Delineating Spatial Boundaries: The Power of Drawing Circles on Maps
Related Articles: Delineating Spatial Boundaries: The Power of Drawing Circles on Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Delineating Spatial Boundaries: The Power of Drawing Circles on Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Delineating Spatial Boundaries: The Power of Drawing Circles on Maps

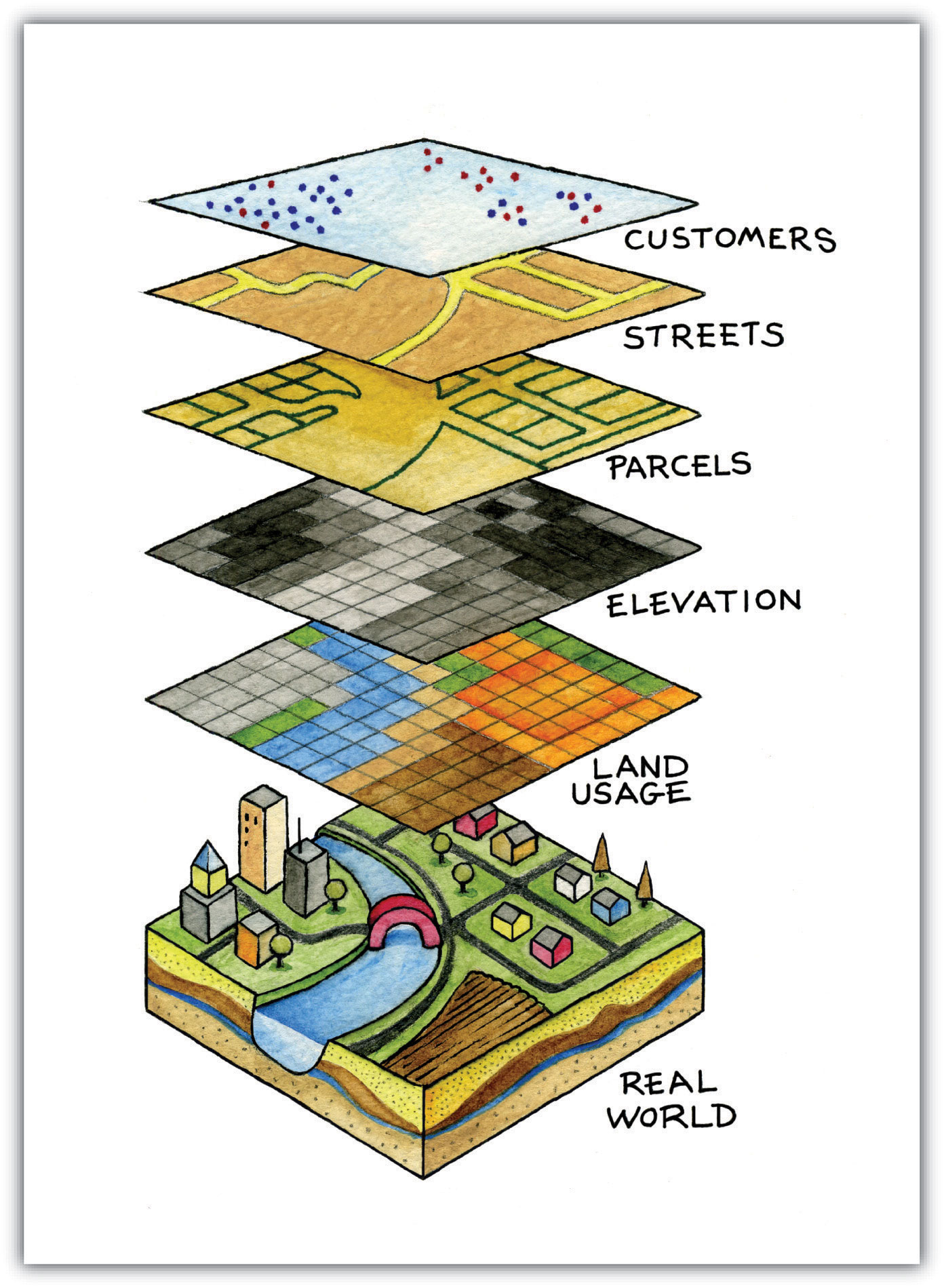
Maps are powerful tools for understanding and navigating our world. They provide a visual representation of geographical features, enabling us to analyze spatial relationships and plan routes. However, maps can be even more informative when augmented with specific data overlays, such as circles that delineate areas of interest.
Drawing circles on maps, often referred to as "buffering," is a fundamental technique in geographic information systems (GIS) and cartography. It involves creating a circular zone around a point of interest, defining a specific radius. This simple act of drawing a circle has profound implications for various applications, from emergency response and resource management to environmental analysis and urban planning.
