A Geographical Exploration of Poland and its Surrounding Region
Related Articles: A Geographical Exploration of Poland and its Surrounding Region
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Geographical Exploration of Poland and its Surrounding Region. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Geographical Exploration of Poland and its Surrounding Region
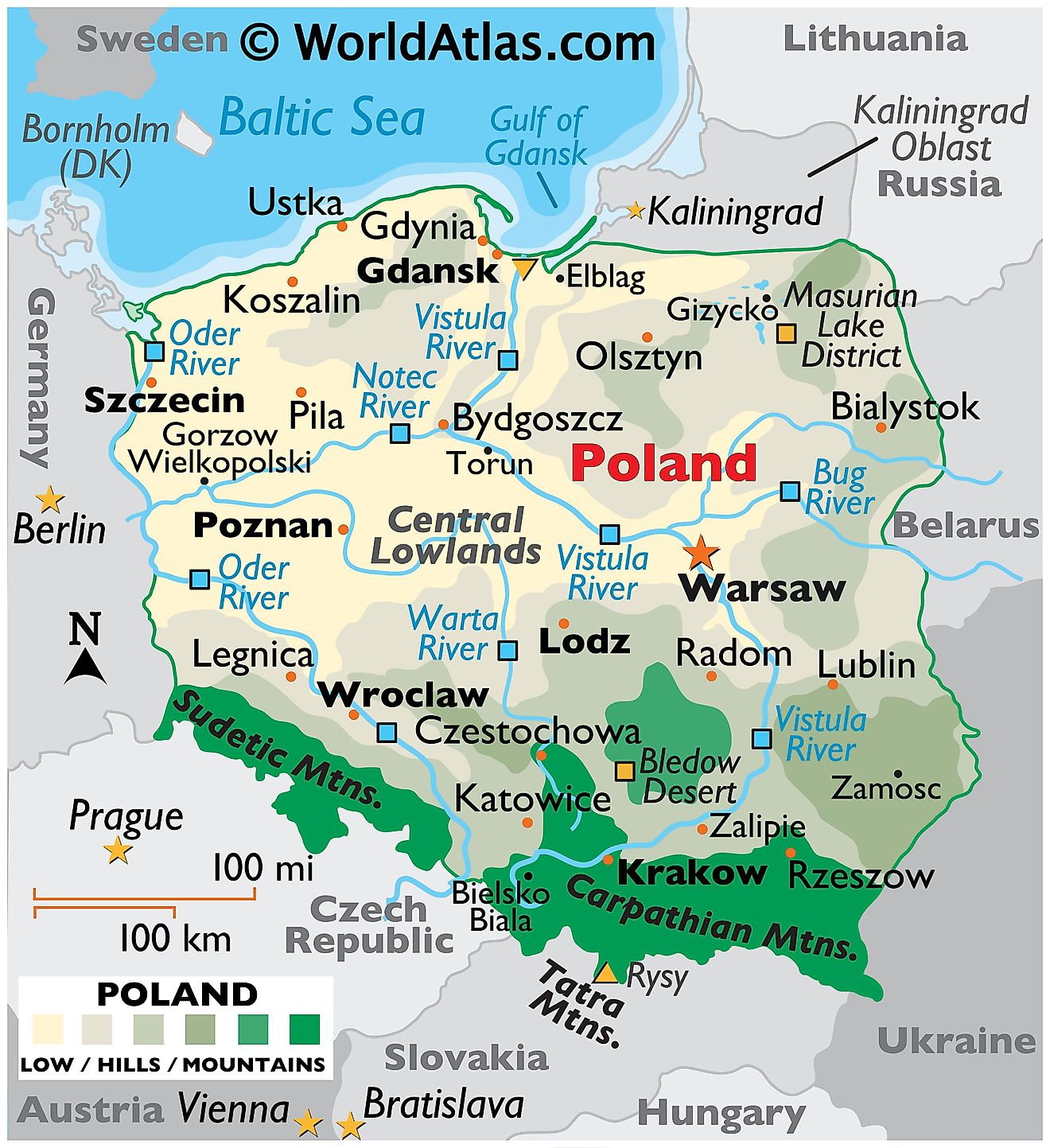
Poland, a nation nestled in the heart of Central Europe, possesses a rich history, diverse landscape, and strategic geographical location that has shaped its destiny. Understanding the map of Poland and its surrounding area reveals a complex interplay of political, economic, and cultural influences that have left an enduring mark on the region.
