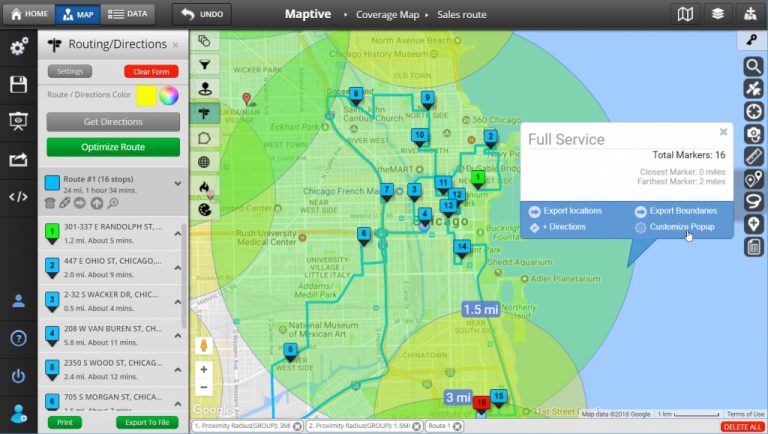
- Logistics and Transportation: Map radius plays a crucial role in optimizing delivery routes, managing fleet operations, and ensuring timely service delivery. It helps identify the most efficient routes for vehicles, minimizing travel time and maximizing efficiency.
- Urban Planning and Development: Urban planners use map radius to analyze population density, identify areas of high traffic congestion, and plan infrastructure development projects based on proximity and accessibility.
- Emergency Management and Disaster Response: In emergency situations, map radius helps define evacuation zones, identify potential points of impact, and optimize resource allocation based on proximity to affected areas.
- Environmental Monitoring and Conservation: Map radius assists in identifying areas of environmental concern, tracking wildlife movement, and managing natural resources based on their proximity to human settlements or critical ecosystems.
Beyond the Basics: Exploring the Nuances of Map Radius
While the concept of map radius might seem straightforward, its implementation can be nuanced and requires careful consideration:
- Choosing the Right Radius: The optimal radius for a specific application depends on various factors, including the nature of the data, the intended purpose, and the scale of the analysis.
- Accounting for Terrain and Obstacles: In real-world scenarios, map radius needs to account for terrain features and physical obstacles that might affect travel time and accessibility.
- Integrating with Other Data Sources: Map radius can be combined with other data sources, such as demographic information, traffic data, or weather patterns, to provide a more comprehensive understanding of geographic relationships.
- Utilizing Advanced Mapping Tools: Specialized mapping software and APIs allow users to create interactive map radius visualizations, perform advanced spatial analysis, and integrate with other data sources.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions about Map Radius
Q: What are the different units used for map radius?
A: Map radius can be measured in various units, including kilometers, miles, meters, and even minutes of travel time. The choice of unit depends on the specific application and the desired level of precision.
Q: How does map radius differ from other geographic tools like distance matrices?
A: While both map radius and distance matrices deal with distance, they differ in their approach. Map radius focuses on visualizing proximity within a circular area, while distance matrices provide a tabular representation of distances between multiple points.
Q: Can map radius be used to analyze data beyond location-based information?
A: While map radius is primarily associated with location-based data, its concept can be extended to analyze other types of data that exhibit spatial relationships. For instance, it can be used to analyze the spread of ideas, the influence of social networks, or the diffusion of innovations.
Tips for Effective Use of Map Radius:
- Clearly define the purpose of your analysis: Determine the specific question you are trying to answer and choose the appropriate radius accordingly.
- Consider the scale and context: Ensure that the chosen radius is relevant to the geographic area and the type of data you are analyzing.
- Utilize advanced mapping tools: Explore specialized software and APIs that offer advanced features for creating interactive map radius visualizations and performing complex spatial analysis.
- Combine map radius with other data sources: Integrate map radius with relevant demographic, economic, or environmental data to gain a more holistic understanding of geographic relationships.
Conclusion: The Enduring Significance of Map Radius
In a world increasingly driven by location-based information, map radius serves as a powerful tool for understanding and visualizing geographic relationships. By providing a simple yet effective way to represent proximity, it empowers users to analyze data, make informed decisions, and optimize processes across various domains. As technology continues to advance, map radius is poised to become even more integral to our understanding of the world around us, facilitating informed decision-making and fostering a deeper appreciation for the interconnectedness of our planet.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Delving into the Realm of Geographic Proximity: Understanding Map Radius and Its Applications. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!