A Comprehensive Guide to World Map Regions: Understanding Our Diverse Planet
Related Articles: A Comprehensive Guide to World Map Regions: Understanding Our Diverse Planet
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to A Comprehensive Guide to World Map Regions: Understanding Our Diverse Planet. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: A Comprehensive Guide to World Map Regions: Understanding Our Diverse Planet
- 2 Introduction
- 3 A Comprehensive Guide to World Map Regions: Understanding Our Diverse Planet
- 3.1 I. North America
- 3.2 II. South America
- 3.3 III. Europe
- 3.4 IV. Asia
- 3.5 V. Africa
- 3.6 VI. Australia & Oceania
- 3.7 VII. Antarctica
- 3.8 FAQs by World Map Regions:
- 3.9 Tips by World Map Regions:
- 3.10 Conclusion by World Map Regions:
- 4 Closure
A Comprehensive Guide to World Map Regions: Understanding Our Diverse Planet

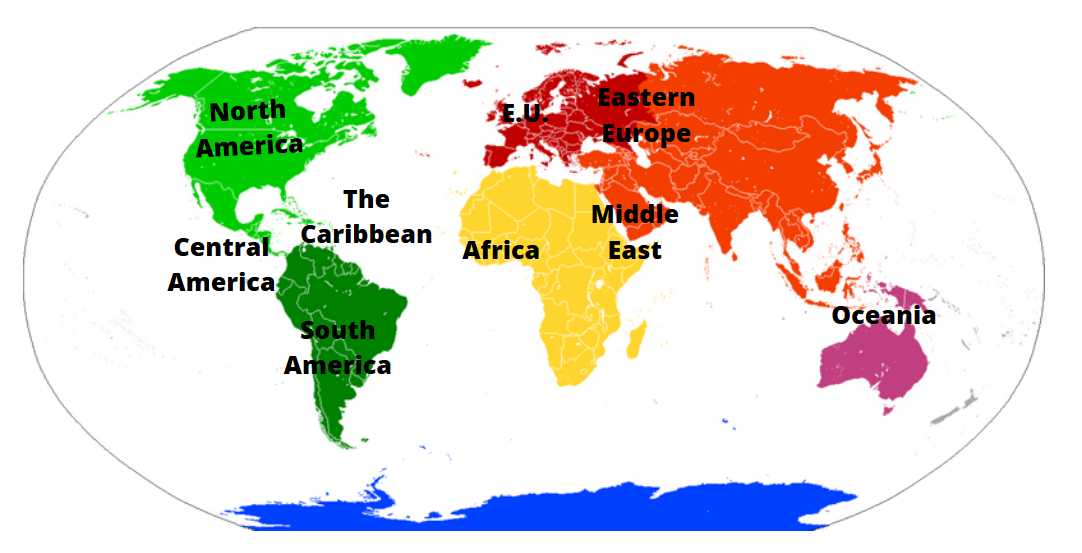
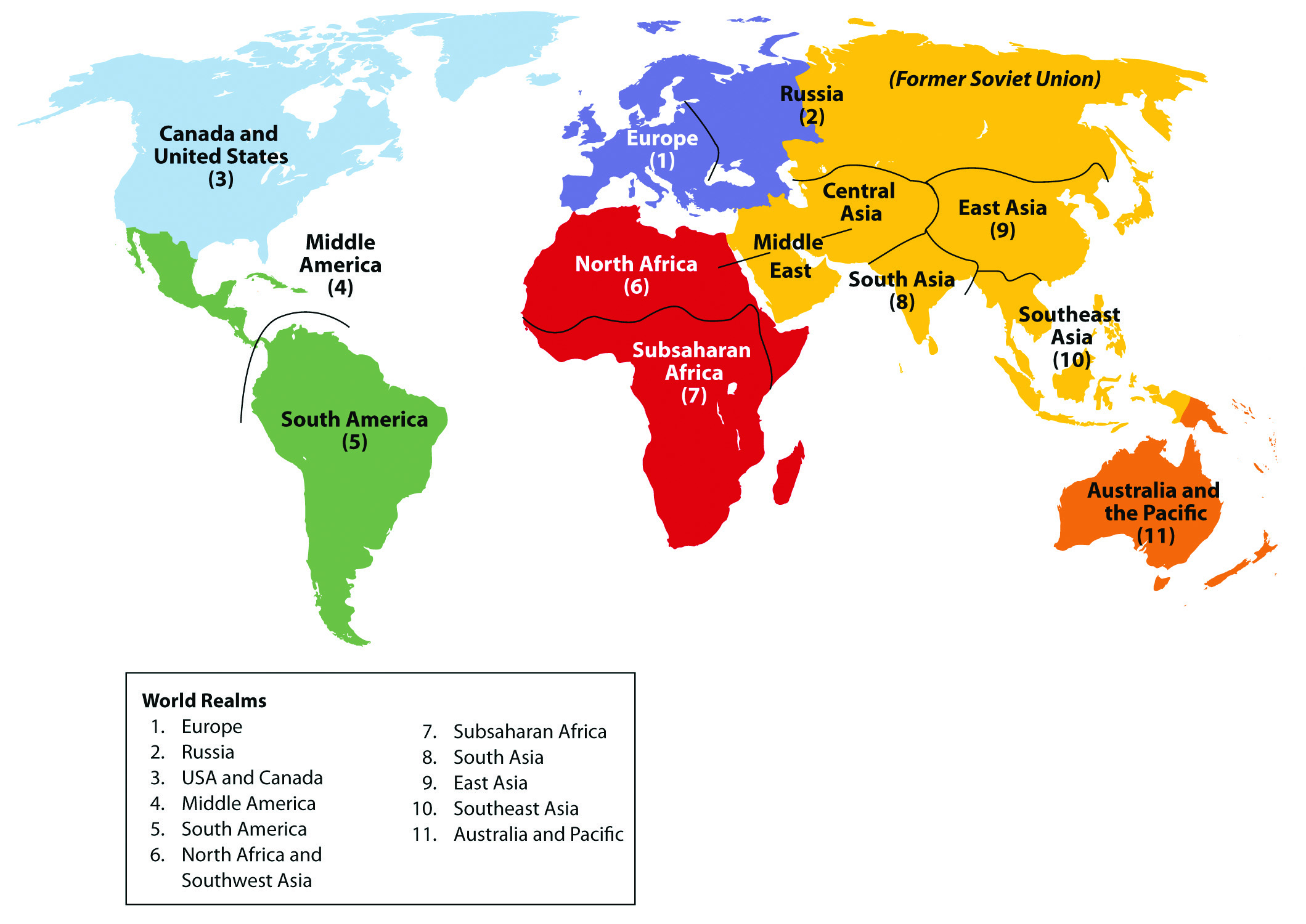
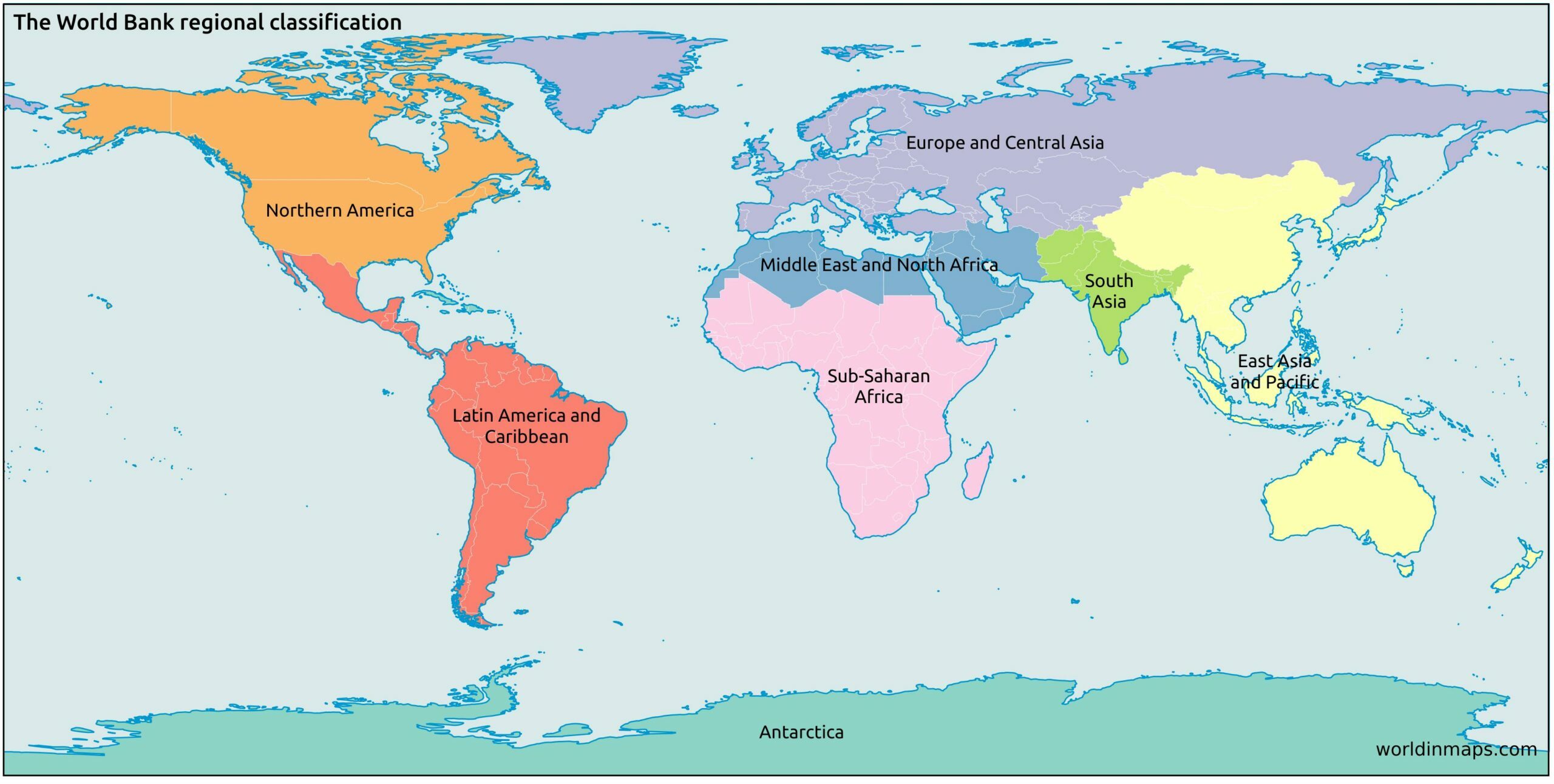
The Earth, a vibrant tapestry of diverse cultures, landscapes, and ecosystems, is often divided into regions for easier understanding and analysis. These regions, based on geographical, cultural, and historical factors, provide a framework for comprehending the complexities of our planet. This article explores the major world map regions, highlighting their unique characteristics, interconnections, and significance in shaping global dynamics.
I. North America
North America, a continent spanning from the Arctic Circle to the tropics, boasts a rich tapestry of diverse landscapes and cultures. From the towering peaks of the Rocky Mountains to the lush rainforests of the Amazon, the continent’s geography is as varied as its history.
Key Features:
- Geography: North America encompasses a vast range of landscapes, including the vast prairies of the Great Plains, the rugged mountains of the Rockies, the fertile Mississippi River valley, and the diverse coastal regions.
- Climate: The continent experiences a wide range of climates, from the frigid Arctic to the subtropical climates of the southern United States and Mexico.
- Culture: North America is a melting pot of cultures, shaped by the legacies of indigenous peoples, European colonization, and ongoing immigration.
