Defining the City’s Reach: Understanding Map Radius and Its Applications
Related Articles: Defining the City’s Reach: Understanding Map Radius and Its Applications
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Defining the City’s Reach: Understanding Map Radius and Its Applications. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Defining the City’s Reach: Understanding Map Radius and Its Applications

The concept of a "map radius" around a city, while seemingly simple, holds profound implications for various fields. It encompasses the geographical area surrounding a city within a specified distance, effectively delineating the city’s influence and reach. This concept finds application in diverse domains, from urban planning and transportation to economic analysis and environmental studies.
Defining the Scope: What is a Map Radius?
A map radius is essentially a circle drawn around a city’s center point on a map. The radius of this circle represents the distance from the city center to the outer boundary of the defined area. This distance can be measured in kilometers, miles, or any other relevant unit. The radius can be fixed at a specific value, or it can be dynamically adjusted based on specific criteria, such as travel time, population density, or economic activity.
Beyond Distance: Factors Influencing Map Radius
While distance is the fundamental parameter, a map radius is not merely a geographical construct. It is influenced by various factors that shape the city’s interaction with its surroundings. These factors include:
- Transportation infrastructure: The quality and availability of roads, rail lines, and other transportation networks significantly impact the accessibility of areas within the map radius. Areas with efficient transportation links are more readily integrated into the city’s sphere of influence.
- Economic activity: The concentration of businesses, industries, and employment opportunities within the map radius contributes to its economic significance. Areas with strong economic activity tend to be more closely linked to the city’s economic engine.
- Population density: The distribution of population within the map radius affects its social and demographic characteristics. Areas with higher population densities often exhibit greater demand for services and infrastructure.
- Environmental factors: Natural features like rivers, mountains, or forests can influence the boundaries of the map radius, creating natural barriers or corridors of connectivity.
Applications of Map Radius: A Multifaceted Tool
The concept of map radius finds practical applications across diverse fields, offering valuable insights into urban dynamics and planning.
1. Urban Planning and Development:
- Identifying growth areas: Analyzing population density and economic activity within the map radius helps urban planners identify areas with potential for growth and development.
- Optimizing infrastructure: By understanding the distribution of population and economic activity, planners can prioritize infrastructure investments to ensure efficient connectivity and service provision within the map radius.
- Assessing environmental impact: Map radius analysis can help assess the environmental impact of urban expansion and infrastructure projects on surrounding areas.
2. Transportation and Logistics:
- Optimizing delivery routes: Logistics companies can use map radius to optimize delivery routes and minimize travel time within a designated area.
- Planning public transportation: Map radius analysis helps determine the optimal location of public transportation hubs and routes to ensure efficient connectivity within the city’s sphere of influence.
- Evaluating accessibility: By analyzing travel time and accessibility within the map radius, transportation planners can assess the effectiveness of existing infrastructure and identify areas requiring improvement.
3. Economic Analysis and Market Research:
- Identifying target markets: Businesses can leverage map radius analysis to identify potential customer segments within a specific geographical area.
- Analyzing market competition: Understanding the distribution of businesses and industries within the map radius allows for a competitive analysis and identification of market opportunities.
- Evaluating investment potential: Map radius analysis can help investors assess the economic viability of projects and investments within a defined area.
4. Environmental Studies and Conservation:
- Monitoring urban sprawl: Map radius analysis can track the expansion of urban areas over time, providing insights into the rate of urban sprawl and its impact on surrounding ecosystems.
- Assessing environmental hazards: Map radius analysis can help identify areas susceptible to environmental hazards, such as flooding or air pollution, and inform mitigation strategies.
- Managing natural resources: Understanding the distribution of natural resources within the map radius allows for better management and conservation efforts.
FAQs on Map Radius:
Q: How is the radius of a map determined?
A: The radius is typically determined based on the specific application and the factors considered relevant. For example, a transportation-focused map radius might be defined by travel time, while an economic analysis might use a radius based on market reach.
Q: What are the limitations of map radius analysis?
A: Map radius analysis is a simplified representation of reality and does not account for complex factors like social networks, cultural influences, or political boundaries. It is essential to consider these factors when interpreting results.
Q: How can map radius be used in conjunction with other data?
A: Map radius analysis can be combined with other data sources, such as demographics, economic indicators, and environmental data, to create more comprehensive and nuanced insights.
Tips for Utilizing Map Radius:
- Clearly define your objectives: Before using map radius, establish specific goals and objectives to ensure the analysis is relevant to your needs.
- Select appropriate radius: Choose a radius that aligns with the scope of your analysis and the factors you are considering.
- Consider multiple data sources: Integrate map radius analysis with other data sources to provide a more comprehensive understanding of the area.
- Interpret results cautiously: Recognize that map radius is a simplification and may not capture all relevant factors.
Conclusion:
The map radius around a city is a powerful tool for understanding and analyzing urban dynamics. By defining the geographical reach of a city based on factors like distance, transportation, economics, and population, it provides valuable insights for urban planning, transportation, economic analysis, and environmental studies. While it is a simplification of complex realities, map radius analysis offers a valuable framework for understanding the interconnectedness of cities and their surrounding areas. Its application across various fields highlights its potential to inform decision-making and foster sustainable urban development.