A Look at the Map:
Poland, with its distinctive shape resembling a crescent moon, occupies an area of 312,679 square kilometers. Its borders touch seven countries: Germany to the west, the Czech Republic and Slovakia to the south, Ukraine and Belarus to the east, and Lithuania and Russia (Kaliningrad Oblast) to the north.
The Baltic Sea and the Vistula River:
The Baltic Sea, a major waterway, forms Poland’s northern border, providing access to international trade routes. The Vistula River, Poland’s longest, flows through the country from south to north, serving as a vital transportation corridor and a source of fresh water. This river has historically played a significant role in shaping the country’s development and culture.
The Carpathian Mountains:
The Carpathian Mountains, a chain of peaks extending from Slovakia to Romania, form a natural barrier along Poland’s southern border. These mountains provide a diverse ecosystem, home to various flora and fauna, and contribute to the country’s natural beauty.
The Polish Lowlands:
The majority of Poland’s territory is occupied by the Polish Lowlands, a vast expanse of flat land that stretches from the Baltic Sea to the Carpathian Mountains. This region is characterized by fertile soil, making it ideal for agriculture.
The Importance of Location:
Poland’s location at the crossroads of Europe has made it a strategic hub for trade and cultural exchange. It has historically served as a bridge between East and West, fostering interaction between different cultures and civilizations. This strategic position has also made Poland a target for both conquest and conflict, contributing to the country’s turbulent history.
The Surrounding Region:
Poland’s surrounding region is equally diverse and historically significant. To the west, Germany, a major economic power, has a deep-rooted relationship with Poland. To the south, the Czech Republic and Slovakia, both former members of the Austro-Hungarian Empire, share historical and cultural ties with Poland. To the east, Ukraine and Belarus, both former Soviet republics, have complex relationships with Poland, influenced by shared history and political developments.
Understanding the Map: A Key to Understanding Poland’s Past and Present
The map of Poland and its surrounding area provides a crucial framework for understanding the country’s historical trajectory, cultural identity, and current geopolitical landscape. It reveals the interconnectedness of the region and highlights the enduring influence of historical events on the present.
FAQs:
Q1: What is the significance of the Baltic Sea for Poland?
A1: The Baltic Sea provides Poland with access to international trade routes, facilitating economic development and cultural exchange. It also serves as a vital source of marine resources.
Q2: How has the Carpathian Mountains impacted Poland’s history and culture?
A2: The Carpathian Mountains have provided a natural barrier, influencing migration patterns and shaping the country’s historical development. They also contribute to Poland’s rich biodiversity and cultural identity.
Q3: What are the key challenges faced by Poland due to its geographical location?
A3: Poland’s location at the crossroads of Europe has made it vulnerable to conflict and geopolitical instability. It has also faced challenges in balancing its relationships with its various neighbors.
Q4: How has Poland’s location influenced its cultural landscape?
A4: Poland’s location has fostered cultural exchange and integration with its neighbors, resulting in a rich and diverse cultural heritage.
Tips for Exploring the Map:
- Focus on the key geographical features: Understanding the Baltic Sea, the Vistula River, the Carpathian Mountains, and the Polish Lowlands is crucial to grasping the country’s landscape and its impact on history and culture.
- Examine the borders: Pay attention to the countries bordering Poland and their historical and cultural connections.
- Consider the historical context: Use the map to trace significant historical events, such as wars, migrations, and political changes.
- Explore the cultural landscape: Use the map to locate key cultural sites, cities, and regions that reflect Poland’s rich heritage.
Conclusion:
The map of Poland and its surrounding area offers a comprehensive perspective on the country’s history, geography, and cultural identity. It highlights the interplay of natural features, historical events, and geopolitical influences that have shaped the region. By understanding the map, we gain valuable insights into the complexities of Poland’s past and present, paving the way for a deeper appreciation of this fascinating and dynamic nation.
