A World Unveiled: Exploring the Significance of the Original World Map
Related Articles: A World Unveiled: Exploring the Significance of the Original World Map
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A World Unveiled: Exploring the Significance of the Original World Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A World Unveiled: Exploring the Significance of the Original World Map

The world map, a ubiquitous symbol of global interconnectedness, has evolved significantly over centuries. From ancient depictions to modern digital representations, the quest to accurately portray the Earth’s surface has driven innovation and spurred understanding. However, the original world map, the very first attempt to capture the planet’s entirety, holds a unique significance, a testament to humanity’s early efforts to comprehend its place in the vastness of the universe.
The Genesis of Mapping the World
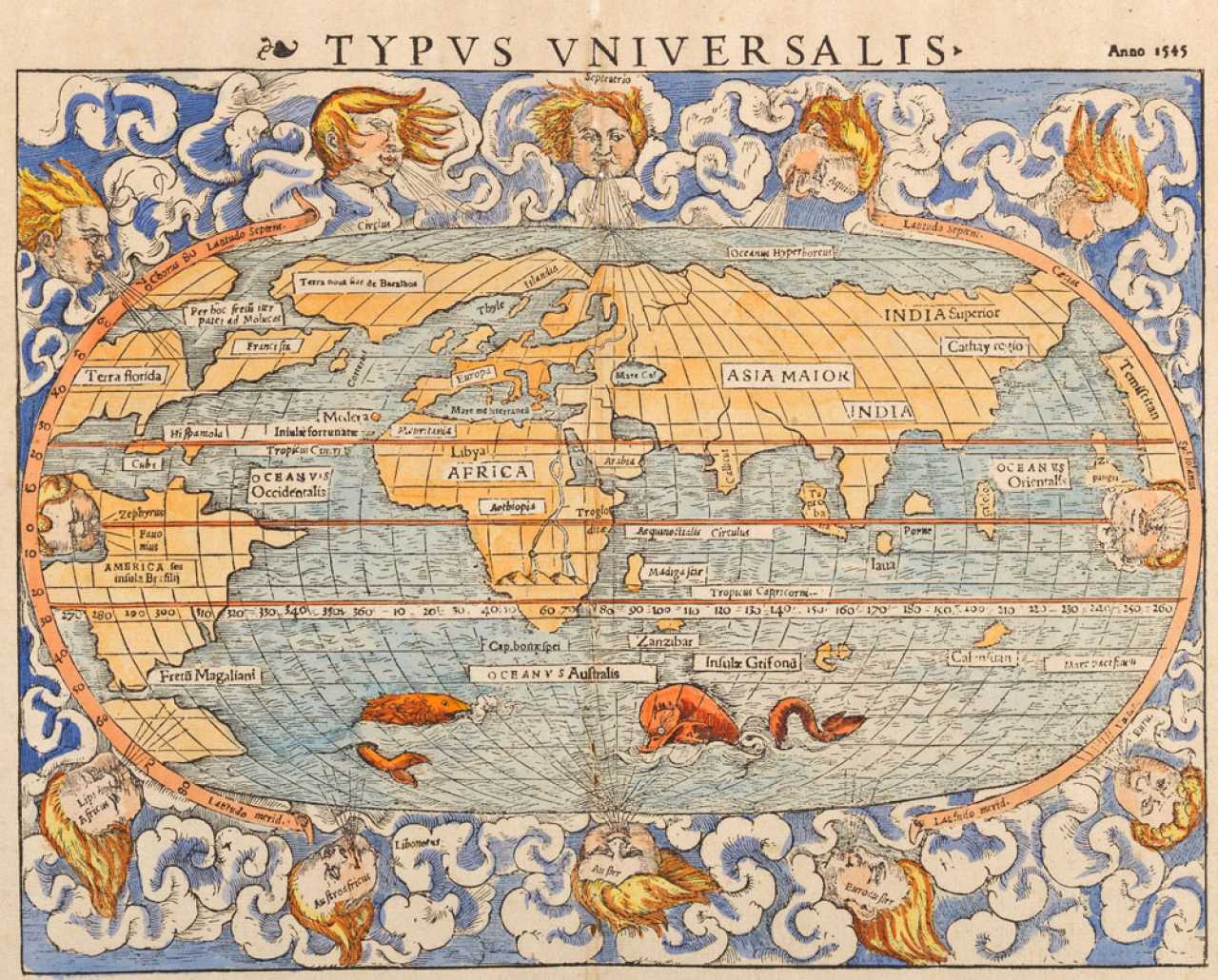
The origins of world maps are deeply intertwined with the dawn of human civilization. Ancient civilizations, driven by a need to navigate, trade, and understand their surroundings, developed rudimentary maps. These early maps were primarily schematic, relying on symbolic representations and limited geographical knowledge.