- Economy: North America is home to some of the world’s largest economies, driven by advanced technology, manufacturing, and services.
Major Subregions:
- Anglo-America: Comprising the United States and Canada, this subregion is characterized by its strong English influence, advanced economies, and democratic institutions.
- Latin America: This region, encompassing Mexico, Central America, and South America, is marked by its Spanish and Portuguese heritage, diverse cultures, and developing economies.
Significance:
North America plays a pivotal role in global affairs, shaping international trade, technological advancements, and cultural trends. Its vast natural resources, diverse population, and powerful economies make it a significant player on the world stage.
II. South America
South America, a continent of vibrant cultures, stunning natural beauty, and rich biodiversity, is a land of contrasts. From the majestic Andes Mountains to the vast Amazon rainforest, its diverse geography reflects its cultural and economic diversity.
Key Features:
- Geography: The continent is dominated by the Andes mountain range, the Amazon River basin, and extensive coastal plains.
- Climate: South America experiences a wide range of climates, from the tropical rainforests of the Amazon to the arid deserts of Chile and Argentina.
- Culture: The continent is a melting pot of indigenous, European, and African cultures, resulting in a vibrant and diverse artistic, musical, and culinary landscape.
- Economy: South America’s economy is characterized by a mix of agriculture, mining, and manufacturing, with significant economic disparities between countries.
Major Subregions:
- Andean Region: This region, encompassing the Andes Mountains and their surrounding areas, is characterized by its high altitude, indigenous cultures, and rich mineral resources.
- Amazon Region: The Amazon rainforest, the largest in the world, is home to an incredible diversity of flora and fauna, indigenous communities, and vast natural resources.
- Southern Cone: This subregion, comprising Argentina, Chile, Uruguay, and Paraguay, is characterized by its temperate climate, agricultural economies, and European influence.
Significance:
South America is a critical player in the global economy, with its vast natural resources, diverse cultures, and growing economies. It also plays a vital role in global conservation efforts, safeguarding the Amazon rainforest and its biodiversity.
III. Europe
Europe, a continent rich in history, culture, and innovation, has been a center of global power and influence for centuries. From the ancient empires of Greece and Rome to the modern European Union, Europe’s legacy continues to shape the world.
Key Features:
- Geography: Europe is characterized by its diverse landscapes, including the Alps, the Pyrenees, the Carpathians, and the Scandinavian mountains, as well as extensive plains and coastlines.
- Climate: Europe experiences a temperate climate, with variations from oceanic to continental, Mediterranean, and subarctic.
- Culture: Europe is home to a rich tapestry of cultures, languages, and traditions, shaped by centuries of interaction and exchange.
- Economy: Europe is a major economic powerhouse, with a highly developed and integrated economy, driven by trade, manufacturing, and services.
Major Subregions:
- Western Europe: This subregion, encompassing France, Germany, Italy, Spain, and the United Kingdom, is characterized by its advanced economies, strong political institutions, and cultural influence.
- Eastern Europe: This region, comprising countries like Poland, Russia, and Ukraine, is marked by its historical ties to the Soviet Union, diverse cultures, and evolving economies.
- Northern Europe: This subregion, encompassing countries like Sweden, Norway, Denmark, and Finland, is known for its high quality of life, advanced social welfare systems, and strong environmental consciousness.
- Southern Europe: This region, comprising countries like Italy, Greece, Spain, and Portugal, is characterized by its Mediterranean climate, vibrant cultures, and tourism industries.
Significance:
Europe plays a significant role in global politics, economics, and culture. Its powerful economies, strong political institutions, and cultural influence continue to shape the world.
IV. Asia
Asia, the largest and most populous continent, is a vast and diverse region, home to ancient civilizations, bustling metropolises, and breathtaking natural landscapes. From the Himalayas to the Arabian Desert, Asia’s geographical diversity reflects its cultural and economic diversity.
Key Features:
- Geography: Asia encompasses a wide range of landscapes, including the Himalayas, the Tibetan Plateau, the Gobi Desert, and the fertile plains of the Ganges and Yangtze rivers.