Understanding the Fundamentals of Circle Drawing on Maps
The process of drawing a circle on a map involves identifying a central point and defining its radius. The central point serves as the origin of the circle, while the radius determines the circle’s size. This seemingly simple operation is facilitated by specialized tools available in GIS software, online mapping platforms, and even some dedicated mobile applications.
The Importance of Accuracy in Defining the Radius
The accuracy of the radius is crucial for the effectiveness of the circle. An inaccurate radius can lead to misinterpretations, potentially impacting decisions based on the analysis. The chosen radius should be relevant to the specific application. For example, in an emergency response scenario, the radius of a circle around a disaster site might represent the potential reach of rescue teams or the area affected by the disaster.
Applications of Circle Drawing on Maps: A Multifaceted Tool
The ability to draw circles on maps has a wide range of applications across diverse fields:
1. Emergency Response and Disaster Management:
- Defining Evacuation Zones: Circles can delineate areas needing evacuation during natural disasters or other emergencies. The radius might be based on the anticipated impact of the event, ensuring the safety of residents.
- Mapping Resource Deployment: Circles can indicate the range of resources available, such as fire stations, ambulances, or search and rescue teams. This allows for efficient allocation of resources based on proximity to the affected area.
2. Urban Planning and Development:
- Analyzing Accessibility: Circles can define areas within a certain distance from public transportation hubs, schools, or healthcare facilities. This information is valuable for urban planning and infrastructure development.
- Identifying Development Zones: Circles can define areas suitable for residential, commercial, or industrial development based on factors like proximity to existing infrastructure and environmental considerations.
3. Environmental Analysis and Conservation:
- Mapping Habitat Ranges: Circles can represent the home range of endangered species, facilitating conservation efforts and habitat protection.
- Monitoring Pollution Levels: Circles can define areas affected by pollution, enabling environmental agencies to track the spread and impact of contaminants.
4. Resource Management and Allocation:
- Optimizing Delivery Routes: Circles can define service areas for utilities, delivery services, or other resource providers, optimizing routes and minimizing travel time.
- Managing Natural Resources: Circles can define areas for logging, mining, or other resource extraction activities, ensuring sustainable practices and minimizing environmental impact.
5. Business and Marketing:
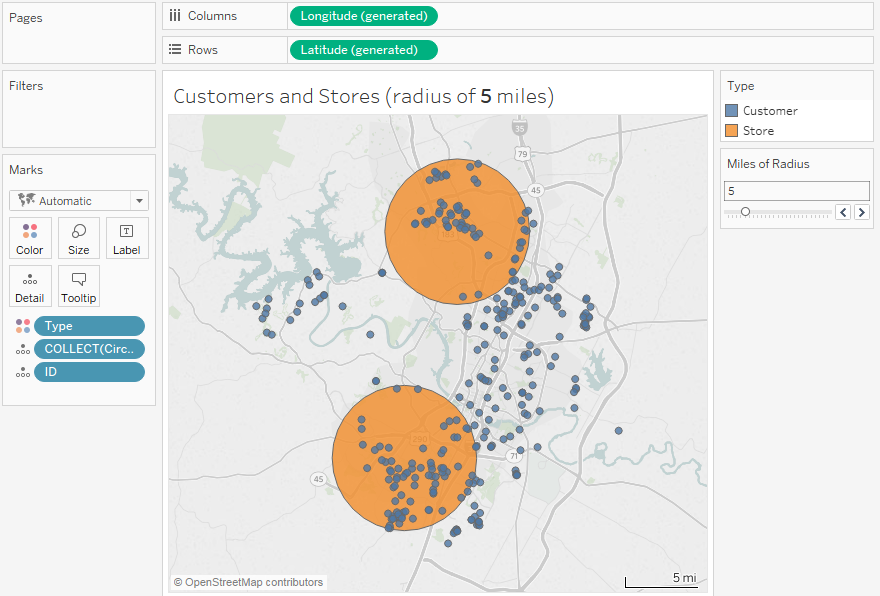
- Defining Target Market Areas: Circles can define areas where a business’s target market resides, helping with marketing strategies and location selection.
- Analyzing Customer Proximity: Circles can represent the geographic distribution of customers, allowing businesses to identify areas with high customer density.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions About Drawing Circles on Maps
Q: What are the different methods for drawing circles on maps?
