A Comprehensive Guide to Poland’s Voivodeships: Understanding the Administrative Landscape
Related Articles: A Comprehensive Guide to Poland’s Voivodeships: Understanding the Administrative Landscape
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to A Comprehensive Guide to Poland’s Voivodeships: Understanding the Administrative Landscape. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
A Comprehensive Guide to Poland’s Voivodeships: Understanding the Administrative Landscape
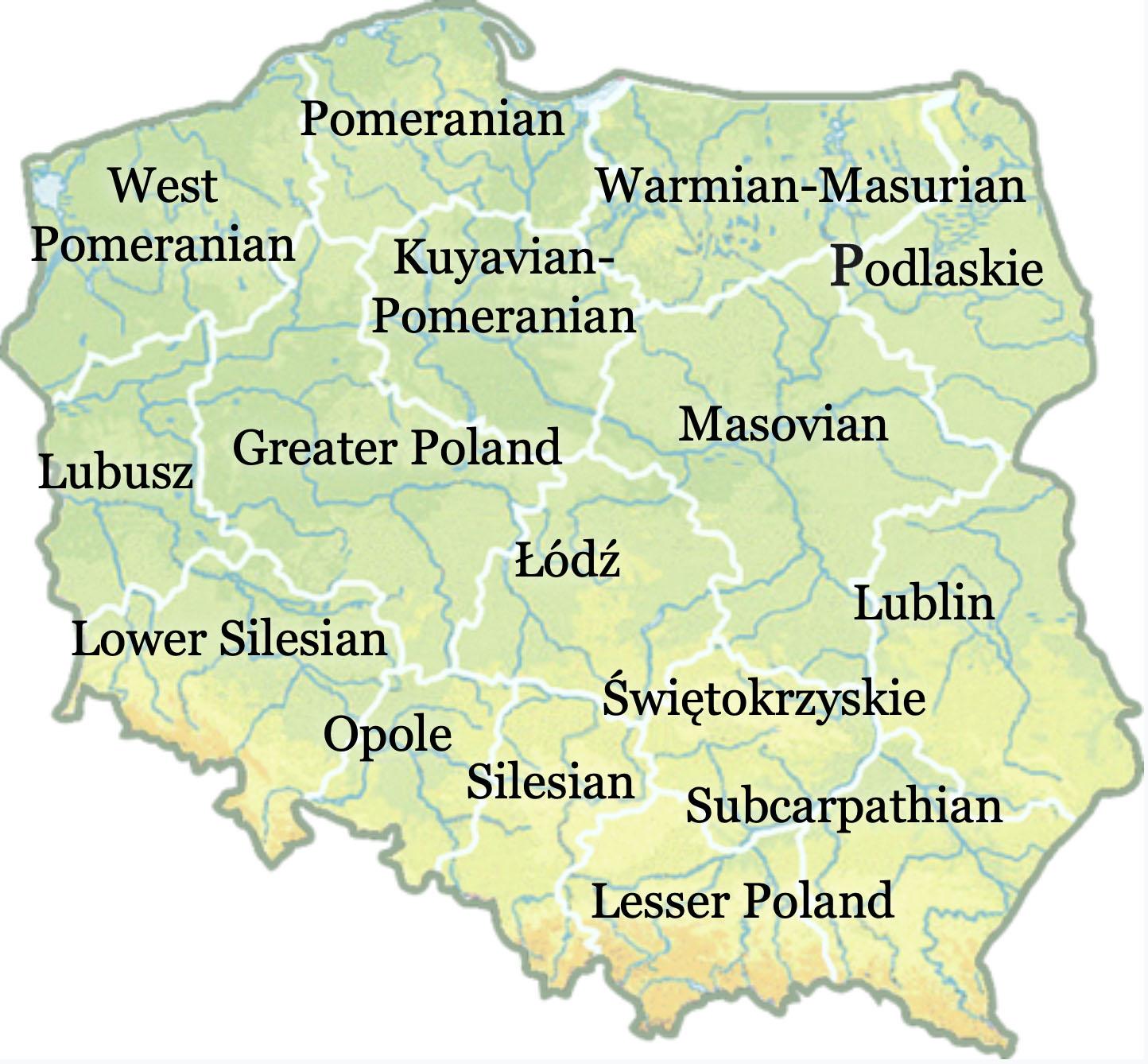
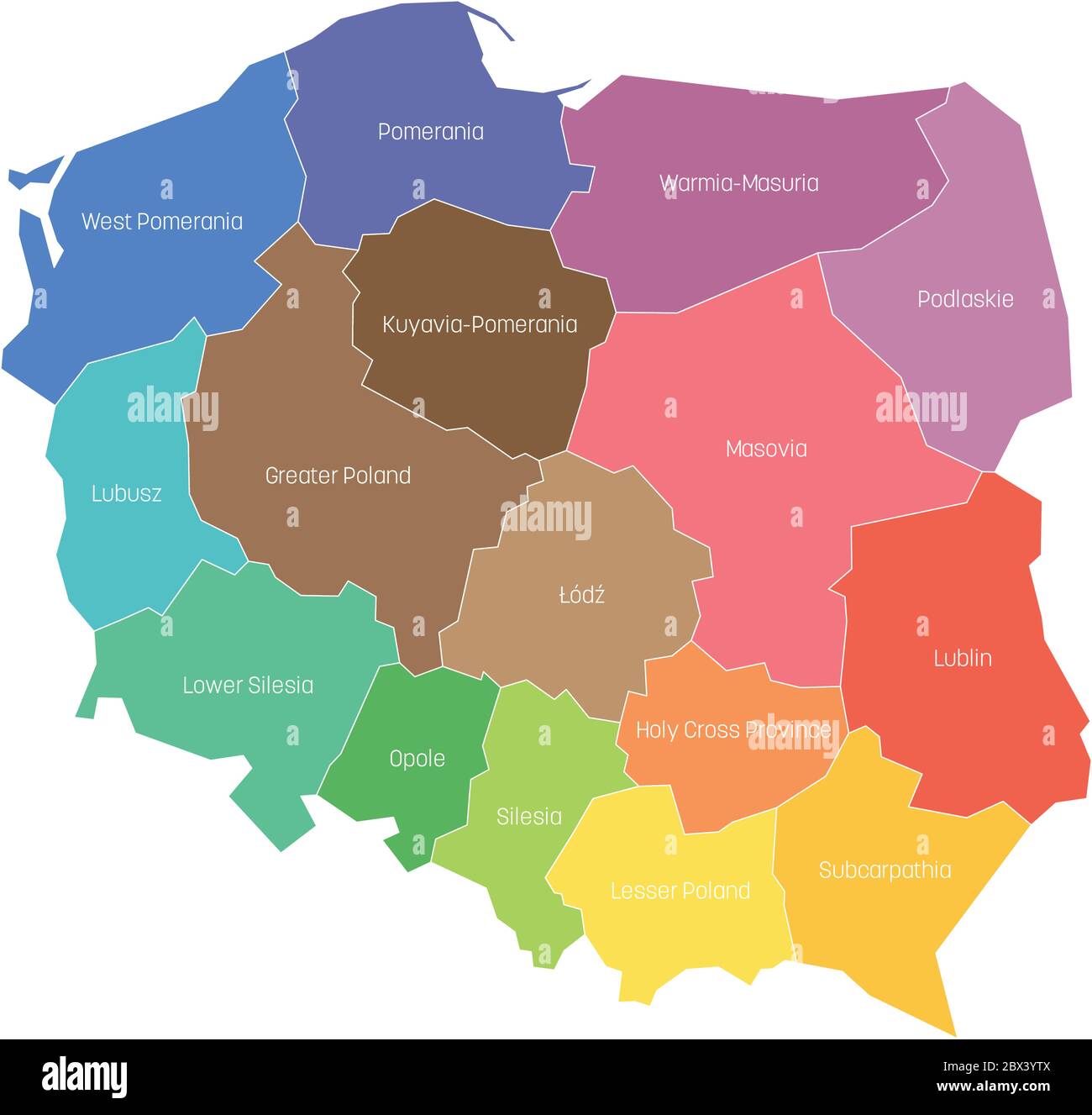
Poland’s administrative structure is organized into 16 voivodeships, each representing a distinct geographical and cultural entity within the nation. Understanding the map of Poland’s voivodeships with their corresponding names is crucial for comprehending the country’s diverse landscape, its historical evolution, and its contemporary administrative framework.
Historical Context: From Partitions to Modernity
The current voivodeship system is a relatively recent development, dating back to the administrative reforms of 1999. Prior to this, Poland’s administrative structure was significantly different, influenced by its turbulent history. During the periods of partition (1772-1918), the territory of Poland was divided among Russia, Prussia, and Austria, each with its own administrative system. This fragmentation left a lasting impact on the country’s political and cultural landscape.
The establishment of the Second Polish Republic in 1918 saw the introduction of a new administrative framework, with the country divided into 16 voivodeships. However, this system was disrupted by the Nazi occupation during World War II, with the territory divided into districts under German control.
Following the war, Poland’s administrative structure underwent further changes, with the introduction of a centralized system of provinces and districts. This system remained in place until the 1999 reforms, which reintroduced the voivodeship model, albeit with a revised territorial organization.
The 16 Voivodeships: A Geographical and Cultural Mosaic
The 16 voivodeships of Poland represent a diverse tapestry of geographical features, cultural traditions, and historical legacies. Each voivodeship possesses unique characteristics that contribute to the richness and complexity of the Polish landscape.