- Climate: Asia experiences a wide range of climates, from the frigid Arctic to the tropical rainforests of Southeast Asia.
- Culture: Asia is home to a vast array of cultures, languages, and religions, shaped by millennia of history and interaction.
- Economy: Asia is home to some of the world’s fastest-growing economies, driven by manufacturing, trade, and technology.
Major Subregions:
- East Asia: This subregion, comprising China, Japan, South Korea, and North Korea, is characterized by its advanced economies, technological innovation, and cultural influence.
- Southeast Asia: This region, encompassing countries like Thailand, Vietnam, Indonesia, and the Philippines, is known for its tropical climate, diverse cultures, and growing economies.
- South Asia: This subregion, comprising countries like India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, and Sri Lanka, is characterized by its large populations, diverse cultures, and rapidly developing economies.
- Central Asia: This region, encompassing countries like Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan, and Turkmenistan, is characterized by its arid climate, vast steppes, and historical connections to the Silk Road.
- West Asia: This region, comprising countries like Saudi Arabia, Iran, and Turkey, is known for its oil reserves, diverse cultures, and strategic location.
Significance:
Asia is a global powerhouse, driving economic growth, technological innovation, and cultural trends. Its vast population, diverse economies, and strategic location make it a key player in global affairs.
V. Africa
Africa, a continent of vast landscapes, diverse cultures, and rich history, is often referred to as the "cradle of humanity." From the Sahara Desert to the Nile River, Africa’s geography reflects its cultural and economic diversity.
Key Features:
- Geography: Africa is characterized by its diverse landscapes, including the Sahara Desert, the Nile River, the Great Rift Valley, and the savannas of the Sahel.
- Climate: Africa experiences a wide range of climates, from the arid Sahara to the tropical rainforests of the Congo Basin.
- Culture: Africa is home to a vast array of cultures, languages, and traditions, shaped by millennia of history and interaction.
- Economy: Africa’s economy is diverse, with some countries heavily reliant on agriculture, while others are emerging as major players in the global economy.
Major Subregions:
- North Africa: This subregion, comprising countries like Egypt, Morocco, and Algeria, is characterized by its proximity to Europe, its Islamic heritage, and its diverse economies.
- Sub-Saharan Africa: This region, encompassing countries south of the Sahara Desert, is marked by its diverse cultures, languages, and economies, and faces challenges related to poverty, conflict, and climate change.
- Southern Africa: This subregion, comprising countries like South Africa, Botswana, and Namibia, is characterized by its rich mineral resources, diverse cultures, and growing economies.
Significance:
Africa is a continent of immense potential, with its vast natural resources, diverse cultures, and growing economies. It plays a crucial role in global trade, agriculture, and development efforts.
VI. Australia & Oceania
Australia and Oceania, a vast and diverse region spanning from the island nation of New Zealand to the tropical islands of the Pacific, are home to unique landscapes, cultures, and ecosystems.
Key Features:
- Geography: This region encompasses the continent of Australia, the island nation of New Zealand, and thousands of islands scattered across the Pacific Ocean.
- Climate: The region experiences a wide range of climates, from the arid deserts of Australia to the tropical rainforests of Papua New Guinea.
- Culture: Australia and Oceania are home to a diverse array of cultures, shaped by indigenous peoples, European colonization, and ongoing immigration.
- Economy: The region’s economy is diverse, with Australia being a major exporter of minerals and agricultural products, while many Pacific island nations rely on tourism and fishing.
Major Subregions:
- Australia: The continent of Australia is characterized by its vast deserts, rugged mountains, and diverse wildlife.
- New Zealand: The island nation of New Zealand is known for its stunning landscapes, including the Southern Alps and geothermal areas.
- Melanesia: This subregion, comprising islands like Papua New Guinea, Fiji, and Vanuatu, is characterized by its diverse cultures, volcanic landscapes, and rich biodiversity.
