Defining the Circle: Understanding Map Radius Around a Point
Related Articles: Defining the Circle: Understanding Map Radius Around a Point
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Defining the Circle: Understanding Map Radius Around a Point. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Defining the Circle: Understanding Map Radius Around a Point
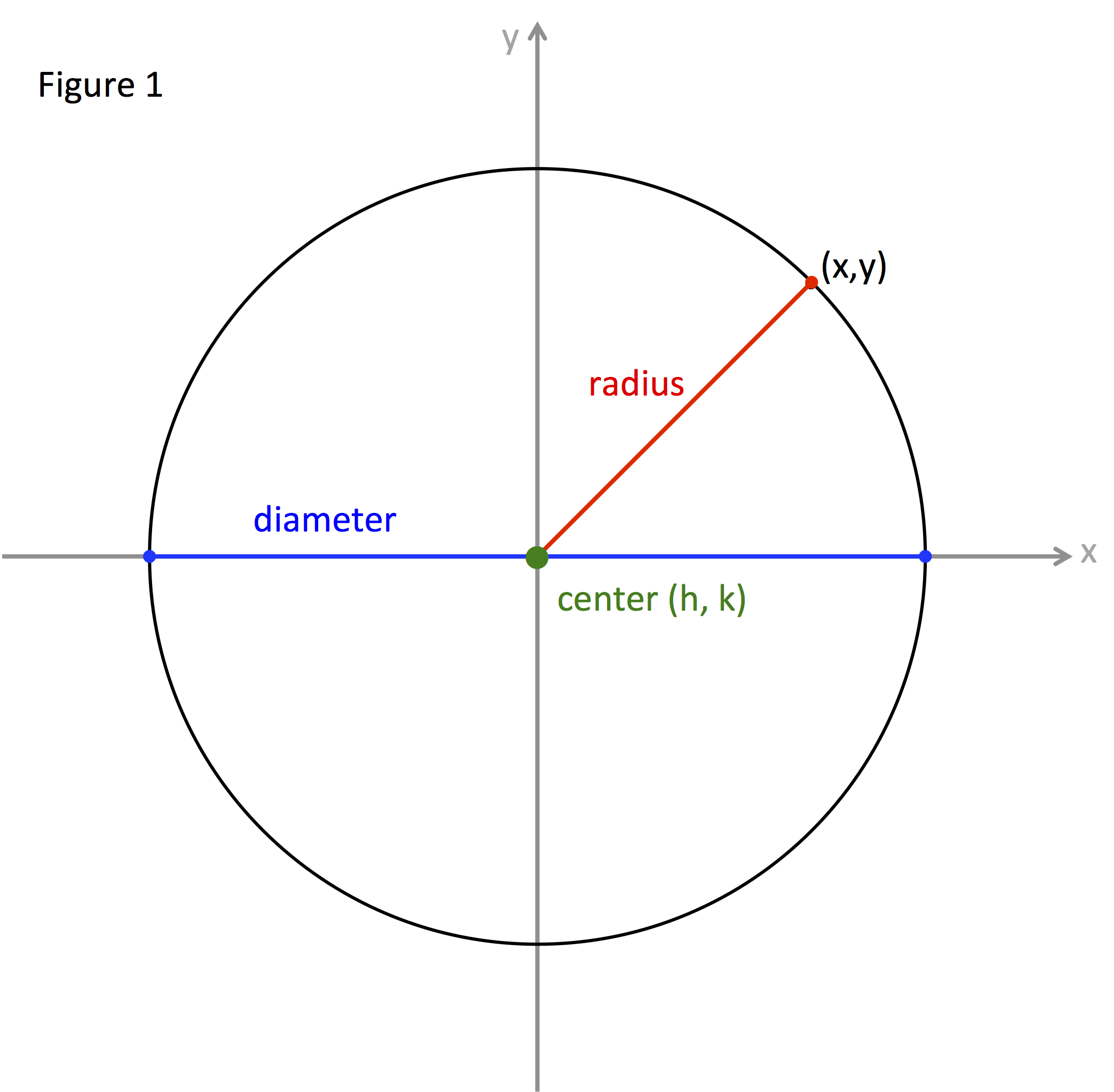
In the realm of spatial data analysis and geographic information systems (GIS), the concept of a "map radius around a point" plays a crucial role. It involves defining a circular area centered on a specific location, encompassing all points within a predetermined distance from the central point. This seemingly simple concept holds immense value in diverse applications, enabling efficient analysis and visualization of spatial data, making it a fundamental tool in various disciplines.