1. Lower Silesian Voivodeship (Dolnośląskie): This voivodeship, located in southwestern Poland, is characterized by its picturesque landscapes, including the Karkonosze Mountains, the Sudetes Mountains, and the Kłodzko Valley. It is home to numerous historical cities, including Wrocław, the capital, known for its vibrant culture and architectural heritage.
2. Kuyavian-Pomeranian Voivodeship (Kujawsko-pomorskie): Situated in central Poland, this voivodeship is renowned for its fertile agricultural lands and its historical cities, including Bydgoszcz and Toruń. The latter, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, is famous for its medieval architecture and its association with Nicolaus Copernicus.
3. Lubelskie Voivodeship: Located in southeastern Poland, this voivodeship is known for its rolling hills, fertile plains, and its rich historical heritage. Lublin, the capital, is a significant cultural center, with a renowned university and a bustling old town.
4. Lubusz Voivodeship: This voivodeship, situated in western Poland, borders Germany and is characterized by its diverse landscape, including the Lubusz Land, a region known for its forests, lakes, and rivers. The capital, Gorzów Wielkopolski, is a center of industry and culture.
5. Łódź Voivodeship: This voivodeship, located in central Poland, is known for its industrial heritage, with Łódź, the capital, once a major textile center. However, in recent years, the region has diversified its economy, with a growing focus on technology and innovation.
6. Małopolskie Voivodeship: Situated in southern Poland, this voivodeship is renowned for its stunning mountain landscapes, including the Tatra Mountains, the highest mountain range in Poland. Krakow, the capital, is a major tourist destination, famous for its medieval architecture, its rich cultural heritage, and its vibrant artistic scene.
7. Masovian Voivodeship (Mazowieckie): This voivodeship, located in central Poland, is the largest and most populous in the country. It encompasses the capital city, Warsaw, a major political, economic, and cultural hub. The region is also home to numerous historical cities and towns, including Płock, Radom, and Siedlce.
8. Opole Voivodeship: Situated in southwestern Poland, this voivodeship is known for its picturesque landscapes, including the Silesian Lowland and the Nysa River Valley. The capital, Opole, is a cultural center, with a renowned opera house and a vibrant arts scene.
9. Podkarpackie Voivodeship: Located in southeastern Poland, this voivodeship is characterized by its mountainous terrain, including the Bieszczady Mountains, a region known for its pristine nature and its rich cultural heritage. The capital, Rzeszów, is a growing industrial and economic center.
10. Podlaskie Voivodeship: Situated in northeastern Poland, this voivodeship is known for its vast forests, its numerous lakes, and its rich cultural heritage. The capital, Białystok, is a cultural center, with a renowned university and a vibrant arts scene.
11. Pomeranian Voivodeship (Pomorskie): This voivodeship, located in northern Poland, is characterized by its Baltic Sea coastline, its numerous lakes, and its rich history. The capital, Gdańsk, is a major port city, known for its medieval architecture and its vibrant cultural scene.
12. Silesian Voivodeship (Śląskie): Situated in southern Poland, this voivodeship is known for its industrial heritage, with Katowice, the capital, once a major coal mining center. However, in recent years, the region has diversified its economy, with a growing focus on technology and innovation.
13. Świętokrzyskie Voivodeship: Located in central Poland, this voivodeship is characterized by its rolling hills, its numerous forests, and its rich historical heritage. The capital, Kielce, is a cultural center, with a renowned university and a vibrant arts scene.
14. Warmia-Masurian Voivodeship (Warmińsko-mazurskie): Situated in northeastern Poland, this voivodeship is known for its picturesque landscapes, including the Masurian Lake District, a region renowned for its numerous lakes, its forests, and its rich cultural heritage. The capital, Olsztyn, is a cultural center, with a renowned university and a vibrant arts scene.
15. Greater Poland Voivodeship (Wielkopolskie): Located in western Poland, this voivodeship is known for its fertile agricultural lands, its numerous forests, and its rich historical heritage. The capital, Poznań, is a major cultural and economic center, with a renowned university and a vibrant arts scene.
16. West Pomeranian Voivodeship (Zachodniopomorskie): Situated in northwestern Poland, this voivodeship is characterized by its Baltic Sea coastline, its numerous lakes, and its rich history. The capital, Szczecin, is a major port city, known for its medieval architecture and its vibrant cultural scene.
The Importance of Voivodeships in Poland’s Administrative Landscape
The voivodeship system plays a crucial role in Poland’s administrative framework, serving as the primary level of regional governance. Each voivodeship is governed by a voivode, appointed by the Prime Minister, and a regional parliament, elected by the local population.
The voivodeships are responsible for a wide range of administrative tasks, including:
- Regional Development: Implementing regional development strategies, attracting investment, and supporting local businesses.
- Infrastructure Management: Maintaining and developing regional infrastructure, including roads, railways, and public utilities.