- Micronesia: This subregion, comprising small island nations like Palau, the Marshall Islands, and Guam, is known for its coral reefs, tropical climate, and unique cultures.
- Polynesia: This subregion, comprising islands like Hawaii, Samoa, and Tahiti, is characterized by its volcanic landscapes, tropical climate, and rich Polynesian cultures.
Significance:
Australia and Oceania play a significant role in global conservation efforts, safeguarding the Great Barrier Reef and other unique ecosystems. The region also plays a role in global trade, tourism, and cultural exchange.
VII. Antarctica
Antarctica, the coldest, driest, and windiest continent on Earth, is a vast and desolate landmass covered in ice. Despite its harsh conditions, Antarctica is home to a unique ecosystem and plays a crucial role in global climate regulation.
Key Features:
- Geography: Antarctica is a vast, icy continent surrounded by a frozen ocean. It is home to the South Pole and the largest ice sheet on Earth.
- Climate: Antarctica is the coldest and windiest continent on Earth, with temperatures often dropping below -90 degrees Celsius.
- Ecosystem: Despite its harsh conditions, Antarctica is home to a unique ecosystem, including penguins, seals, whales, and a variety of marine life.
- Research: Antarctica is a major site for scientific research, with research stations from various countries studying climate change, geology, and biology.
Significance:
Antarctica plays a crucial role in global climate regulation, absorbing vast amounts of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. It is also a vital source of information about Earth’s history and climate change.
FAQs by World Map Regions:
North America:
-
Q: What are the major languages spoken in North America?
- A: English, Spanish, French, and Indigenous languages are widely spoken in North America.
-
Q: What are the major economic sectors in North America?
- A: The major economic sectors in North America include technology, manufacturing, services, agriculture, and tourism.
-
Q: What are some of the major environmental challenges facing North America?
- A: North America faces challenges related to climate change, deforestation, pollution, and water scarcity.
South America:
-
Q: What are the major indigenous cultures in South America?
- A: South America is home to a wide range of indigenous cultures, including the Inca, Maya, and Aztec civilizations.
-
Q: What are the major agricultural products produced in South America?
- A: South America is a major producer of coffee, soybeans, sugar, and beef.
-
Q: What are some of the major environmental challenges facing South America?
- A: South America faces challenges related to deforestation, biodiversity loss, and pollution.
Europe:
-
Q: What are the major historical events that have shaped Europe?
- A: Major historical events that have shaped Europe include the Roman Empire, the Renaissance, the Reformation, the Industrial Revolution, and the World Wars.
-
Q: What are the major political institutions in Europe?
- A: Major political institutions in Europe include the European Union, the Council of Europe, and the NATO.
-
Q: What are some of the major cultural contributions of Europe?
- A: Europe has made significant contributions to art, music, literature, science, and philosophy.
Asia:
-
Q: What are the major religions practiced in Asia?
- A: Major religions practiced in Asia include Buddhism, Hinduism, Islam, Christianity, and Confucianism.
-
Q: What are the major economic powers in Asia?
- A: Major economic powers in Asia include China, Japan, India, and South Korea.
-
Q: What are some of the major environmental challenges facing Asia?
- A: Asia faces challenges related to air pollution, water scarcity, deforestation, and biodiversity loss.
Africa:
-
Q: What are the major ethnic groups in Africa?
- A: Africa is home to a vast array of ethnic groups, each with its own unique language, culture, and traditions.
-
Q: What are the major challenges facing Africa?
- A: Africa faces challenges related to poverty, conflict, disease, and climate change.
-
Q: What are some of the major contributions of Africa to the world?
- A: Africa has made significant contributions to art, music, literature, and science.
Australia & Oceania:
-
Q: What are the major indigenous cultures in Australia and Oceania?
- A: Australia and Oceania are home to a diverse array of indigenous cultures, each with its own unique language, art, and traditions.
-
Q: What are the major environmental issues facing Australia and Oceania?
