Defining a Geographic Area: The Utility of Radius Drawing on Maps
Related Articles: Defining a Geographic Area: The Utility of Radius Drawing on Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Defining a Geographic Area: The Utility of Radius Drawing on Maps. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Defining a Geographic Area: The Utility of Radius Drawing on Maps
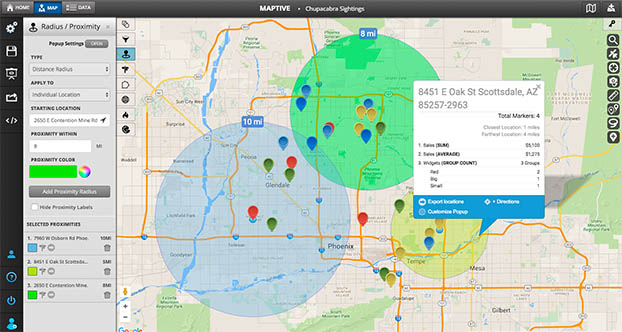
The ability to define and visualize a specific geographic area is crucial for a wide range of applications. Whether it’s for planning a delivery route, analyzing customer demographics, or assessing the impact of a natural disaster, understanding the spatial extent of a particular location is paramount. This is where the concept of drawing a radius on a map comes into play.
Understanding the Concept:
Drawing a radius on a map involves creating a circular area around a central point. This circle represents a defined distance from the central point, encompassing all locations within that specified radius. This simple yet powerful tool allows for the visualization and quantification of geographic space, offering a clear and concise representation of a defined area.
Applications of Radius Drawing:
The applications of radius drawing are extensive and diverse, spanning across various fields:
1. Business and Marketing:
- Market Analysis: By drawing a radius around a store location, businesses can analyze the potential customer base within a specific distance, aiding in market research and targeted advertising campaigns.
- Delivery Route Optimization: Logistics companies can utilize radius drawing to define service areas, optimize delivery routes, and calculate estimated delivery times.
- Competitive Analysis: Drawing a radius around a competitor’s location helps businesses understand the competitive landscape and identify potential market opportunities.
2. Emergency Management and Disaster Response:
- Evacuation Planning: During natural disasters, radius drawing can be used to define evacuation zones, ensuring efficient and timely evacuation of affected populations.
- Resource Allocation: Drawing radii around affected areas facilitates the allocation of emergency resources, such as medical supplies, food, and shelter, to those in need.
- Damage Assessment: Radius drawing can be used to assess the extent of damage caused by natural disasters, aiding in the prioritization of relief efforts.
3. Environmental Management and Conservation:
- Protected Area Management: Drawing a radius around protected areas helps in defining and enforcing boundaries, ensuring the preservation of biodiversity and natural resources.
- Environmental Impact Assessment: Radius drawing allows for the analysis of potential environmental impacts of development projects, ensuring responsible and sustainable land use.
- Pollution Monitoring: Drawing radii around pollution sources enables the monitoring of pollutant dispersal and the identification of areas at risk.
4. Urban Planning and Development:
- Infrastructure Planning: Radius drawing helps in identifying areas within a specific distance from key infrastructure, such as schools, hospitals, and transportation hubs, aiding in planning and development.
- Urban Renewal Projects: Drawing radii around targeted areas allows for the assessment of potential impacts of urban renewal projects on surrounding communities.
- Public Services Accessibility: Radius drawing can be used to analyze the accessibility of public services, such as libraries, parks, and community centers, ensuring equitable access for all citizens.
5. Research and Data Analysis:
- Spatial Data Analysis: Radius drawing is a fundamental tool for spatial data analysis, allowing for the aggregation and analysis of data within defined areas.
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS): Radius drawing is a core functionality of GIS software, enabling the creation of buffer zones, proximity analysis, and other spatial operations.
- Social Science Research: Radius drawing can be used to analyze the spatial distribution of populations, social phenomena, and other geographical patterns.
Tools for Radius Drawing:
Numerous tools and software are available for drawing radii on maps, catering to different needs and levels of expertise:
1. Online Mapping Services:
- Google Maps: Offers a simple and intuitive interface for drawing circles around a location.
- Bing Maps: Provides similar functionality to Google Maps, with additional features for customizing radius parameters.
- MapQuest: Offers a radius tool with the ability to adjust the radius size and visualize the area within the circle.
2. Geographic Information Systems (GIS) Software:
- ArcGIS: A powerful GIS software with advanced functionality for drawing radii, creating buffers, and performing complex spatial analysis.
- QGIS: A free and open-source GIS software with a user-friendly interface and comprehensive spatial analysis capabilities.
- GRASS GIS: A free and open-source GIS software known for its advanced geospatial analysis tools, including radius drawing and buffer creation.
