Charting the World: A History of the World Map
Related Articles: Charting the World: A History of the World Map
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Charting the World: A History of the World Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Charting the World: A History of the World Map

The world map, a seemingly simple representation of our planet, has a history as rich and complex as the Earth itself. It is a testament to humanity’s enduring fascination with understanding our place in the vastness of the cosmos, a desire to map not just physical landscapes but also the boundaries of knowledge and understanding.
The Early Beginnings: From Ancient to Medieval
The earliest known world maps emerged from ancient civilizations, driven by practical needs for navigation and trade. The Babylonians, for instance, developed celestial maps for astronomical observations, which influenced their understanding of the world’s geography. The ancient Greeks, known for their intellectual pursuits, developed a more sophisticated understanding of the Earth’s shape and size. Their maps, often based on observations and calculations, laid the foundation for future cartographic developments.
The Roman Empire, with its vast territorial expanse, embraced mapmaking for administrative and military purposes. The Tabula Peutingeriana, a medieval copy of a Roman road map, provides a glimpse into the intricate network of roads that connected the empire. It showcases the importance of maps for communication, trade, and military strategy.
During the Middle Ages, the influence of religious beliefs shaped the understanding of the world. Maps, often influenced by biblical narratives, presented a "T-O" model, with Jerusalem at the center and the three continents of Asia, Europe, and Africa forming a "T" within a circular world. These maps, while reflecting the prevailing worldview, also served as tools for pilgrimage and missionary endeavors.
The Age of Exploration and the Rise of Modern Cartography
The Renaissance witnessed a surge in exploration and scientific inquiry, leading to a revolution in cartography. The invention of the printing press facilitated the dissemination of maps, while advancements in navigation, such as the compass and astrolabe, enabled more accurate mapping.
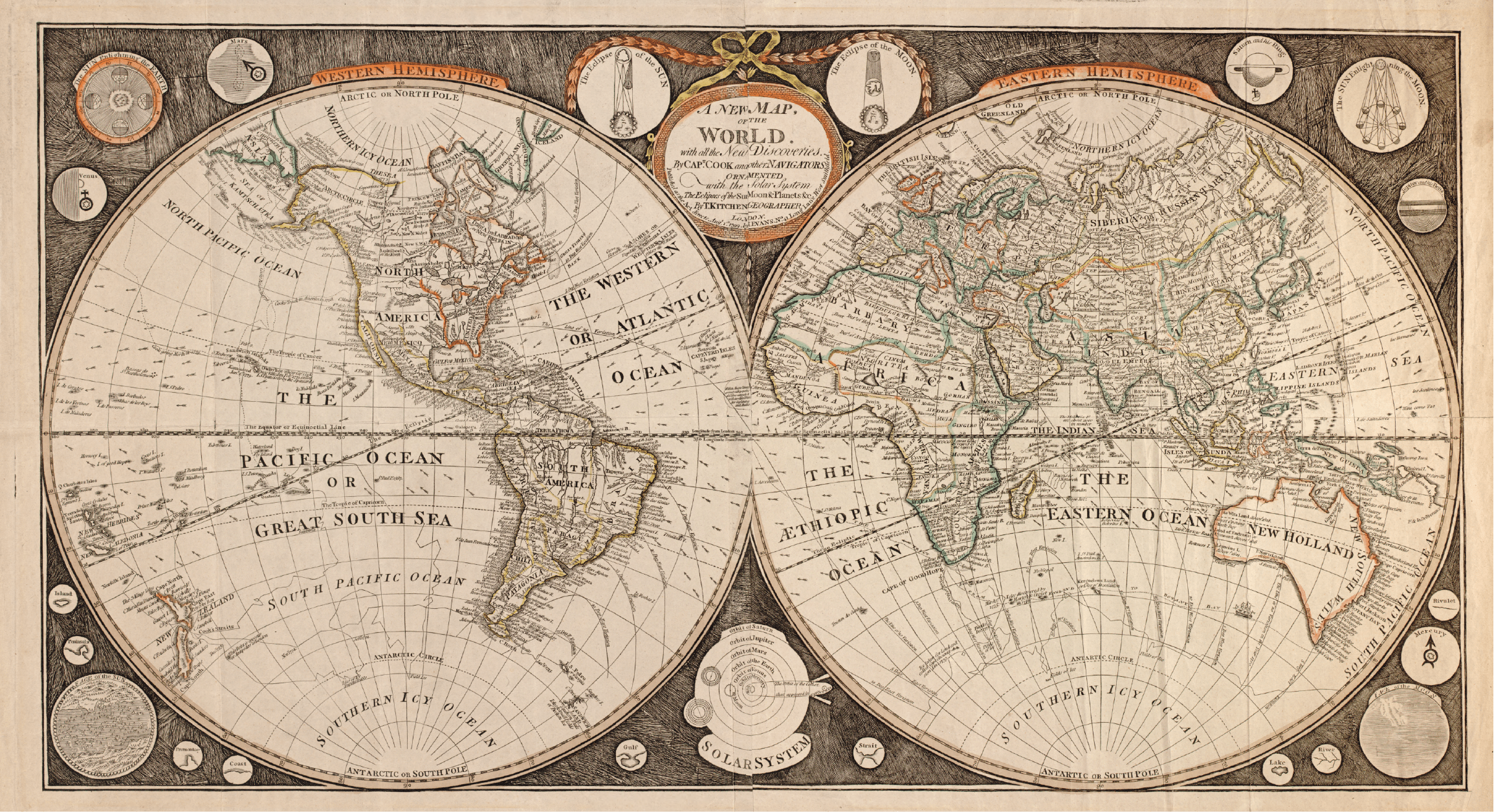
The voyages of Christopher Columbus, Vasco da Gama, and Ferdinand Magellan, among others, expanded European knowledge of the world. Their explorations led to the creation of new maps, challenging the old T-O model and revealing the true extent of the globe. The Portuguese cartographer, Pedro Reinel, is credited with creating the first world map to incorporate the newly discovered lands, paving the way for more accurate and detailed representations of the Earth.