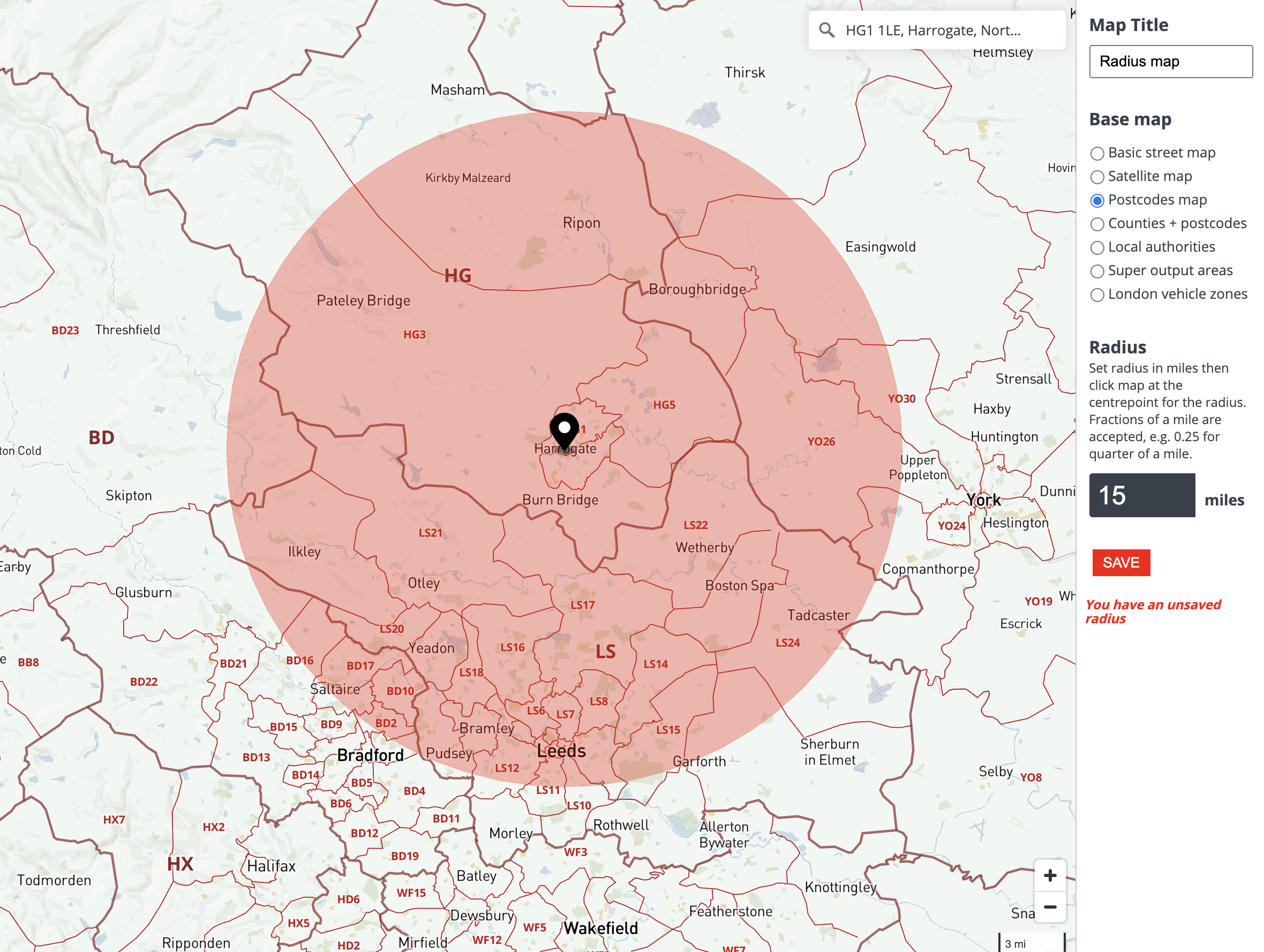


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Defining the City’s Reach: Understanding Map Radius and Its Applications. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!