Conceptualizing the Radius:
Imagine a map, a visual representation of the world, with a specific point marked on it. The "radius" refers to the distance from this central point to the edge of a circular area drawn around it. This distance, expressed in units such as miles, kilometers, or any other relevant measurement, defines the extent of the circle.
Visualizing the Circle:
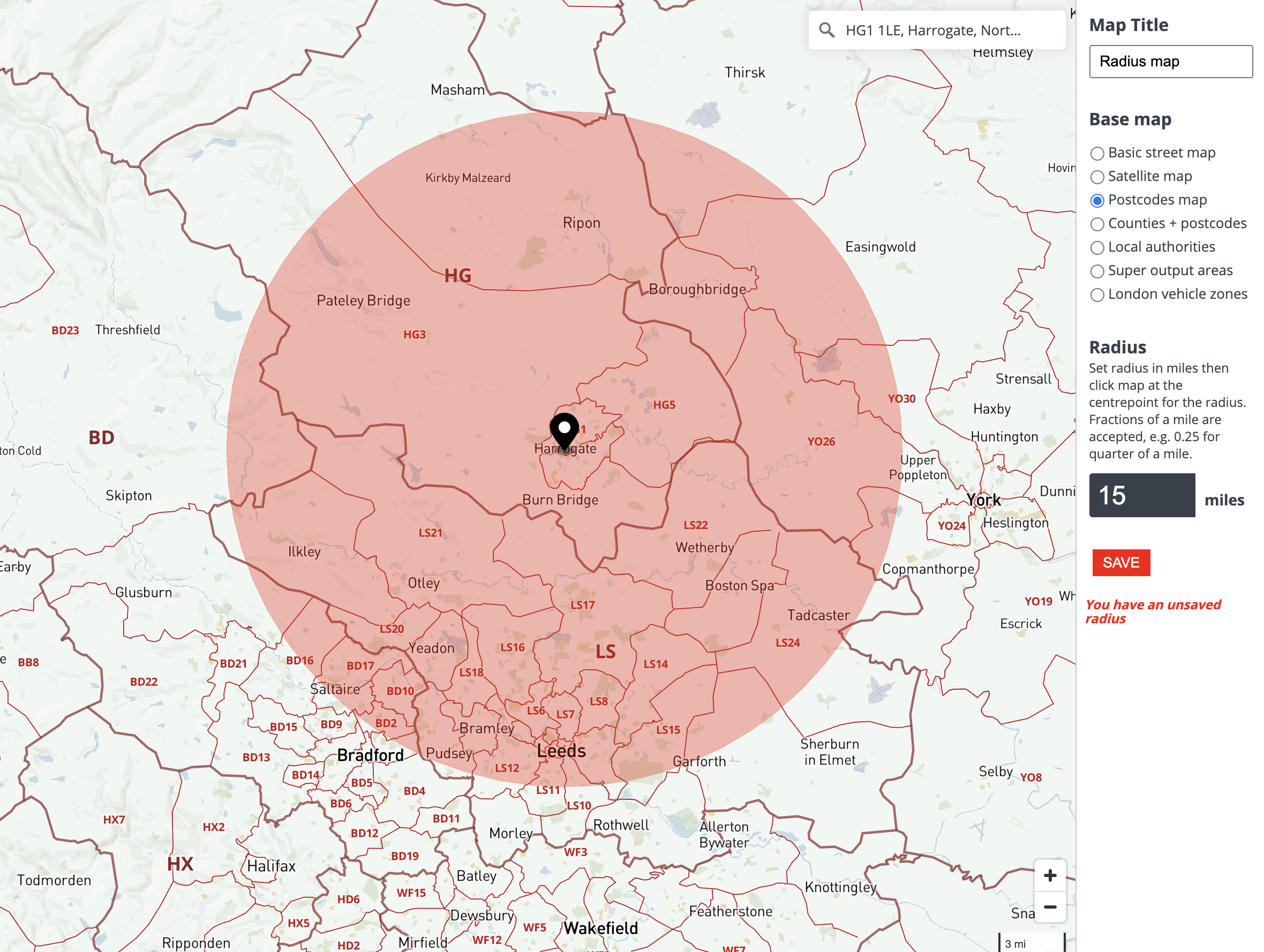
The "map radius around a point" is essentially a circle drawn on a map, representing a specific geographic area. This circle encompasses all points located within the specified distance from the central point. The radius, acting as the circle’s defining characteristic, determines the size of the area covered.