The 16th and 17th centuries saw a flourishing of mapmaking, with individuals like Gerardus Mercator and Abraham Ortelius producing landmark maps that revolutionized cartography. Mercator’s projection, still widely used today, enabled the accurate representation of large-scale maps while preserving angles and shapes. Ortelius’s "Theatrum Orbis Terrarum," the first modern atlas, compiled a collection of maps, marking a significant step towards standardized cartographic practices.
The Enlightenment and Beyond: The Evolution of Mapmaking
The Enlightenment period brought about a renewed emphasis on reason and scientific observation, leading to further advancements in cartography. The development of surveying techniques and the use of astronomical observations allowed for more precise measurements and the creation of more accurate maps.
The 19th century witnessed the rise of national surveys and the standardization of cartographic practices. The invention of photography and the use of aerial surveys further revolutionized mapmaking, allowing for more detailed and comprehensive representations of the Earth.
The 20th century brought about the rise of digital mapping, with the advent of computers and satellite imagery. Geographic Information Systems (GIS) transformed the field of cartography, enabling the creation of interactive and dynamic maps with vast amounts of data.
The World Map: More Than Just Lines and Borders
The world map, in its various forms, has served not only as a tool for navigation and exploration but also as a powerful symbol of human understanding and interconnectedness. It reflects our evolving knowledge of the world, our changing perspectives, and our ongoing quest to make sense of our place within the global landscape.
FAQs
Q: What is the oldest known world map?
A: The oldest known world map is the Babylonian clay tablet known as the "World Map of Imago Mundi," dating back to 600 BC.
Q: What is the significance of the T-O model in world maps?
A: The T-O model, a medieval representation of the world with Jerusalem at the center, reflects the influence of religious beliefs on cartography. It showcased a world centered on the Holy Land, with Asia, Europe, and Africa forming a "T" within a circular world.
Q: What are some of the most influential world maps in history?
A: Some of the most influential world maps include:
- The Tabula Peutingeriana: A medieval copy of a Roman road map, showcasing the intricate network of roads that connected the empire.
- The World Map of Imago Mundi: The oldest known world map, dating back to 600 BC.
- Gerardus Mercator’s World Map: A landmark map, using a projection that enabled the accurate representation of large-scale maps while preserving angles and shapes.
- Abraham Ortelius’s "Theatrum Orbis Terrarum": The first modern atlas, compiling a collection of maps and marking a significant step towards standardized cartographic practices.
Q: What is the difference between a world map and a globe?
A: A world map is a flat representation of the Earth, while a globe is a three-dimensional model. Globes are more accurate in representing the Earth’s curvature and the distances between locations, while world maps use projections to represent the spherical Earth on a flat surface.
Q: How has the world map evolved over time?
A: The world map has evolved from simple, inaccurate representations to increasingly detailed and accurate representations, driven by advancements in technology, exploration, and scientific understanding. From the T-O model to modern digital maps, the world map has reflected our evolving understanding of the Earth and its inhabitants.
Tips for Understanding and Using World Maps
- Consider the projection: Different map projections distort the Earth’s shape in different ways. Understanding the projection used can help you interpret the map accurately.
- Pay attention to scale: The scale of a map indicates the ratio between the distance on the map and the actual distance on the Earth. A larger scale map shows more detail, while a smaller scale map shows a larger area.
- Look for key features: World maps often highlight key features, such as continents, oceans, major cities, and mountain ranges. These features can help you understand the map’s content and the relationships between different locations.
- Use multiple maps: Comparing different world maps can provide a more comprehensive understanding of the world’s geography and the various perspectives on its representation.
- Explore digital maps: Online mapping tools offer interactive and dynamic maps with vast amounts of data, providing a powerful tool for exploring the world.
Conclusion
The world map, a seemingly simple representation of our planet, has a rich and complex history, reflecting humanity’s enduring fascination with understanding our place in the world. From ancient civilizations to the digital age, the world map has evolved alongside our knowledge, technology, and perspectives. It serves not only as a tool for navigation and exploration but also as a powerful symbol of our interconnectedness and our ongoing quest to understand the vast and complex world around us.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Charting the World: A History of the World Map. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!