- Education and Healthcare: Providing access to quality education and healthcare services for the local population.
- Cultural Preservation: Promoting and preserving local cultural heritage and traditions.
- Environmental Protection: Implementing environmental protection policies and managing natural resources.
The voivodeship system ensures a balance between national and local governance, allowing for regional autonomy while maintaining a strong national framework. It also facilitates the development of regional identities and fosters a sense of local pride.
Benefits of Understanding the Voivodeship Map
Understanding the map of Poland’s voivodeships with their corresponding names offers numerous benefits, including:
- Enhanced Geographical Knowledge: Provides a deeper understanding of Poland’s diverse geography, including its natural features, urban centers, and historical landmarks.
- Improved Administrative Insight: Facilitates a clearer understanding of the country’s administrative structure and the roles and responsibilities of regional authorities.
- Cultural Appreciation: Enables a greater appreciation for the rich cultural diversity of Poland, with each voivodeship possessing unique traditions, customs, and artistic expressions.
- Travel Planning: Serves as a valuable tool for planning trips to Poland, allowing travelers to explore different regions and experience the country’s unique cultural offerings.
- Business Development: Provides valuable information for businesses seeking to invest in Poland, enabling them to identify regions with specific economic strengths and opportunities.
FAQs about Poland’s Voivodeships
Q1: What is the difference between a voivodeship and a province?
A: In Poland, the terms "voivodeship" and "province" are often used interchangeably. However, "voivodeship" is the official term used in the Polish administrative system.
Q2: How are the boundaries of the voivodeships determined?
A: The boundaries of the voivodeships are determined by historical, geographical, and economic factors. They are designed to create administrative units that are geographically cohesive, economically viable, and culturally distinct.
Q3: What are the responsibilities of the voivode?
A: The voivode is responsible for overseeing the implementation of national policies at the regional level, coordinating the activities of local authorities, and representing the voivodeship in national government.
Q4: How can I learn more about the voivodeships of Poland?
A: There are numerous resources available to learn more about Poland’s voivodeships, including online maps, travel guides, and historical accounts. You can also visit the official websites of the Polish government and the individual voivodeships.
Tips for Understanding Poland’s Voivodeships
- Consult a Map: Utilize a detailed map of Poland’s voivodeships with their corresponding names to familiarize yourself with their geographical locations and boundaries.
- Explore Regional Websites: Visit the official websites of the individual voivodeships to learn about their specific cultural, historical, and economic characteristics.
- Engage in Travel: Plan a trip to different voivodeships to experience their unique cultural offerings, natural landscapes, and historical landmarks firsthand.
- Read Historical Accounts: Explore historical accounts and literature to gain a deeper understanding of the historical evolution of the voivodeship system and its impact on the development of Poland.
Conclusion
Understanding the map of Poland’s voivodeships with their corresponding names is crucial for gaining a comprehensive understanding of the country’s diverse landscape, its historical evolution, and its contemporary administrative framework. Each voivodeship represents a distinct geographical and cultural entity, contributing to the richness and complexity of the Polish nation. By exploring the map and learning about the individual voivodeships, individuals can develop a deeper appreciation for Poland’s unique character and its multifaceted identity.
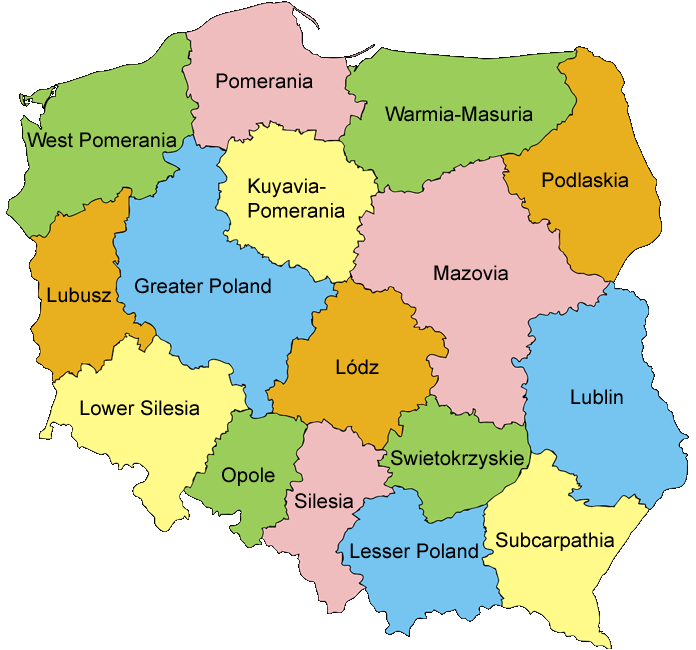




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into A Comprehensive Guide to Poland’s Voivodeships: Understanding the Administrative Landscape. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!