Applications Across Disciplines:
The concept of a map radius around a point finds applications in a wide range of disciplines, including:
- Urban Planning: Analyzing the impact of new infrastructure projects on surrounding areas, identifying suitable locations for public facilities, and assessing the accessibility of services within a specific radius.
- Environmental Science: Studying the impact of pollution sources, mapping the spread of invasive species, and analyzing the distribution of natural resources within a defined area.
- Emergency Management: Identifying potential evacuation zones, locating resources in disaster-affected areas, and assessing the impact of natural hazards within a specified radius.
- Retail and Marketing: Analyzing customer demographics and purchasing patterns within a specific distance from a store, identifying potential target markets, and optimizing marketing campaigns.
- Transportation and Logistics: Optimizing delivery routes, identifying potential traffic congestion zones, and analyzing the accessibility of transportation networks within a defined area.
Benefits and Importance:
The use of a map radius around a point offers several key benefits:
- Spatial Analysis: It facilitates the analysis of spatial data by focusing on areas of interest within a defined radius. This allows for the identification of patterns, trends, and relationships within specific geographic areas.
- Data Visualization: The visual representation of a circular area on a map provides a clear and concise way to present spatial data, enhancing understanding and communication.
- Targeted Analysis: By focusing on a specific area defined by the radius, it allows for more targeted analysis and decision-making, streamlining efforts and maximizing efficiency.
- Efficient Resource Allocation: It helps optimize resource allocation by identifying areas within a defined radius that require specific attention, ensuring resources are utilized effectively.
- Improved Decision-Making: By providing a comprehensive understanding of spatial relationships and data within a defined area, it facilitates informed decision-making across various fields.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Q: How is the radius determined?
A: The radius is determined based on the specific application and the desired area of analysis. It can be fixed to a specific distance, calculated based on factors like travel time, or adjusted dynamically based on user inputs.
Q: What are the units used for the radius?
A: The units used for the radius depend on the context and the scale of the map. Common units include miles, kilometers, meters, or any other relevant measurement.
Q: How can I create a map radius around a point?
A: Several tools and software applications are available to create a map radius around a point. Geographic Information Systems (GIS) software like ArcGIS and QGIS provide advanced functionalities for defining and analyzing map radii. Online mapping platforms like Google Maps also offer basic tools for drawing circles around specific locations.
Q: What are some examples of how map radius around a point is used in real-world applications?
A: Examples include:
- Analyzing the impact of a new highway on surrounding neighborhoods within a 5-mile radius.
- Mapping the distribution of endangered species within a 10-kilometer radius of a protected area.
- Identifying potential customers within a 2-mile radius of a new retail store.
- Analyzing traffic congestion patterns within a 1-mile radius of a major intersection.
Tips for Utilizing Map Radius Around a Point:
- Define the Radius Carefully: The radius should be chosen based on the specific application and the desired area of analysis. Consider factors like travel time, accessibility, and the scale of the map.
- Utilize Visualizations: Use clear and concise visualizations to represent the map radius and the data within it. This will enhance understanding and communication.
- Combine with Other Spatial Data: Integrate the map radius with other relevant spatial data, such as demographic information, land use patterns, or environmental data. This will provide a more comprehensive analysis.
- Consider Dynamic Radii: Explore the use of dynamic radii that can be adjusted based on user inputs or specific criteria. This will allow for more flexible and targeted analysis.
- Evaluate Results Critically: Always critically evaluate the results obtained from using map radius around a point, considering potential biases and limitations.
Conclusion:
The concept of a map radius around a point, though seemingly simple, holds immense value in various disciplines. It provides a powerful tool for spatial analysis, data visualization, and decision-making. By understanding the principles behind this concept and its applications, individuals can leverage its potential to enhance their understanding of geographic data and make informed decisions in diverse fields. The future of spatial analysis and GIS relies on the continued development and application of such fundamental concepts, enabling us to navigate and understand our world more effectively.






/Geometry-of-a-Circle-589cbe2c5f9b58819c160fc7.jpg)
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Defining the Circle: Understanding Map Radius Around a Point. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!