3. Mobile Mapping Apps:
- GPS Navigation Apps: Many GPS navigation apps, such as Google Maps and Waze, offer the ability to draw radii around a location, facilitating the planning of routes and exploring nearby areas.
- Field Data Collection Apps: Apps designed for field data collection, such as Survey123 and Collector for ArcGIS, often include tools for drawing radii and collecting data within defined areas.
FAQs:
Q: How do I draw a radius on a map?
A: The process for drawing a radius on a map varies depending on the tool being used. Generally, you will need to:
- Select the location: Choose the central point around which you want to draw the radius.
- Set the radius: Specify the distance you want to encompass within the circle. This can be done using units such as miles, kilometers, or feet.
- Draw the circle: Use the drawing tool provided by the software or app to create the circle around the central point.
Q: What are the limitations of radius drawing?
A: While radius drawing is a valuable tool, it has some limitations:
- Curvature of the Earth: Radius drawing assumes a flat surface, which can introduce inaccuracies when dealing with large distances or areas with significant curvature.
- Irregular Boundaries: Radius drawing creates a perfect circle, which may not accurately represent areas with irregular boundaries, such as coastlines or mountain ranges.
- Data Availability: The accuracy of radius drawing relies on the availability and quality of underlying spatial data.
Tips for Effective Radius Drawing:
