A Working Manual on Map Projections: Understanding the Transformation of the Earth onto a Flat Surface
Related Articles: A Working Manual on Map Projections: Understanding the Transformation of the Earth onto a Flat Surface
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Working Manual on Map Projections: Understanding the Transformation of the Earth onto a Flat Surface. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Working Manual on Map Projections: Understanding the Transformation of the Earth onto a Flat Surface
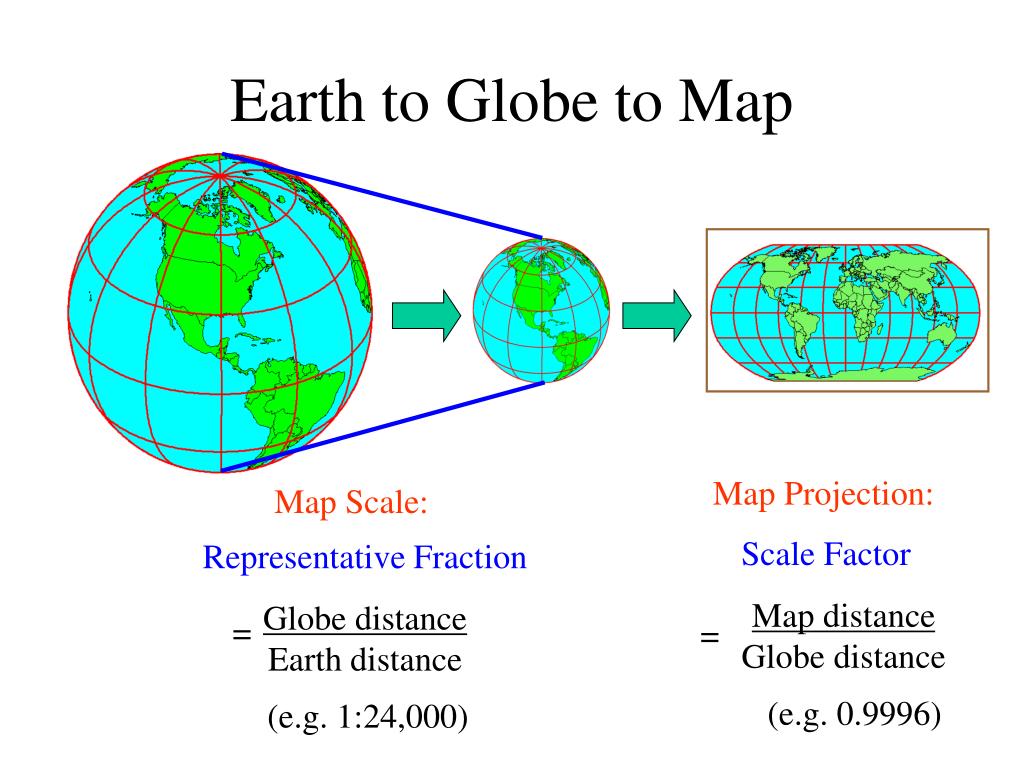
The Earth is a sphere, a three-dimensional object. Maps, however, are flat, two-dimensional representations of the Earth’s surface. To bridge this gap, map projections are employed. These are mathematical formulas that translate the Earth’s curved surface onto a flat plane, enabling us to visualize and analyze geographical information. This process inevitably introduces distortions, as it is impossible to perfectly represent a sphere on a flat surface without altering some of its properties.