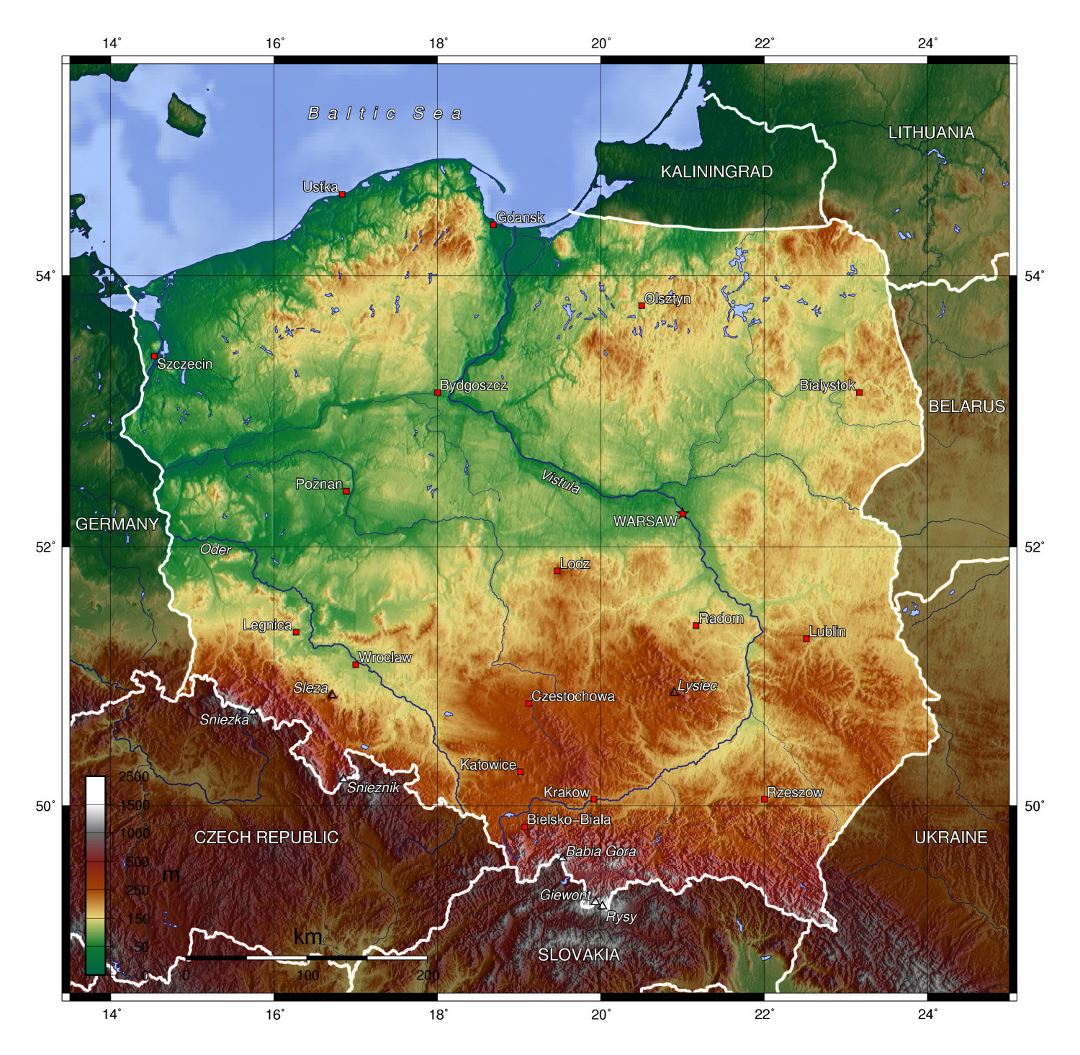




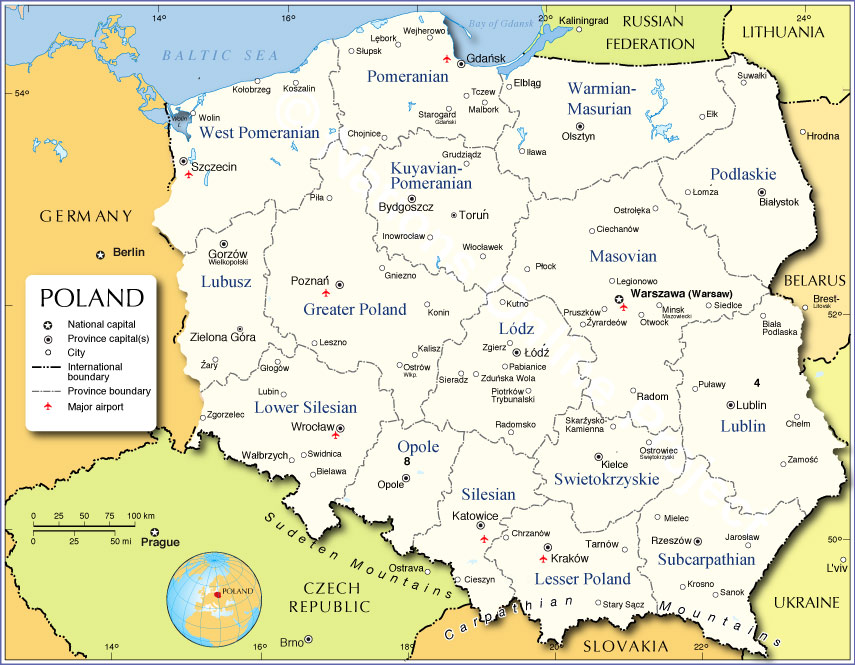
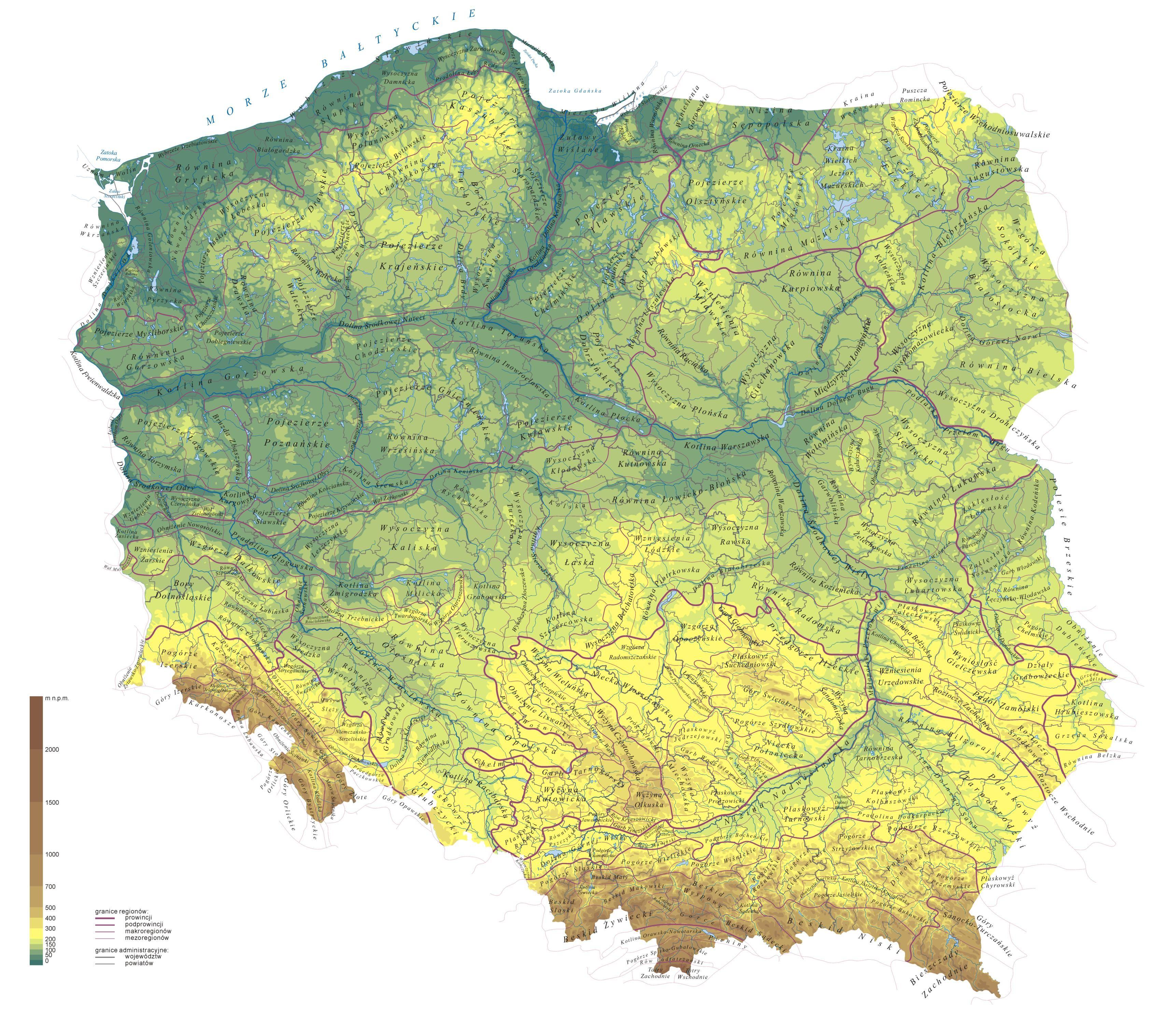

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Geographical Exploration of Poland and its Surrounding Region. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!