One of the earliest known world maps, the Babylonian World Map (c. 6th century BC), is a clay tablet depicting a circular world with a central island representing Mesopotamia, surrounded by a ring of water. This map, while simplistic, illustrates the human desire to conceptualize the world and its place within it.
Ancient Greek Contributions
The ancient Greeks, renowned for their philosophical and scientific advancements, made significant contributions to mapmaking. Anaximander (c. 6th century BC) is credited with creating the first known world map based on a cylindrical projection, a system that aimed to represent the spherical Earth on a flat surface. This innovation paved the way for more accurate and detailed maps.
Eratosthenes (c. 3rd century BC), a Greek scholar, made groundbreaking contributions to geography. He calculated the Earth’s circumference with remarkable accuracy and developed a map that included parallels and meridians, laying the foundation for the grid system used in modern maps.
The Roman Era and Beyond
The Roman Empire, known for its extensive road network, developed detailed maps for military and administrative purposes. The Peutinger Table (c. 4th century AD), a parchment scroll depicting the Roman road system, is a testament to the Romans’ cartographic skills.
Following the decline of the Roman Empire, the development of world maps slowed. The Beatus Map (c. 8th century AD), a medieval map depicting a biblical view of the world, highlights the influence of religious beliefs on cartography during this period.
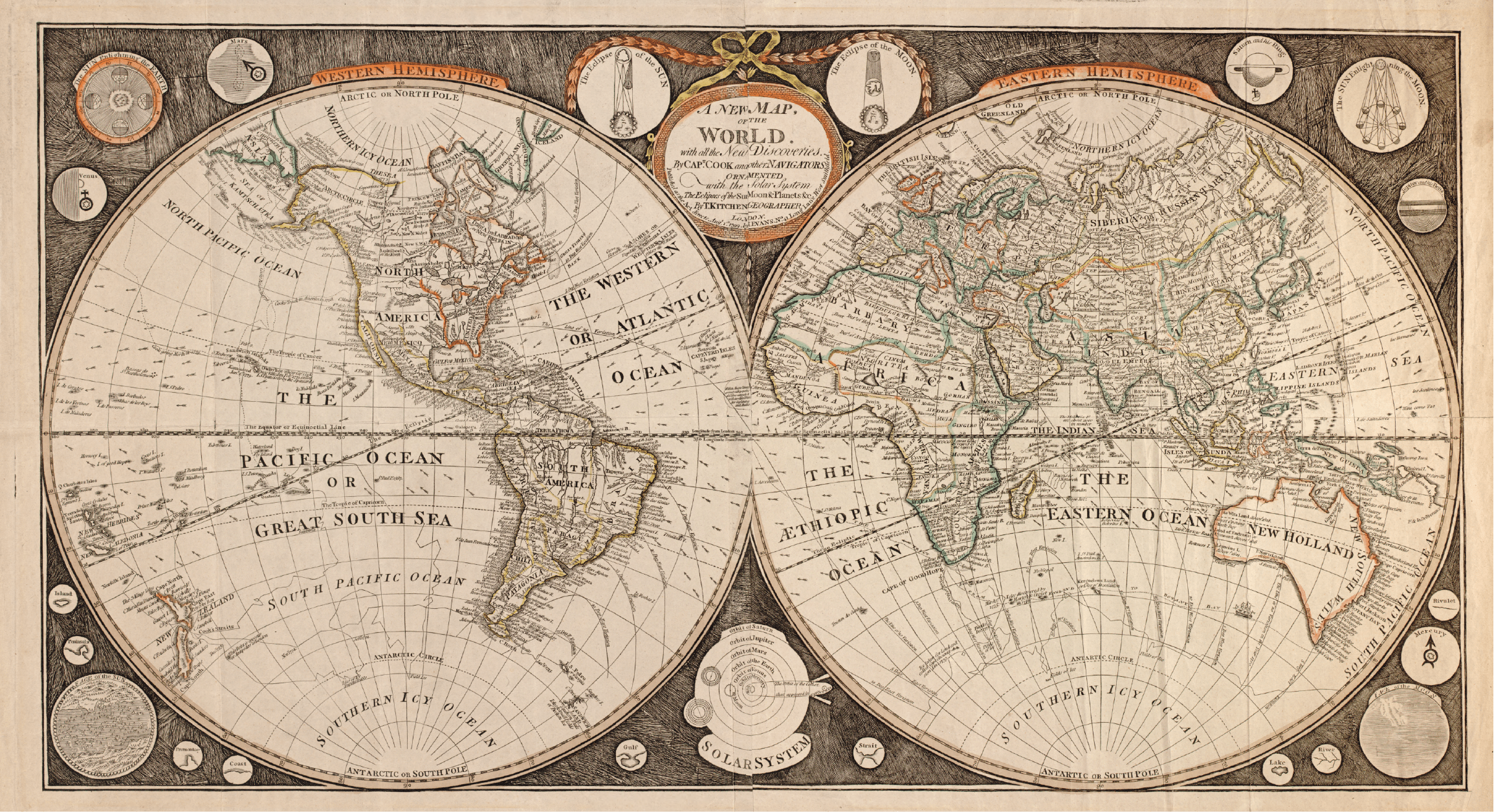
The Age of Exploration and the Rise of Modern Maps
The Age of Exploration, beginning in the 15th century, marked a turning point in mapmaking. Driven by the desire to discover new lands and trade routes, European explorers and cartographers embarked on expeditions that yielded vast amounts of geographical data.