Understanding the Fundamentals:
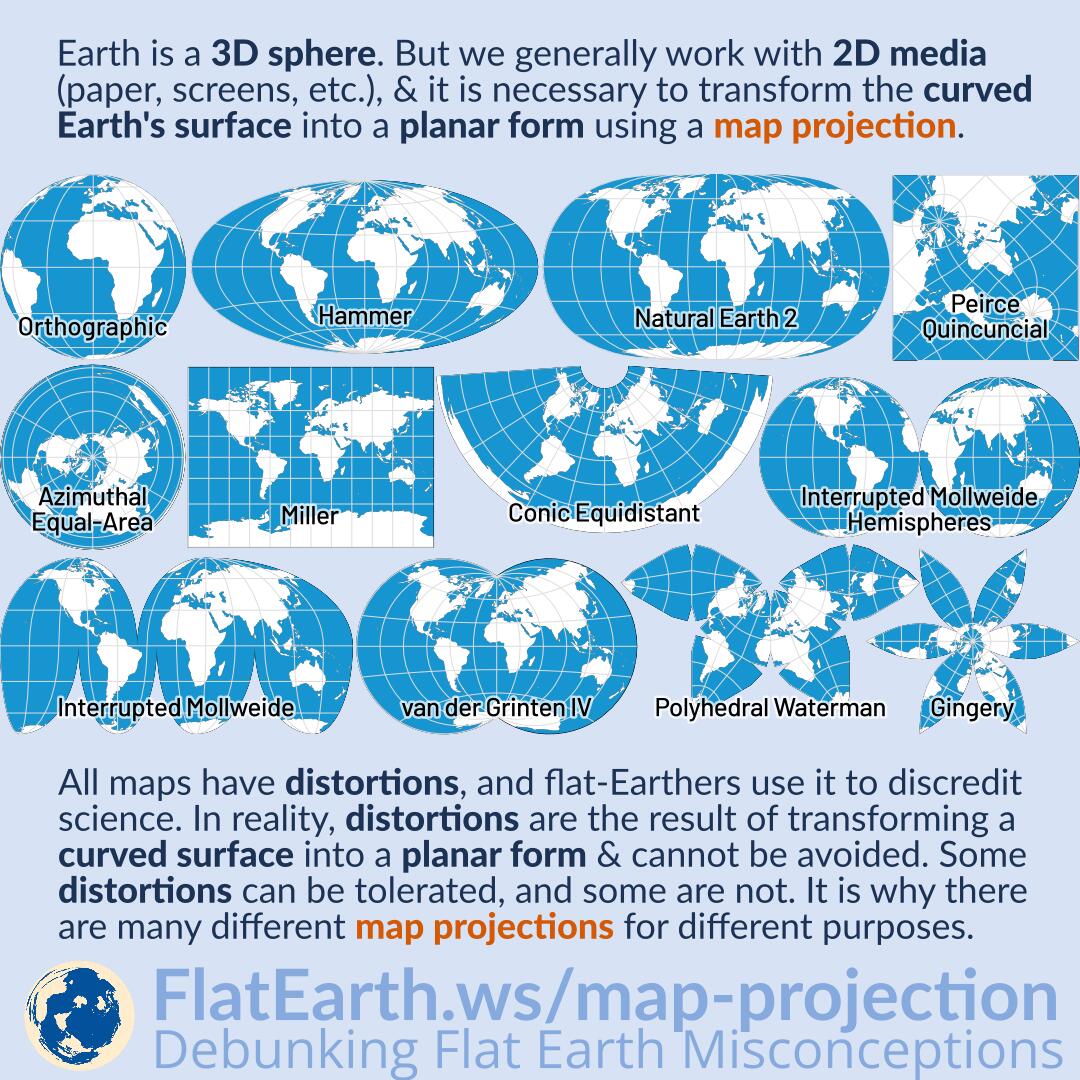
Map projections are classified based on the surface onto which the Earth’s surface is projected. Common surfaces include:
- Cylindrical Projections: Imagine a cylinder wrapped around the Earth. Points on the Earth’s surface are projected onto this cylinder, which is then unrolled to create a flat map.
- Conic Projections: A cone is placed over the Earth, with its apex touching the North or South Pole. Points are projected onto the cone, which is then unrolled to form a map.
- Planar Projections: This projection uses a plane tangent to the Earth’s surface at a specific point, usually a pole or a point on the equator. Points are projected onto this plane, resulting in a map centered on the chosen point.
Types of Distortion:
Distortion is an inherent feature of map projections. Depending on the chosen projection, certain aspects of the Earth’s surface may be exaggerated or minimized. Common types of distortion include:
- Area Distortion: The relative size of landmasses can be altered, with some areas appearing larger or smaller than they actually are.
- Shape Distortion: The shapes of continents and countries can be distorted, appearing stretched or compressed.
- Distance Distortion: The distances between points on the map can be inaccurate, leading to misrepresentations of actual distances.
