A World in Pieces: Understanding the Political Map
Related Articles: A World in Pieces: Understanding the Political Map
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A World in Pieces: Understanding the Political Map. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A World in Pieces: Understanding the Political Map
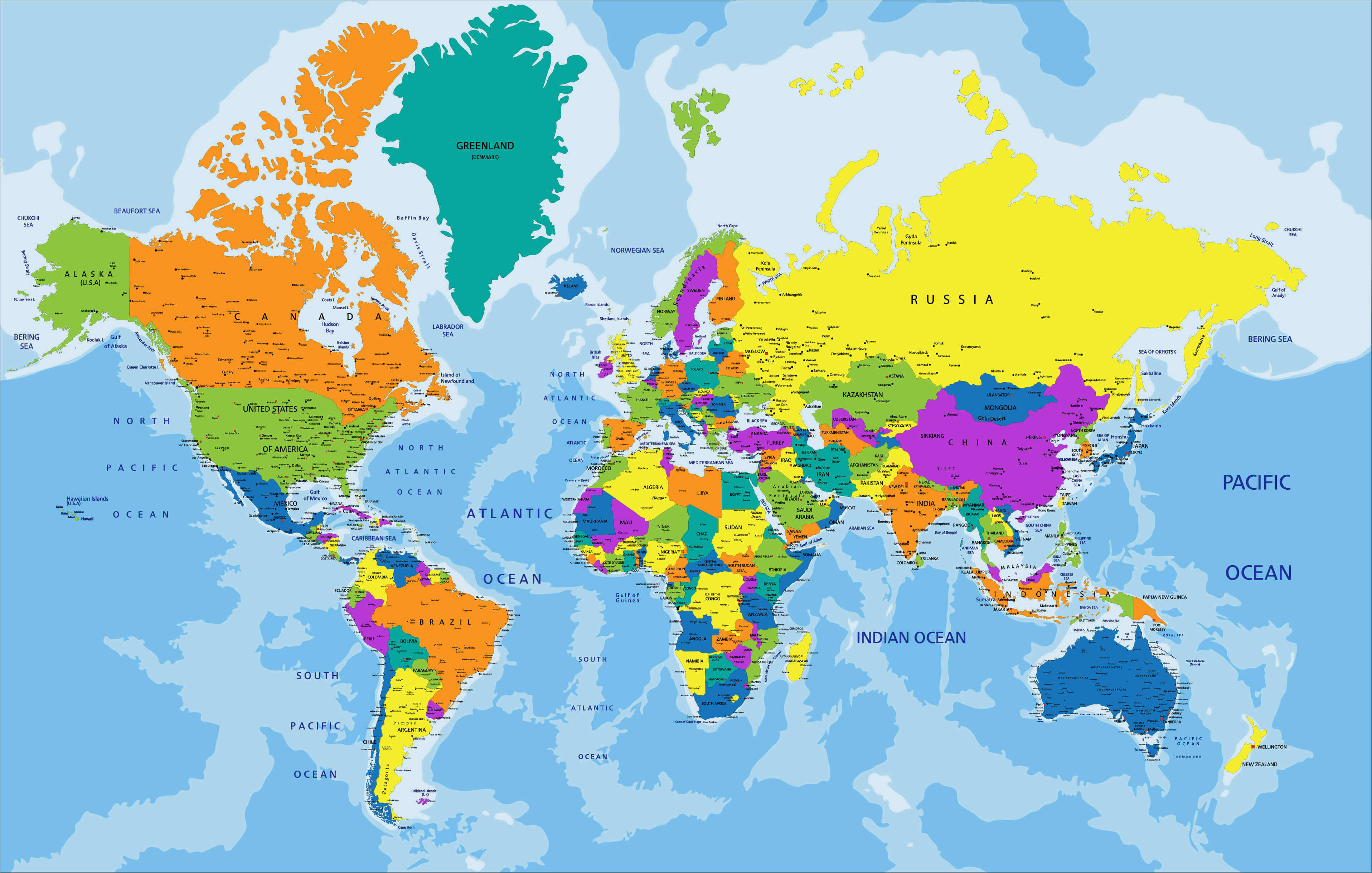
The world, a vast and intricate tapestry of cultures, landscapes, and histories, is often depicted in a simplified form: a political map. This seemingly basic tool, with its colorful borders and labels, offers a powerful lens through which to view the complex geopolitical landscape of our planet. It is a visual representation of the division of the world into sovereign states, each with its own unique identity, governance, and international relations.