- A: Australia and Oceania face challenges related to climate change, coral bleaching, and deforestation.
-
Q: What are some of the major tourist destinations in Australia and Oceania?
- A: Major tourist destinations in Australia and Oceania include the Great Barrier Reef, Uluru, the Southern Alps, and the tropical islands of the Pacific.
Antarctica:
-
Q: What are the major scientific research areas in Antarctica?
- A: Major scientific research areas in Antarctica include climate change, geology, biology, and astronomy.
-
Q: What are the major environmental challenges facing Antarctica?
- A: Antarctica faces challenges related to climate change, pollution, and invasive species.
-
Q: What are the international agreements governing Antarctica?
- A: Antarctica is governed by the Antarctic Treaty System, which promotes international cooperation and conservation.
Tips by World Map Regions:
North America:
- Travel Tip: Explore the diverse landscapes of North America, from the rugged mountains of the Rockies to the lush rainforests of the Amazon.
- Learning Tip: Learn about the history of North America, including the legacies of indigenous peoples, European colonization, and ongoing immigration.
- Business Tip: North America is a hub for innovation and entrepreneurship, offering opportunities for businesses in a variety of sectors.
South America:
- Travel Tip: Immerse yourself in the vibrant cultures of South America, from the bustling cities to the remote villages.
- Learning Tip: Learn about the diverse languages and traditions of South America, reflecting its rich cultural heritage.
- Business Tip: South America offers opportunities for businesses in agriculture, mining, and renewable energy.
Europe:
- Travel Tip: Explore the rich history and culture of Europe, from the ancient ruins of Rome to the modern cities of Paris and London.
- Learning Tip: Learn about the major historical events that have shaped Europe, from the Roman Empire to the European Union.
- Business Tip: Europe is a major economic powerhouse, offering opportunities for businesses in a variety of sectors.
Asia:
- Travel Tip: Discover the diverse landscapes and cultures of Asia, from the Himalayas to the bustling cities of Tokyo and Shanghai.
- Learning Tip: Learn about the major religions and philosophies of Asia, reflecting its rich spiritual heritage.
- Business Tip: Asia is home to some of the world’s fastest-growing economies, offering opportunities for businesses in a variety of sectors.
Africa:
- Travel Tip: Explore the vast landscapes and diverse cultures of Africa, from the Sahara Desert to the savannas of the Sahel.
- Learning Tip: Learn about the rich history and traditions of Africa, reflecting its diverse cultural heritage.
- Business Tip: Africa offers opportunities for businesses in agriculture, mining, and renewable energy.
Australia & Oceania:
- Travel Tip: Explore the unique landscapes and cultures of Australia and Oceania, from the Great Barrier Reef to the tropical islands of the Pacific.
- Learning Tip: Learn about the indigenous cultures of Australia and Oceania, reflecting their unique traditions and art.
- Business Tip: Australia and Oceania offer opportunities for businesses in tourism, mining, and agriculture.
Antarctica:
- Travel Tip: Experience the unique and challenging environment of Antarctica, home to penguins, seals, and whales.
- Learning Tip: Learn about the scientific research being conducted in Antarctica, contributing to our understanding of climate change and Earth’s history.
- Business Tip: Antarctica offers opportunities for businesses in tourism and scientific research.
Conclusion by World Map Regions:
North America:
North America continues to be a global leader in technology, innovation, and economic power. Its diverse cultures and landscapes offer a rich tapestry of experiences for visitors and residents alike.
South America:
South America is a continent of vibrant cultures, stunning natural beauty, and immense potential. Its diverse economies and rich cultural heritage make it a fascinating and dynamic region.
Europe:
Europe remains a center of global influence, shaping politics, economics, and culture. Its rich history, diverse cultures, and advanced economies make it a vibrant and influential region.
Asia:
Asia is a global powerhouse, driving economic growth, technological innovation, and cultural trends. Its vast population




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comprehensive Guide to World Map Regions: Understanding Our Diverse Planet. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!