- Consider the scale: Choose a radius that is appropriate for the scale of the map and the purpose of the analysis.
- Use appropriate units: Select units of measurement that are consistent with the map data and the intended application.
- Visualize the area: Ensure that the drawn radius accurately represents the intended geographic area and consider any potential distortions.
- Experiment with different tools: Explore various tools and software to find the best option for your specific needs and level of expertise.
Conclusion:
Drawing a radius on a map is a simple yet powerful tool that enables the definition, visualization, and quantification of geographic space. Its applications are wide-ranging, spanning across various fields, from business and marketing to emergency management and research. By understanding the concept, exploring the available tools, and considering the limitations, individuals and organizations can leverage the power of radius drawing to enhance their decision-making, planning, and analysis capabilities.
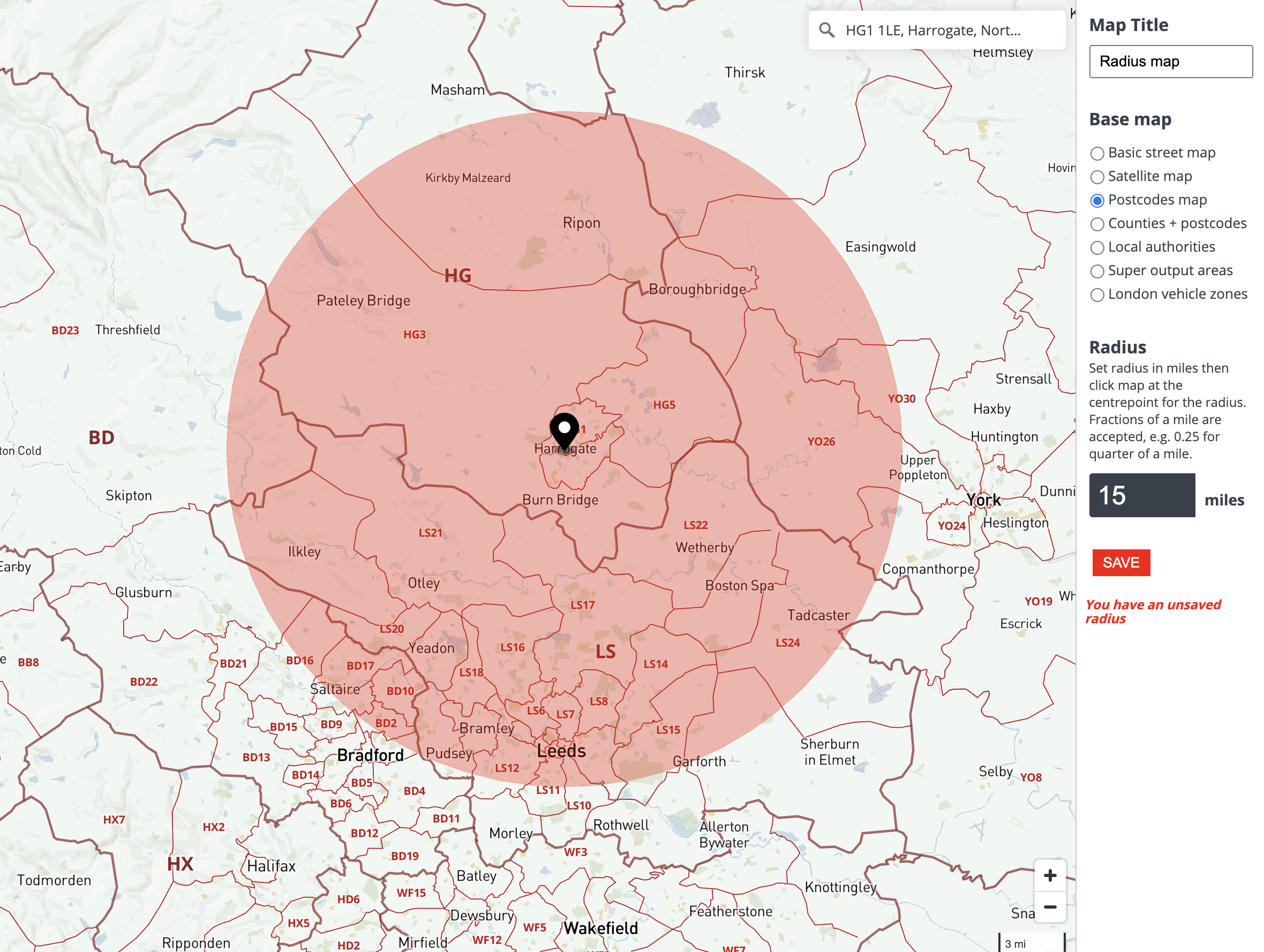

![Radius Map [Tool For Drawing & Creation] Distance & Driving Tim - Smappen](https://www.smappen.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/radiusmap-1024x671.jpg)

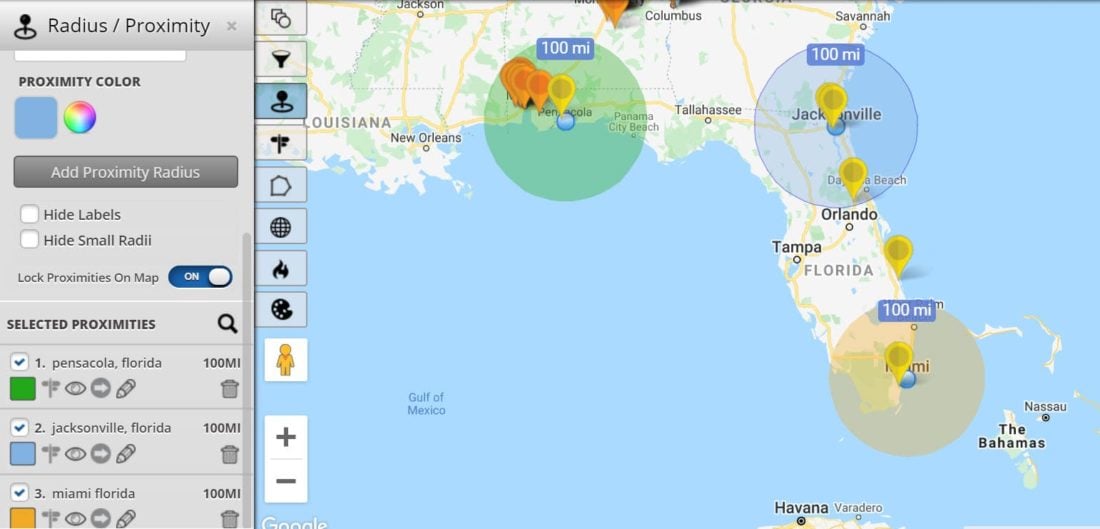

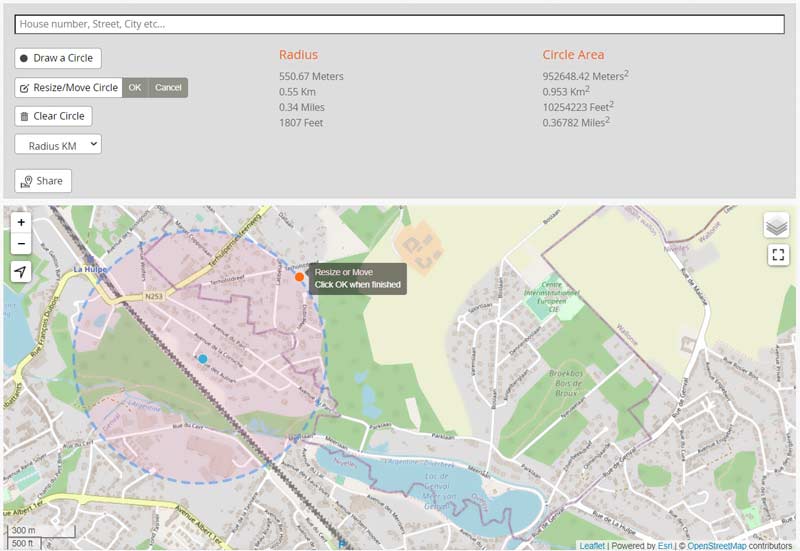

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Defining a Geographic Area: The Utility of Radius Drawing on Maps. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!