The Building Blocks of the Map:
The political map, in its essence, is a reflection of power dynamics and historical events. Each nation represented on the map is a product of centuries of conflict, negotiation, and evolution. Borders, often appearing as clear-cut lines on the map, are in reality, dynamic entities, subject to change through treaties, revolutions, and other historical forces.
The map’s significance lies not only in its depiction of existing political entities but also in its ability to illuminate the relationships between them. It reveals alliances, rivalries, and historical grievances that often shape international relations. The map serves as a visual reminder of the interconnectedness of the world, where the actions of one nation can have far-reaching consequences for others.
Beyond the Lines: Understanding the Nuances:
While the political map provides a basic framework for understanding global politics, it is essential to recognize its inherent limitations. The simplified depiction of borders often overlooks the complex realities of ethnicity, religion, and cultural identity within nations. It fails to capture the nuances of internal political structures, the presence of disputed territories, or the existence of transnational movements that transcend national boundaries.
Furthermore, the map’s static nature can be misleading. The world is a dynamic entity, constantly evolving. Boundaries shift, alliances change, and new political entities emerge. A static political map, while offering a snapshot of a particular moment in time, cannot fully encompass the fluidity and complexity of the global political landscape.
The Importance of Context:
To fully appreciate the significance of the political map, it is crucial to consider the context in which it is viewed. The map’s interpretation is influenced by factors such as historical events, current geopolitical tensions, and individual perspectives. It is essential to approach the map with a critical eye, recognizing its limitations and seeking out diverse perspectives to gain a more comprehensive understanding of the world.
The Political Map in the 21st Century:
In the 21st century, the political map faces new challenges and opportunities. The rise of globalization, the increasing interconnectedness of economies, and the emergence of new global actors have all contributed to a more complex and dynamic geopolitical landscape. The map, as a tool for understanding this changing world, must evolve to reflect these new realities.
FAQs about the Political Map:
1. Why are there so many different countries on the map?
The number and distribution of countries on the map reflect a complex interplay of historical, cultural, and political factors. The process of nation-building, often driven by factors such as language, religion, and shared history, has led to the emergence of distinct sovereign entities.
2. How are borders determined?
Borders are determined through a combination of historical events, treaties, and negotiations. Some borders are based on natural features, such as rivers or mountain ranges, while others are defined by political agreements.
3. What are some examples of disputed territories on the map?
Disputed territories are areas where the sovereignty of a particular nation is contested by another. Examples include the Kashmir region between India and Pakistan, the Western Sahara between Morocco and the Polisario Front, and the South China Sea, claimed by several nations.
4. How does the political map reflect the changing world?
The political map is constantly evolving to reflect changes in the global political landscape. The dissolution of the Soviet Union in the 1990s led to the emergence of new nations, while ongoing conflicts in the Middle East continue to reshape the political map of the region.
5. What are some of the limitations of the political map?
The political map is a simplified representation of a complex reality. It fails to capture the nuances of internal political structures, the presence of ethnic and cultural diversity within nations, and the influence of transnational movements.
Tips for Understanding the Political Map:
- Consider the historical context: Understanding the historical events that have shaped the current political landscape is essential for interpreting the map.
- Recognize the limitations of the map: The map is a simplified representation of a complex reality. It is important to be aware of its limitations and seek out diverse perspectives.
- Explore the map beyond borders: Focus on the relationships between nations, the presence of disputed territories, and the influence of global actors.
- Engage with current events: Stay informed about current events to understand how they are shaping the political map.
- Use the map as a starting point: The political map is a valuable tool for understanding global politics but should be used in conjunction with other sources of information.