A: Circles can be drawn using various methods:
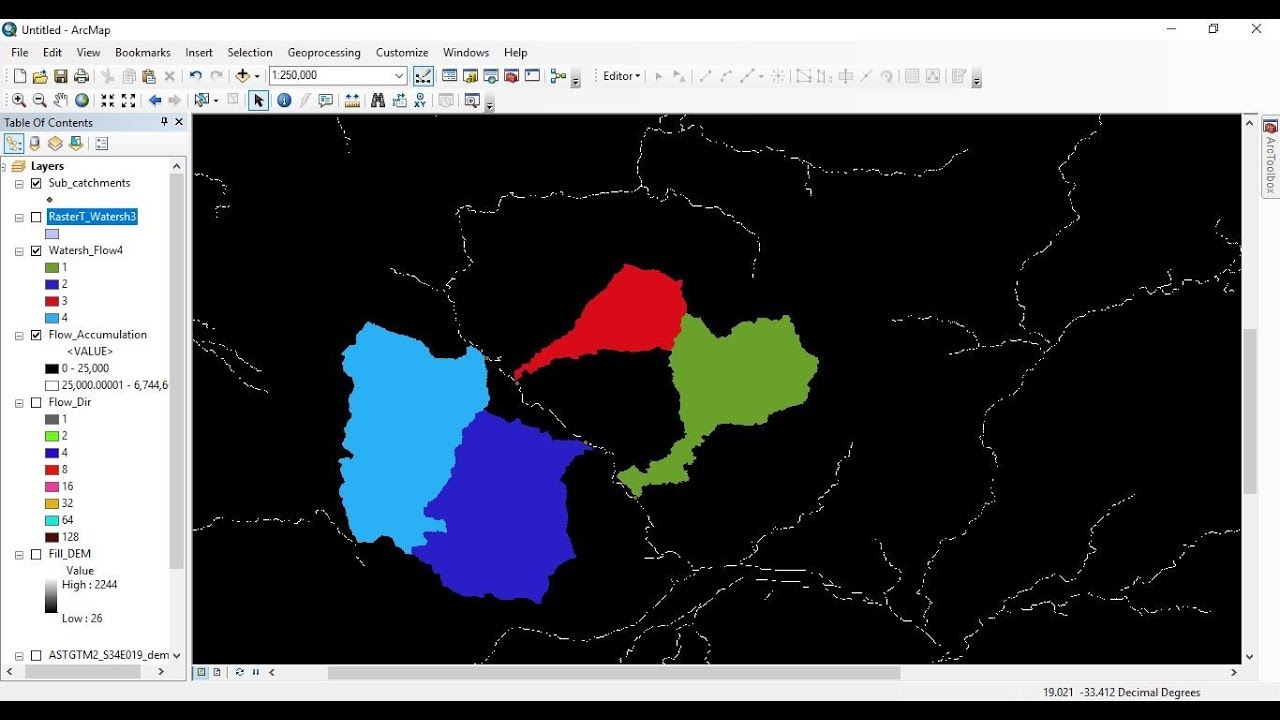
- GIS Software: Specialized software like ArcGIS, QGIS, and MapInfo offer powerful tools for drawing circles with accurate radii and customizable properties.
- Online Mapping Platforms: Platforms like Google Maps, Bing Maps, and OpenStreetMap provide basic tools for drawing circles, often with limited customization options.
- Mobile Applications: Mobile apps designed for mapping and navigation often include features for drawing circles, typically for finding points of interest within a specific radius.
Q: What factors should be considered when choosing the radius of a circle?
A: The radius should be determined based on the specific application and the information being analyzed. Factors to consider include:
- Distance: The radius should be relevant to the distance being analyzed, such as travel time, resource reach, or impact zone.
- Scale: The radius should be appropriate for the map’s scale. A radius that is too large or too small might not be useful for the intended purpose.
- Data: The radius should be based on available data, such as population density, resource availability, or environmental factors.
Q: How can I ensure the accuracy of the circle’s radius?
A: Accuracy is crucial for reliable analysis. To ensure accuracy:
- Use reliable data sources: Ensure the central point and radius are based on accurate data.
- Verify the map’s projection: The map projection can affect the accuracy of distances and therefore the radius.
- Calibrate the radius: If possible, use ground truth data to verify the accuracy of the radius.
Tips for Effective Circle Drawing on Maps
- Clearly define the purpose: Establish the specific reason for drawing the circle before starting the process.
- Choose the appropriate tool: Select a tool that offers the necessary features and accuracy for the intended application.
- Use appropriate units: Ensure the radius is measured in the correct units, such as meters, kilometers, or miles.
- Consider the map’s scale: Choose a radius that is appropriate for the map’s scale to avoid distortion or misinterpretation.
- Label the circle: Add a label to the circle indicating its radius and the reason for its creation.
Conclusion: The Power of Spatial Analysis
Drawing circles on maps is a simple yet powerful technique that unlocks a wealth of spatial analysis possibilities. By defining areas of interest and analyzing spatial relationships, it enables us to make informed decisions in various fields, from emergency response and urban planning to environmental conservation and business development. As technology continues to advance, the tools for drawing circles on maps will become even more sophisticated, further enhancing our ability to understand and interact with the world around us.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Delineating Spatial Boundaries: The Power of Drawing Circles on Maps. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!