Choosing the Right Projection:
The choice of map projection depends on the specific purpose of the map and the geographic area being represented. For example:
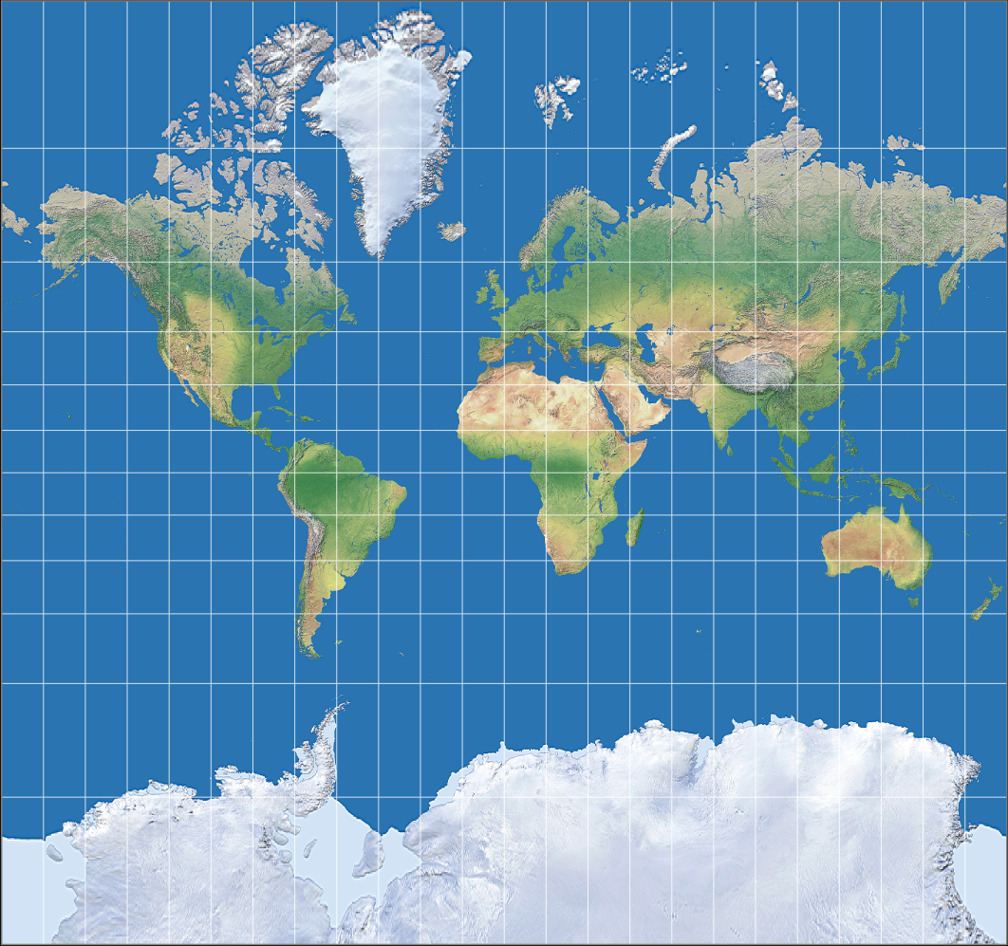
- Mercator Projection: Commonly used for navigation, this cylindrical projection preserves angles, making it ideal for plotting straight lines representing shortest distances (rhumb lines). However, it significantly distorts areas near the poles.
- Robinson Projection: A compromise projection that aims to minimize distortion in both area and shape. It is often used for general-purpose maps, offering a balanced representation of the Earth’s surface.
- Mollweide Projection: This equal-area projection accurately represents the relative sizes of landmasses. However, it distorts shapes, particularly near the poles.
Benefits of Map Projections:
- Visualization and Analysis: Map projections allow us to visualize and analyze geographic data, aiding in understanding spatial relationships and patterns.
- Navigation and Cartography: Projections are crucial for navigation, cartography, and mapping applications, providing a framework for representing the Earth’s surface.
- Scientific Research: Projections are used in various scientific fields, including geography, geology, and climate science, to analyze and visualize spatial data.
FAQs:
1. Are all map projections equally accurate?
No, map projections are not equally accurate. Each projection introduces different types of distortions, making some more suitable for specific purposes than others.
2. How can I choose the best projection for my needs?
Consider the specific purpose of the map, the geographic area being represented, and the type of distortion that is most acceptable for your application.
3. What are the limitations of map projections?
Map projections are inherently limited by the impossibility of perfectly representing a sphere on a flat surface. All projections introduce some degree of distortion.
4. Why are there so many different map projections?
The diversity of map projections reflects the various needs and applications of maps. Different projections excel in representing specific aspects of the Earth’s surface, such as area, shape, or distance.
Tips:
- Understand the purpose of the map: Before choosing a projection, consider what information you want to convey and what types of distortions are acceptable for your application.
- Research different projections: Explore various projections and their characteristics to determine the most suitable one for your needs.
- Be aware of distortions: Recognize that all map projections introduce distortions, and choose a projection that minimizes distortion in the aspects most important for your map.
- Use software tools: Geographic information system (GIS) software offers a range of projection options and tools to assist in selecting and applying the appropriate projection.
Conclusion:
Map projections are fundamental tools in cartography and geography. They enable us to represent the Earth’s curved surface on a flat plane, enabling visualization, analysis, and communication of spatial information. By understanding the principles of map projections, their strengths, and limitations, we can make informed decisions about which projection best serves our specific needs and ensure accurate and meaningful representation of geographic data.

![[PDF] Map Projections: A Working Manual Semantic Scholar](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/27bc00d177cdc325e49053043e52a455e16a491a/62-Figure10-1.png)




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Working Manual on Map Projections: Understanding the Transformation of the Earth onto a Flat Surface. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!