Conclusion:
The political map is a powerful tool for understanding the world’s geopolitical landscape. It provides a visual representation of the division of the world into sovereign states, highlighting the relationships between them and the complexities of global politics. While the map offers a simplified view of reality, it serves as a valuable starting point for exploring the intricate tapestry of the world’s political landscape. By recognizing its limitations and approaching it with a critical eye, we can use the political map to gain a deeper understanding of the world we live in.


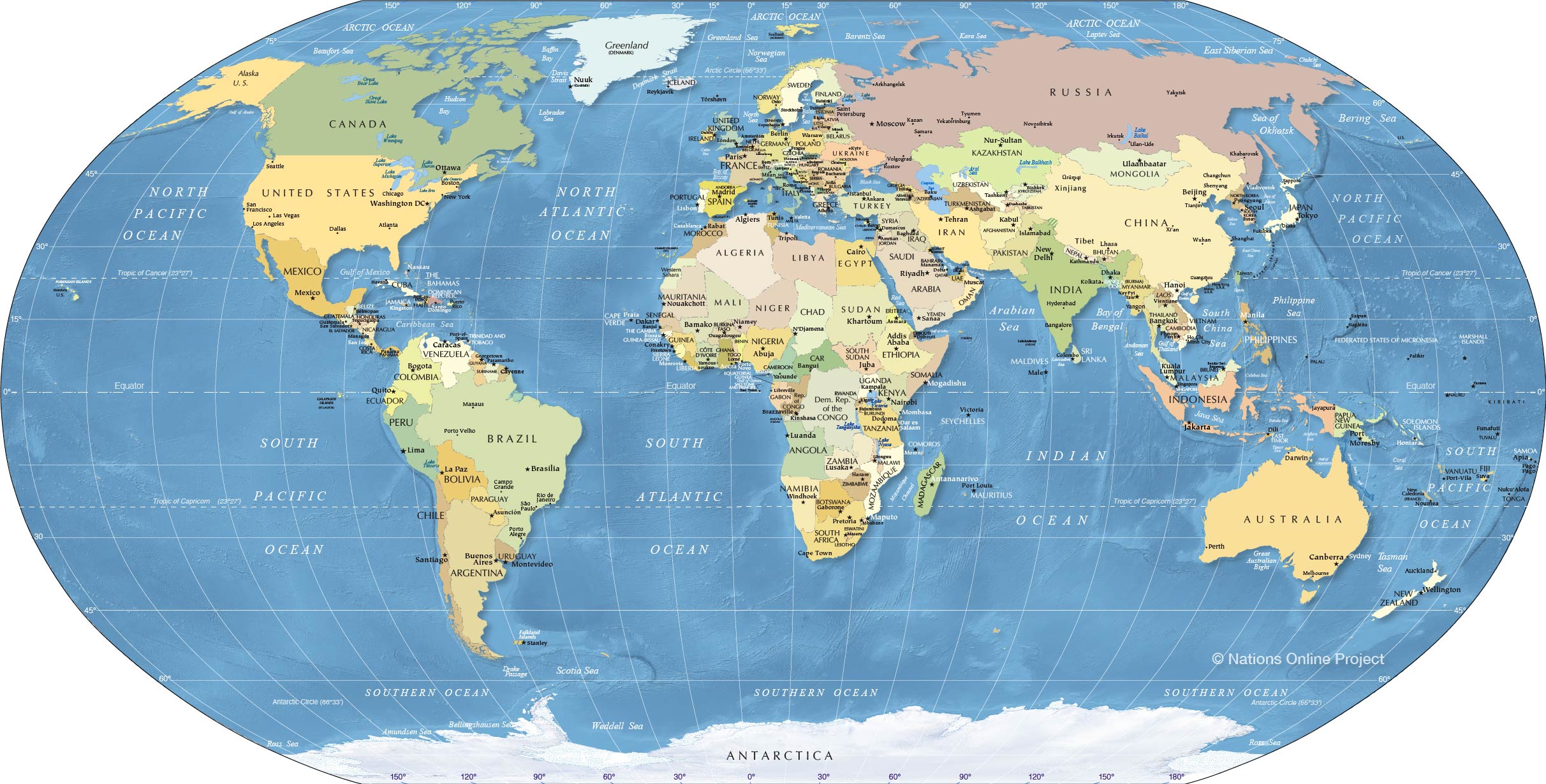


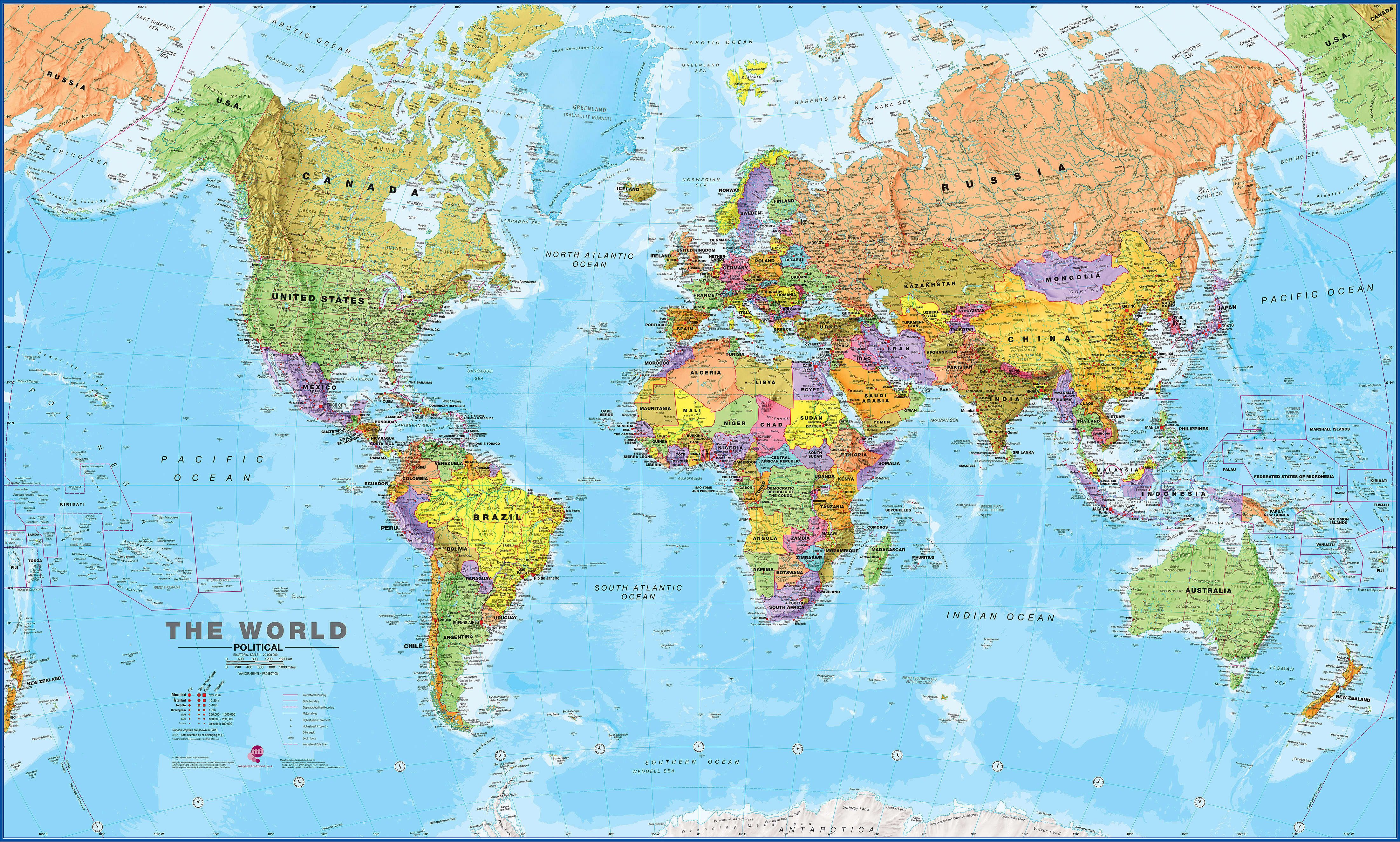

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A World in Pieces: Understanding the Political Map. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!