Gerardus Mercator (1512-1594), a Flemish cartographer, revolutionized mapmaking with his Mercator Projection, a cylindrical projection that maintained accurate angles and shapes, making it ideal for navigation. This projection, still widely used today, has become synonymous with the modern world map.
The Significance of the Original World Map
The original world map, while rudimentary in its representation, holds profound significance. It embodies the human desire to understand and navigate the world, to comprehend our place within it. This first attempt to map the Earth represents the beginning of a journey, a quest to continually refine our understanding of the planet and its intricate systems.
The Importance of Accuracy and Inclusivity
The evolution of world maps has been driven by the pursuit of accuracy. As technological advancements and scientific knowledge progressed, maps became increasingly precise, incorporating detailed geographic features and accurate measurements. However, the quest for accuracy is not merely a technical endeavor; it is also a matter of inclusivity.
Historically, world maps often reflected the biases and perspectives of the dominant cultures, leading to distortions and omissions. The Eurocentric view of the world, for instance, often marginalized other cultures and continents.
In recent times, there has been a growing recognition of the need for more inclusive and equitable representations of the world. Initiatives like the "World in Data" project utilize data visualization to create maps that reflect global realities more accurately, highlighting disparities and promoting understanding across diverse cultures.
The Ongoing Evolution of World Maps
The world map continues to evolve, driven by advancements in technology, data collection, and our understanding of the planet. Digital maps, powered by satellite imagery and geographic information systems (GIS), offer unprecedented levels of detail and interactivity.
The development of three-dimensional (3D) maps further enhances our understanding of the Earth’s surface, providing immersive experiences that go beyond traditional two-dimensional representations. These advancements not only improve navigation and spatial awareness but also contribute to research, planning, and environmental management.
FAQs
Q: What is the purpose of a world map?
A: The primary purpose of a world map is to visually represent the Earth’s surface, providing a framework for understanding geographic relationships, locations, and distances. Maps serve various purposes, including navigation, exploration, communication, education, and research.
Q: How is a world map created?
A: World maps are created through a process of data collection, projection, and visualization. Data is gathered from various sources, including satellite imagery, aerial photography, and ground surveys. This data is then projected onto a flat surface using different map projections, which distort the Earth’s spherical shape to represent it on a two-dimensional plane.
Q: What are the limitations of a world map?
A: All world maps have limitations due to the inherent difficulty in representing a three-dimensional sphere on a flat surface. Map projections inevitably distort shapes, areas, or distances. Additionally, maps can be influenced by cultural biases and political agendas, leading to inaccuracies or incomplete representations.
Q: How do world maps impact our understanding of the world?
A: World maps provide a visual framework for understanding global connections, cultural diversity, and environmental challenges. They help us visualize the distribution of resources, populations, and ecosystems, fostering awareness of global issues and promoting a more interconnected perspective.
Tips
- Explore different map projections: Each projection distorts the Earth differently, emphasizing certain features while minimizing others. Understanding different projections can provide a more nuanced understanding of the world.
- Use interactive maps: Online maps offer dynamic features, allowing users to zoom, pan, and explore specific regions in detail.
- Consider the context of a map: Maps are not neutral representations; they reflect the perspectives and priorities of their creators. It is important to consider the context of a map, including its purpose, intended audience, and potential biases.
- Engage with multiple sources: Consult different maps and sources to gain a comprehensive understanding of the world.
Conclusion
The original world map, a testament to human ingenuity and the desire to understand our place in the universe, marked the beginning of a journey of cartographic exploration. Through centuries of innovation, maps have evolved from rudimentary representations to sophisticated tools that empower us to navigate, understand, and connect with the world around us. As technology continues to advance, the world map will continue to evolve, providing ever-more accurate and insightful representations of our planet. The journey of mapmaking is a testament to the human spirit of exploration and the enduring quest to understand the world in all its complexity.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A World Unveiled: Exploring the Significance of the Original World Map. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!